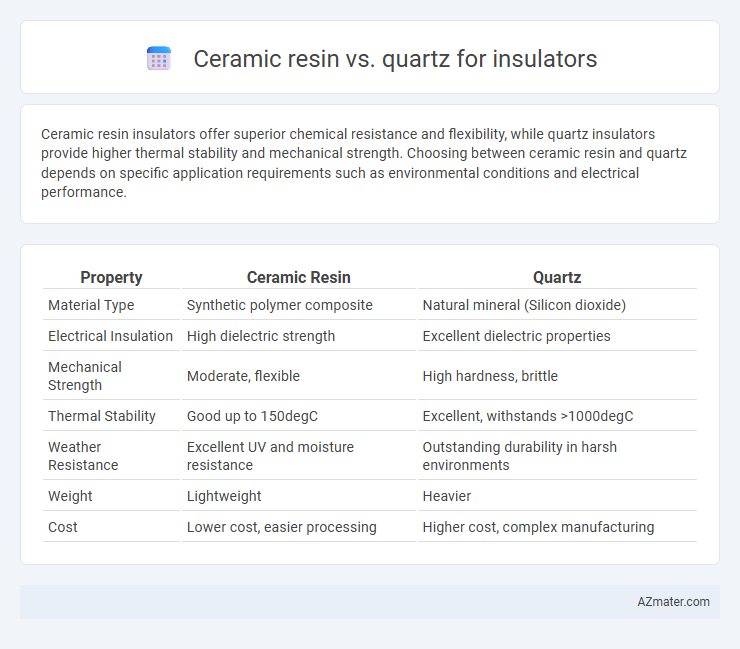
Ceramic resin insulators offer superior chemical resistance and flexibility, while quartz insulators provide higher thermal stability and mechanical strength. Choosing between ceramic resin and quartz depends on specific application requirements such as environmental conditions and electrical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Resin | Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer composite | Natural mineral (Silicon dioxide) |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength | Excellent dielectric properties |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, flexible | High hardness, brittle |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 150degC | Excellent, withstands >1000degC |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent UV and moisture resistance | Outstanding durability in harsh environments |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Lower cost, easier processing | Higher cost, complex manufacturing |
Overview of Ceramic Resin and Quartz Insulators
Ceramic resin insulators consist of porcelain combined with polymer resin, providing enhanced mechanical strength, weather resistance, and electrical insulation performance suitable for high-voltage applications. Quartz insulators leverage the high purity and crystalline structure of quartz to offer exceptional thermal stability, low dielectric loss, and superior resistance to environmental degradation. Both materials are fundamental in power transmission, with ceramic resin excelling in mechanical durability and quartz favored for its superior insulation properties under extreme thermal conditions.
Material Composition and Structure
Ceramic resin insulators are primarily composed of silicone rubber combined with fiberglass reinforcement, offering a lightweight and hydrophobic surface that resists contamination and moisture. Quartz insulators, on the other hand, are made from fused quartz or silica glass, characterized by high purity and excellent thermal stability with a dense, crystalline microstructure that ensures superior electrical insulation. The organic matrix of ceramic resin provides flexibility and reduced maintenance, while the inorganic quartz structure delivers enhanced mechanical strength and thermal resistance in high-voltage applications.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Ceramic resin insulators exhibit superior dielectric strength and higher resistance to electrical breakdown compared to quartz insulators, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. The intrinsic material composition of ceramic resin provides better moisture resistance and reduces leakage currents, enhancing overall insulation performance. Quartz, while offering good thermal stability, generally has lower electrical insulation properties and is more prone to surface contamination, which can degrade its insulating effectiveness.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Ceramic resin insulators exhibit superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to quartz insulators, withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC without significant degradation. Quartz insulators, while offering excellent electrical insulation, typically tolerate lower thermal thresholds around 870degC, limiting their use in extreme heat environments. The enhanced thermal properties of ceramic resin make it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications requiring durability and long-term reliability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic resin insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their high compressive strength and excellent resistance to cracking under stress, making them ideal for heavy-load applications. Quartz insulators offer exceptional durability because of their inherent hardness and resistance to thermal shock, which enhances performance in fluctuating environmental conditions. When comparing the two, ceramic resin excels in impact resistance while quartz provides longevity in abrasive and high-temperature environments.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Ceramic resin insulators exhibit superior resistance to UV radiation, chemical corrosion, and moisture ingress compared to quartz insulators, making them highly durable in harsh environments. Quartz insulators, while offering excellent thermal stability and high mechanical strength, tend to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to pollutants and acidic rain. The performance of ceramic resin insulators in contaminated and coastal areas is notably better due to their hydrophobic properties and self-cleaning surfaces, ensuring reliable electrical insulation and extended service life.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Ceramic resin insulators generally exhibit a lower upfront cost compared to quartz insulators, making them a budget-friendly option for many electrical applications. Quartz insulators, while initially more expensive, offer superior durability and longer lifespan, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Economic factors such as installation scale, environmental conditions, and total cost of ownership strongly influence the cost-effectiveness of choosing ceramic resin over quartz for insulators.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Ceramic resin insulators offer lighter weight and easier handling during installation compared to quartz insulators, reducing labor and equipment needs. Maintenance for ceramic resin is typically minimal due to its hydrophobic surface, which resists contamination and reduces cleaning frequency. Quartz insulators, while robust, are heavier and more prone to contamination, requiring more frequent inspections and cleaning to maintain performance.
Application Suitability and Industry Usage
Ceramic resin insulators offer excellent resistance to high voltage and environmental stress, making them ideal for power transmission and distribution in harsh weather conditions. Quartz insulators provide superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, commonly used in high-frequency and high-temperature industrial applications such as telecommunications and semiconductor manufacturing. Industry usage of ceramic resin is prevalent in electrical utilities, while quartz insulators dominate specialized sectors requiring precise electrical insulation and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic resin insulators generally exhibit higher environmental sustainability due to their natural clay and quartz composition, which are abundant and non-toxic materials with excellent recyclability. Quartz insulators, made primarily of silicon dioxide, offer durability but involve more energy-intensive extraction and processing, leading to a larger carbon footprint. The long service life and lower maintenance requirements of ceramic resin insulators contribute to reduced environmental impact over their operational lifespan compared to quartz alternatives.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Quartz for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com