Ceramic coating provides a durable, heat-resistant layer that enhances filter longevity and particle capture efficiency. Ceramic foam offers a porous, high-surface-area structure that improves filtration performance and reduces airflow resistance.
Table of Comparison
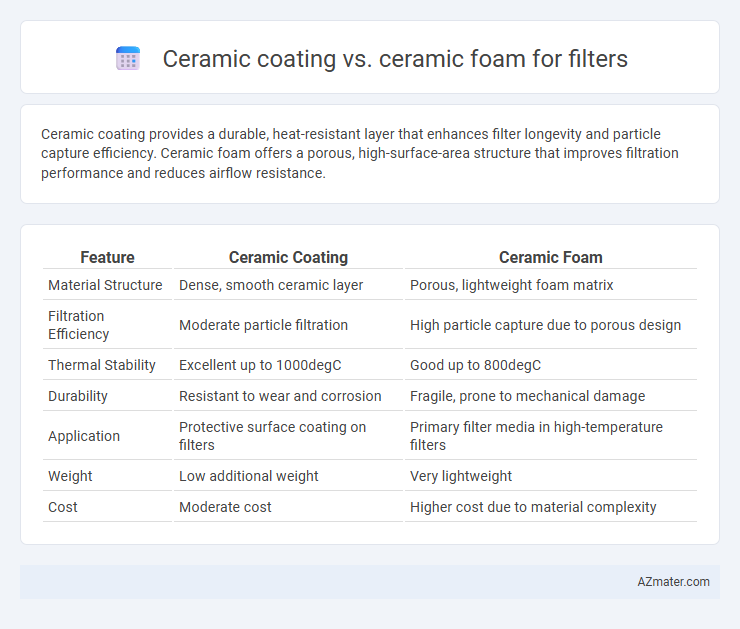
| Feature | Ceramic Coating | Ceramic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Dense, smooth ceramic layer | Porous, lightweight foam matrix |
| Filtration Efficiency | Moderate particle filtration | High particle capture due to porous design |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent up to 1000degC | Good up to 800degC |
| Durability | Resistant to wear and corrosion | Fragile, prone to mechanical damage |
| Application | Protective surface coating on filters | Primary filter media in high-temperature filters |
| Weight | Low additional weight | Very lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to material complexity |
Introduction to Filter Technologies
Ceramic coating enhances filter performance by providing a durable, heat-resistant layer that improves particle adhesion and durability in industrial and automotive filters. Ceramic foam, characterized by its porous structure, offers exceptional filtration efficiency by trapping contaminants while allowing high airflow and thermal stability in applications such as air and water filtration. Both technologies leverage ceramic materials' thermal resistance and chemical inertness, but ceramic foam's open-cell design enables superior filtering capacity compared to the solid-layer protection of ceramic coatings.
What is Ceramic Coating?
Ceramic coating is a thin, protective layer composed of silica or titanium dioxide applied to surfaces to enhance durability and resistance against corrosion, heat, and wear. In filtration systems, ceramic coatings improve the filter media by providing a smooth, chemically inert barrier that repels contaminants and reduces clogging. Unlike ceramic foam filters, which are porous and designed to physically trap particles, ceramic coatings primarily serve as a protective and functional surface treatment.
What is Ceramic Foam?
Ceramic foam is a porous material consisting of interconnected ceramic struts creating a lightweight, high-surface-area structure ideal for filtration. Unlike solid ceramic coatings that form a thin protective layer, ceramic foam offers enhanced particle capture and fluid flow due to its open-cell network. This makes ceramic foam highly effective for filters in industrial applications requiring durability, thermal resistance, and high particulate filtration efficiency.
Material Composition and Structure
Ceramic coatings for filters typically consist of dense, thin layers of silicon dioxide or aluminum oxide, providing a hard, smooth surface that enhances chemical resistance and reduces fouling. In contrast, ceramic foam filters are made from porous alumina or zirconia with an open-cell structure, allowing high permeability and effective particle capture while maintaining thermal stability. The dense microstructure of ceramic coatings prioritizes surface protection, whereas the interconnected porosity of ceramic foams enables superior filtration efficiency and gas flow.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Ceramic coatings provide a dense, smooth surface that enhances filtration efficiency by reducing pore size and preventing particle adhesion, making them ideal for high-precision filtration applications. Ceramic foam filters offer a highly porous structure with interconnected cells, allowing for efficient trapping of larger particles while maintaining high flow rates. Comparing filtration efficiency, ceramic coatings excel in fine particulate retention, whereas ceramic foam achieves superior performance in coarse filtration and fluid flow management.
Durability and Longevity
Ceramic coatings offer a thin, durable layer that enhances filter surfaces by providing excellent resistance to heat, corrosion, and wear, thereby extending filter lifespan significantly. Ceramic foam filters, constructed from porous ceramic material, deliver enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, allowing them to withstand harsh operating conditions while maintaining filtration efficiency. The longevity of ceramic foam filters generally surpasses that of ceramic coatings due to their structural integrity and ability to endure repeated thermal cycles and abrasive particulates.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Ceramic coatings provide superior thermal resistance by forming a dense, protective layer that withstands temperatures above 1000degC, making them ideal for high-heat filter applications. Ceramic foam filters offer enhanced chemical resistance due to their porous structure, which facilitates the trapping and neutralization of corrosive substances. Both materials excel in durability, but ceramic coatings are preferred for extreme thermal environments, while ceramic foams are advantageous in chemically aggressive filtration processes.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Ceramic foam filters typically cost more upfront than ceramic coatings but offer superior durability and easier maintenance due to their porous structure, which can be cleaned and reused multiple times. Ceramic coatings have lower initial costs but require more frequent replacement or recoating, increasing long-term expenses. Maintenance for ceramic foam involves less downtime and fewer consumable expenses, making it more cost-effective in high-use industrial filtration settings.
Best Applications for Each Technology
Ceramic coatings excel in high-temperature environments requiring durable, wear-resistant surfaces, making them ideal for automotive exhaust systems and industrial machinery filters. Ceramic foams provide superior filtration and lightweight structural support, best suited for air and liquid filtration in chemical processing and HVAC systems. Choosing between the two depends on the application's temperature tolerance, filtration needs, and mechanical strength requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Filter Solution
Ceramic coating enhances filter durability and corrosion resistance by providing a thin, protective layer ideal for high-temperature environments. Ceramic foam offers superior filtration efficiency with its porous structure, enabling better contaminant capture and higher flow rates. Selecting the right filter depends on specific application needs: choose ceramic coating for enhanced surface protection and ceramic foam for optimal filtration performance.
Infographic: Ceramic coating vs Ceramic foam for Filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com