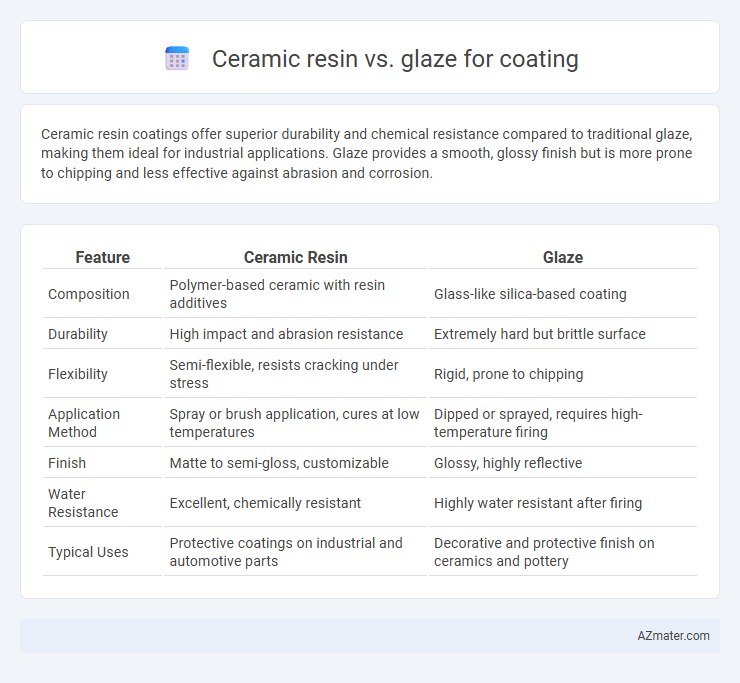
Ceramic resin coatings offer superior durability and chemical resistance compared to traditional glaze, making them ideal for industrial applications. Glaze provides a smooth, glossy finish but is more prone to chipping and less effective against abrasion and corrosion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Resin | Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polymer-based ceramic with resin additives | Glass-like silica-based coating |
| Durability | High impact and abrasion resistance | Extremely hard but brittle surface |
| Flexibility | Semi-flexible, resists cracking under stress | Rigid, prone to chipping |
| Application Method | Spray or brush application, cures at low temperatures | Dipped or sprayed, requires high-temperature firing |
| Finish | Matte to semi-gloss, customizable | Glossy, highly reflective |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, chemically resistant | Highly water resistant after firing |
| Typical Uses | Protective coatings on industrial and automotive parts | Decorative and protective finish on ceramics and pottery |
Introduction to Ceramic Resin and Glaze
Ceramic resin is a composite material combining ceramic particles with polymer resins, offering enhanced durability, heat resistance, and corrosion protection for surfaces. Glaze, a glassy coating typically applied and fired on ceramics, provides a smooth, glossy finish that improves aesthetics and waterproofing. Both coatings serve distinct purposes: ceramic resin emphasizes structural reinforcement and chemical resistance, while glaze focuses on surface sealing and decorative effects.
Key Differences Between Ceramic Resin and Glaze
Ceramic resin coatings provide enhanced durability and chemical resistance by forming a strong, flexible film, while glaze creates a hard, glass-like surface through vitrification during firing. Ceramic resin is suitable for applications requiring impact resistance and ease of repair, whereas glaze excels in offering a smooth, glossy finish with superior waterproofing and heat resistance. The key difference lies in ceramic resin's polymer-based composition granting flexibility, contrasted with glaze's inorganic silicate matrix that delivers hardness and permanence.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Ceramic resin coatings consist primarily of organic polymers combined with ceramic fillers, providing enhanced flexibility and impact resistance due to their hybrid organic-inorganic structure. Glaze coatings are predominantly composed of vitreous silica-based materials fused at high temperatures, resulting in a glassy, hard surface with excellent chemical inertness and abrasion resistance. The chemical properties of ceramic resin include superior thermal shock resistance and lower brittleness, whereas glaze offers high hardness, chemical stability, and resistance to corrosion and staining.
Application Methods and Techniques
Ceramic resin coatings are typically applied using spray, brush, or roller methods, allowing for precise control and uniform coverage on various surfaces, often requiring curing at elevated temperatures for optimal hardness. Glazes, in contrast, are usually applied by dipping, spraying, or brushing onto ceramics before being fired in a kiln, where the heat causes the glaze to melt and form a smooth, glass-like surface. The choice of application method impacts adhesion, finish quality, and durability, with ceramic resins favoring more versatile and lower-temperature processes, while glazes demand high-temperature firing for permanent coating formation.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Ceramic resin coatings provide superior durability by forming a flexible, impact-resistant layer that withstands scratches, UV exposure, and chemical damage better than traditional glazes. Glaze coatings, while offering an aesthetically glossy finish, tend to be more brittle and prone to cracking or wear over time, reducing their lifespan. The longevity of ceramic resin significantly outperforms glaze, often lasting several years without degradation in protection or appearance.
Aesthetic Effects and Surface Finish
Ceramic resin coatings provide a durable, matte to semi-gloss finish with excellent scratch resistance, enhancing texture and depth for a modern aesthetic. Glaze coatings offer a high-gloss, smooth surface that accentuates color vibrancy and creates a reflective, glass-like shine ideal for classic or decorative styles. The choice between ceramic resin and glaze affects both the tactile feel and visual impact, with resin emphasizing rugged elegance and glaze delivering sleek brilliance.
Protection Against Stains and Scratches
Ceramic resin coatings provide superior protection against stains and scratches due to their durable, non-porous surface that repels dirt and resists abrasion effectively. Glaze coatings offer a glossy finish but are generally more susceptible to wear, making them less effective in preventing surface damage over time. Ceramic resin's chemical resistance and hardness make it the preferred choice for long-lasting stain and scratch protection.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Ceramic resin coatings offer superior durability and resistance to scratches and chemicals, requiring minimal maintenance such as regular washing and occasional use of pH-neutral cleaners. Glaze coatings, while providing a glossy finish, are more prone to wear and require frequent polishing and touch-ups to maintain their appearance. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of ceramic resin significantly compared to glaze, reducing the need for costly refinishing.
Cost Considerations and Value
Ceramic resin coatings typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to traditional glaze applications, making them attractive for budget-conscious projects. While glazes may require higher initial investment due to specialized materials and labor, they provide superior durability and aesthetic depth, resulting in longer-lasting value. Evaluating cost considerations alongside performance needs ensures the best balance between affordability and long-term benefits in coating selection.
Ideal Uses and Recommendations
Ceramic resin coatings offer superior durability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications and surfaces exposed to high wear or corrosive environments. Glaze coatings provide a smooth, glossy finish best suited for decorative ceramics and food-safe surfaces due to their heat resistance and aesthetic appeal. Choosing between ceramic resin and glaze depends on the need for mechanical strength versus visual enhancement and surface protection in specific use cases.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Glaze for Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com