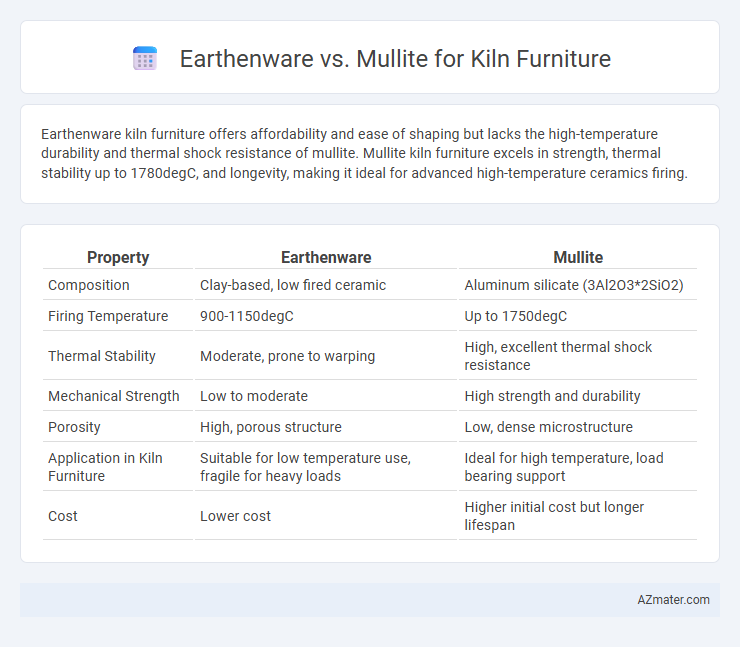
Earthenware kiln furniture offers affordability and ease of shaping but lacks the high-temperature durability and thermal shock resistance of mullite. Mullite kiln furniture excels in strength, thermal stability up to 1780degC, and longevity, making it ideal for advanced high-temperature ceramics firing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay-based, low fired ceramic | Aluminum silicate (3Al2O3*2SiO2) |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1150degC | Up to 1750degC |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, prone to warping | High, excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High strength and durability |
| Porosity | High, porous structure | Low, dense microstructure |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Suitable for low temperature use, fragile for heavy loads | Ideal for high temperature, load bearing support |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Kiln furniture materials such as earthenware and mullite serve critical roles in supporting ceramics during firing processes. Earthenware, made from porous clay, offers affordability and ease of shaping but lacks the high-temperature stability and resistance to thermal shock found in mullite. Mullite, a crystalline alumino-silicate, provides superior mechanical strength and durability at temperatures exceeding 1400degC, making it ideal for advanced kiln furniture applications requiring longevity and consistent performance.
Overview of Earthenware in Kiln Furniture
Earthenware kiln furniture offers cost-effective support for ceramics during firing, characterized by its porosity and lower firing temperature range of 1000-1150degC. This material is ideal for low-temperature firings, providing sufficient thermal insulation and a lightweight structure that helps reduce energy consumption. The primary limitation of earthenware is its lower mechanical strength and durability compared to mullite, making it less suitable for high-temperature or heavy-duty kiln furniture applications.
Mullite: Composition and Key Properties
Mullite, primarily composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, offers exceptional high-temperature stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for kiln furniture in industrial ceramics. Its low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent mechanical strength enhance durability under prolonged exposure to temperatures exceeding 1750degC. Compared to earthenware, mullite's superior structural integrity and chemical inertness ensure consistent performance during repeated firing cycles.
Thermal Resistance: Earthenware vs Mullite
Mullite kiln furniture exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to earthenware, tolerating temperatures up to 1750degC without deformation, while earthenware typically withstands only up to 1200degC. Mullite's low thermal expansion and high strength ensure dimensional stability during rapid temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for high-temperature firing cycles. Earthenware, with its porous structure and lower melting point, is better suited for low to medium temperature firings but risks structural damage under extreme heat.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Mullite kiln furniture exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to earthenware, with flexural strengths often exceeding 60 MPa, while earthenware typically ranges between 10-25 MPa. The enhanced mechanical strength of mullite, attributed to its crystalline structure and high-temperature stability, allows it to withstand greater thermal stress and load-bearing demands in kiln environments. Earthenware, composed primarily of clay minerals, offers lower durability and is more prone to cracking under cyclic heating, making mullite the preferred choice for industrial and high-performance kiln furniture applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Earthenware kiln furniture offers a lower initial cost compared to mullite, making it economically feasible for small-scale or low-temperature firing operations. Mullite, while more expensive upfront, provides superior thermal stability and longevity, reducing replacement frequency and overall long-term expenses in high-temperature or commercial kiln settings. Cost analysis shows mullite's durability offsets its price in continuous production environments, whereas earthenware suits budget-sensitive projects with less intense firing cycles.
Lifespan and Durability Considerations
Earthenware kiln furniture typically offers lower lifespan due to its porous structure that absorbs moisture and is prone to cracking under thermal stress, whereas mullite provides superior durability with high thermal shock resistance and minimal water absorption, extending kiln furniture service life significantly. Mullite's high melting point (approximately 1840degC) and excellent mechanical strength at elevated temperatures ensure consistent performance in demanding firing cycles compared to the comparatively fragile earthenware, which deteriorates faster under repeated use. Choosing mullite results in reduced replacement frequency and improved kiln efficiency, making it ideal for high-temperature ceramics production and industrial applications requiring robust kiln supports.
Suitability for High-Temperature Applications
Mullite offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength at temperatures exceeding 1300degC, making it highly suitable for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Earthenware, composed primarily of clay with lower firing temperatures around 1000degC to 1150degC, lacks the thermal resistance and durability required for sustained high-heat environments. Therefore, mullite's excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion ensures longer service life and better performance in demanding kiln operations compared to traditional earthenware.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Earthenware kiln furniture, made from natural clay, tends to have a lower carbon footprint due to its lower firing temperatures and biodegradable composition, making it more environmentally friendly. Mullite kiln furniture, composed primarily of aluminum silicate, offers exceptional durability and thermal shock resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacement but requires higher energy consumption during manufacturing. Choosing between earthenware and mullite involves balancing the initial energy input with lifecycle sustainability, where earthenware favors renewable, low-impact sourcing and mullite emphasizes longevity and reduced waste.
Choosing the Right Material for Kiln Furniture
Choosing the right material for kiln furniture depends on temperature resistance, thermal shock stability, and load-bearing capacity, where mullite outperforms earthenware with higher melting points above 1800degC and superior durability in repeated firing cycles. Earthenware is suitable for lower temperature firings up to 1100degC, offering cost-effectiveness but limited lifespan and increased risk of warping or cracking under intense heat. Mullite kiln furniture ensures longer kiln life and consistent dimensional stability, making it ideal for industrial and high-temperature ceramic processes.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Mullite for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com