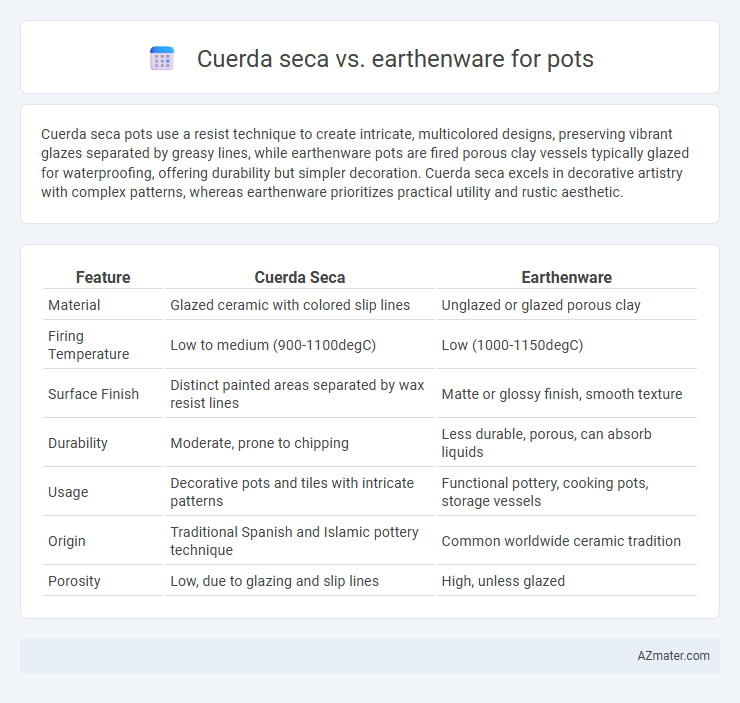
Cuerda seca pots use a resist technique to create intricate, multicolored designs, preserving vibrant glazes separated by greasy lines, while earthenware pots are fired porous clay vessels typically glazed for waterproofing, offering durability but simpler decoration. Cuerda seca excels in decorative artistry with complex patterns, whereas earthenware prioritizes practical utility and rustic aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cuerda Seca | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glazed ceramic with colored slip lines | Unglazed or glazed porous clay |
| Firing Temperature | Low to medium (900-1100degC) | Low (1000-1150degC) |
| Surface Finish | Distinct painted areas separated by wax resist lines | Matte or glossy finish, smooth texture |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | Less durable, porous, can absorb liquids |
| Usage | Decorative pots and tiles with intricate patterns | Functional pottery, cooking pots, storage vessels |
| Origin | Traditional Spanish and Islamic pottery technique | Common worldwide ceramic tradition |
| Porosity | Low, due to glazing and slip lines | High, unless glazed |
Introduction to Cuerda Seca and Earthenware
Cuerda Seca is a traditional decorative technique used on ceramics where colored glazes are separated by thin lines of greasy material, preventing the colors from mixing during firing and creating intricate patterns. Earthenware refers to pottery made from porous clay fired at low temperatures, resulting in a somewhat porous and less durable material often glazed to hold liquids. Understanding the differences between Cuerda Seca technique and general earthenware helps highlight the artistic and functional qualities unique to each pottery style.
Historical Background of Cuerda Seca Pottery
Cuerda seca pottery, originating from 10th-century Islamic Spain, is distinguished by its use of a greasy resist line to separate vibrant glazes, a technique that allowed intricate, colorful designs without color blending. This method contrasts with traditional earthenware, which relies on simpler glazing techniques and often features earthy, monotone hues. The historical significance of cuerda seca lies in its influence on later Moorish and Spanish ceramic art, showcasing a blend of technical innovation and decorative artistry that elevated ceramic production in the medieval period.
Origin and Development of Earthenware Pots
Earthenware pots originated over 10,000 years ago, crafted from natural clay and fired at low temperatures, making them porous and suitable for everyday cooking and storage. Cuerda seca, a decorative technique developed in Islamic pottery around the 10th century, uses a resist method to create vibrant, multicolored designs, primarily on glazed ceramic surfaces rather than raw earthenware. The evolution of earthenware pots reflects early human innovation in utilitarian ceramics, while cuerda seca represents a later artistic advancement in ceramic decoration within Islamic art traditions.
Key Techniques: Cuerda Seca Glazing Process
The Cuerda Seca glazing process involves applying different colored glazes separated by a greasy resist line made from a manganese oxide and oil mixture, preventing colors from running during firing. This technique allows for intricate, multi-colored designs on ceramics, creating sharp, distinct patterns, unlike earthenware, which typically uses single glaze coats without resist lines. Cuerda Seca is particularly valued for its vibrant decorative appeal and precise color delineation on pot surfaces.
Material Composition: Earthenware vs Cuerda Seca
Earthenware is made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and softer ceramic that requires glazing for durability and water resistance. Cuerda seca technique involves applying a resist line with manganese oxide to create distinct, colored geometric patterns on glazed tiles, often used on earthenware bases but enhancing the surface with intricate designs. The material composition of earthenware provides a sturdy clay foundation, while cuerda seca adds decorative functionality by controlling glaze separation and color precision.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Possibilities
Cuerda seca pottery features intricate, multicolored patterns with sharp outlines created by a resist technique that separates pigments, offering detailed and vibrant aesthetics ideal for decorative art pieces. Earthenware pots display a more rustic and organic appearance with warm, earthy tones and a matte or slightly glossy finish, emphasizing natural textures and handmade craftsmanship. Design possibilities in cuerda seca include complex geometric and floral motifs using a broad color palette, while earthenware allows for varied forms and surface treatments, including glazing and incising for subtle decorative effects.
Durability and Functional Uses of Each Pot Type
Cuerda seca pottery, characterized by its intricate glaze-resistant lines, offers enhanced durability due to its fired clay and glazed surface, making it resistant to moisture and heat, ideal for decorative and functional kitchenware. Earthenware pots, made from porous clay and fired at lower temperatures, are less durable, more prone to chipping and moisture absorption, but excel in retaining heat for slow cooking and baking applications. For long-lasting use, cuerda seca suits decorative or everyday kitchen use, while earthenware serves best for heat retention and traditional cooking methods.
Maintenance and Care Considerations
Cuerda seca pots require careful cleaning to prevent glaze damage, typically using gentle hand washing without abrasive materials to maintain their intricate designs. Earthenware pots, being more porous, need regular seasoning with oil to enhance durability and avoid cracking, along with avoiding sudden temperature changes to prevent thermal shock. Proper storage in a dry environment is crucial for both types to prolong their lifespan and preserve their aesthetic qualities.
Cost and Accessibility Comparison
Cuerda seca pottery often incurs higher costs due to its intricate glazing technique and the skilled labor required, making it less accessible for mass production compared to earthenware. Earthenware pots are generally more affordable and widely available, benefiting from simpler manufacturing processes and readily sourced materials. This cost-efficiency and accessibility make earthenware a popular choice for everyday use, while cuerda seca remains favored in artisanal and decorative markets.
Choosing Between Cuerda Seca and Earthenware for Your Needs
Choosing between cuerda seca and earthenware pots depends on your aesthetic preferences and functional requirements. Cuerda seca, characterized by its intricate, colorful glaze patterns separated by greasy lines, offers a decorative appeal ideal for display or light use, whereas earthenware provides durability and porosity suited for cooking and everyday utility. Consider that earthenware retains heat well and adds a rustic touch, while cuerda seca pots excel in ornamental value and vibrant surface designs.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com