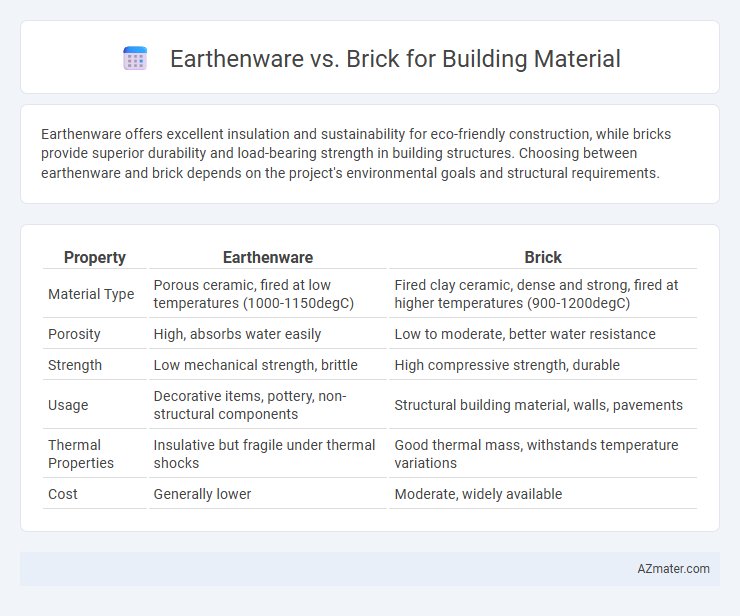
Earthenware offers excellent insulation and sustainability for eco-friendly construction, while bricks provide superior durability and load-bearing strength in building structures. Choosing between earthenware and brick depends on the project's environmental goals and structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous ceramic, fired at low temperatures (1000-1150degC) | Fired clay ceramic, dense and strong, fired at higher temperatures (900-1200degC) |
| Porosity | High, absorbs water easily | Low to moderate, better water resistance |
| Strength | Low mechanical strength, brittle | High compressive strength, durable |
| Usage | Decorative items, pottery, non-structural components | Structural building material, walls, pavements |
| Thermal Properties | Insulative but fragile under thermal shocks | Good thermal mass, withstands temperature variations |
| Cost | Generally lower | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction: Comparing Earthenware and Brick as Building Materials
Earthenware and brick are both traditional building materials with distinct properties influencing their application in construction. Earthenware, made from natural clay and fired at lower temperatures, offers excellent thermal insulation but lower structural strength compared to fired bricks. Bricks, typically kiln-fired at higher temperatures, provide greater durability, weather resistance, and load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for a wide range of structural uses.
Historical Overview of Earthenware and Brick Construction
Earthenware construction dates back to ancient Mesopotamia, where sun-dried mud bricks formed the basis of early structures, showcasing its longstanding use in sustainable building practices. Brick construction, emerging more prominently in the Indus Valley Civilization and ancient Egypt, evolved with kiln-firing techniques that enhanced durability and strength. Both materials reflect significant technological advancements, with earthenware emphasizing natural resources and brick demonstrating human innovation in thermal resilience across historical architectures.
Material Composition: Earthenware vs Brick
Earthenware is primarily composed of natural clay, sand, and water, fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and softer material suitable for decorative and non-structural uses. Bricks are made from clay or shale, mixed with water and other additives, then fired at higher temperatures to achieve greater strength, density, and durability for structural applications. The higher firing temperature in brick production causes vitrification, enhancing resistance to moisture and mechanical stress compared to earthenware.
Durability and Longevity
Earthenware offers moderate durability but is more susceptible to weathering and erosion compared to brick, which is known for its high compressive strength and long-lasting resilience. Bricks, manufactured from fired clay, exhibit superior resistance to moisture, heat, and mechanical stress, making them a preferred choice for structures requiring enhanced longevity. In contrast, earthenware's porous nature limits its use in load-bearing construction but remains suitable for decorative or non-structural applications.
Insulation and Thermal Properties
Earthenware offers superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure, which helps regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and releasing heat slowly. Brick, while durable and strong, typically has higher thermal conductivity, allowing heat to transfer more quickly and less effectively insulating buildings. Earthenware's natural insulating properties make it an energy-efficient choice for maintaining comfortable indoor environments in both hot and cold climates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Earthenware and brick differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with earthenware boasting low energy consumption during production due to its natural clay composition and minimal firing intensity. Brick manufacturing involves higher carbon emissions and energy use associated with kiln drying and firing at elevated temperatures. Earthenware is more sustainable and biodegradable, offering better eco-friendliness, while bricks provide durability but contribute to resource depletion and environmental pollution.
Cost Comparison: Earthenware vs Brick
Earthenware offers a more cost-effective building material compared to brick, primarily due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Brick production involves higher energy consumption and longer processing times, leading to increased overall costs. Savings with earthenware are significant in large-scale construction projects where budget constraints are critical.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Earthenware offers a unique, natural aesthetic with warm, earthy tones that enhance rustic and traditional designs, while bricks provide a uniform, versatile appearance suitable for both modern and classic architecture. The porous nature of earthenware allows for intricate textures and finishes, promoting artisanal craftsmanship, whereas bricks offer consistent shapes and sizes, enabling precise construction and diverse patterning options. Design flexibility in earthenware caters to organic, handcrafted styles, contrasted by brick's adaptability to structured, sleek, and varied architectural forms.
Maintenance Requirements
Earthenware requires regular sealing and protection from moisture to prevent cracking and erosion, making maintenance more frequent and intensive compared to brick. Brick offers greater durability and resistance to weathering, reducing the need for repairs and allowing for simpler upkeep routines. Choosing brick can result in lower long-term maintenance costs, while earthenware demands careful monitoring to maintain structural integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Earthenware offers excellent thermal insulation and sustainability, making it ideal for eco-friendly projects and moderate climates. Brick provides superior durability, strength, and resistance to weather, suited for structural stability and long-lasting construction. Selecting the right material depends on project requirements such as climate, budget, and desired aesthetic, with earthenware favoring natural appeal and bricks ensuring robust performance.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Brick for Building Material
 azmater.com
azmater.com