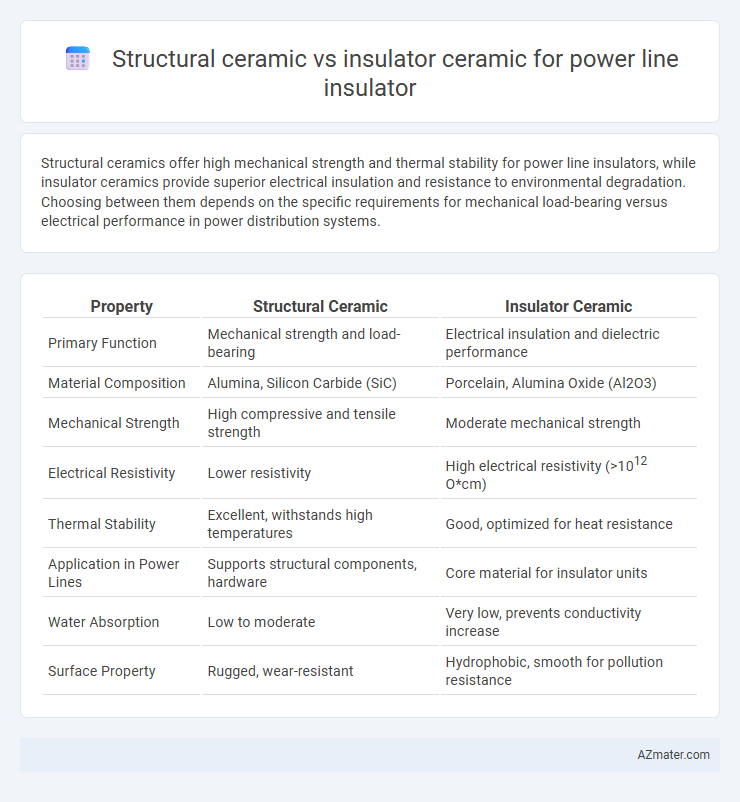
Structural ceramics offer high mechanical strength and thermal stability for power line insulators, while insulator ceramics provide superior electrical insulation and resistance to environmental degradation. Choosing between them depends on the specific requirements for mechanical load-bearing versus electrical performance in power distribution systems.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Structural Ceramic | Insulator Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Mechanical strength and load-bearing | Electrical insulation and dielectric performance |
| Material Composition | Alumina, Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Porcelain, Alumina Oxide (Al2O3) |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive and tensile strength | Moderate mechanical strength |
| Electrical Resistivity | Lower resistivity | High electrical resistivity (>1012 O*cm) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, withstands high temperatures | Good, optimized for heat resistance |
| Application in Power Lines | Supports structural components, hardware | Core material for insulator units |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate | Very low, prevents conductivity increase |
| Surface Property | Rugged, wear-resistant | Hydrophobic, smooth for pollution resistance |
Introduction to Ceramic Materials in Power Line Insulation
Structural ceramics in power line insulators provide exceptional mechanical strength and resistance to environmental stress, ensuring durability under high tension and mechanical loads. Insulator ceramics, primarily composed of alumina and porcelain, offer excellent electrical insulation properties by preventing leakage currents and withstanding high voltages. The choice between structural and insulator ceramics depends on balancing mechanical durability with dielectric performance to optimize power line reliability.
Defining Structural Ceramics: Properties and Uses
Structural ceramics for power line insulators exhibit high mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to wear and corrosion, making them ideal for load-bearing applications and harsh environmental conditions. These ceramics, such as alumina and silicon carbide, provide necessary structural integrity while maintaining electrical insulation properties. Unlike purely insulator ceramics, structural ceramics combine durability with electrical insulation to support and protect power transmission infrastructure efficiently.
Insulator Ceramics: Key Characteristics for Electrical Insulation
Insulator ceramics for power line insulators exhibit exceptional electrical insulation properties, high dielectric strength, and resistance to electrical breakdown under high voltage stress. These ceramics, commonly composed of materials like alumina and porcelain, offer excellent mechanical durability and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, pollution, and temperature fluctuations. Their low conductivity and high surface resistivity ensure reliable insulation performance, making them critical for maintaining safety and efficiency in power transmission systems.
Mechanical Strength: Structural vs Insulator Ceramics
Structural ceramics for power line insulators exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength compared to insulator ceramics due to their dense microstructure and enhanced fracture toughness. Insulator ceramics prioritize electrical insulation properties, often resulting in lower mechanical stiffness and strength relative to structural ceramics. The superior mechanical performance of structural ceramics makes them ideal for withstanding mechanical stresses and environmental loads in high-voltage power line applications.
Electrical Properties and Resistivity Comparison
Structural ceramics used in power line insulators exhibit high mechanical strength but moderate electrical resistivity, typically ranging from 10^8 to 10^12 ohm-cm, making them suitable for withstanding physical stress but less effective in preventing leakage currents. Insulator ceramics, specifically designed for power line applications, demonstrate superior electrical resistivity often exceeding 10^12 ohm-cm, which enhances their ability to resist electrical conduction and ensure insulation reliability under high voltage conditions. The optimized electrical properties of insulator ceramics minimize power losses and improve performance in harsh environments compared to structural ceramics with lower resistivity values.
Thermal Stability and Performance Under Voltage Stress
Structural ceramics used in power line insulators exhibit exceptional thermal stability, maintaining mechanical integrity at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, which ensures durability in harsh environmental conditions. Insulator ceramics, typically composed of alumina or porcelain, provide superior performance under voltage stress by offering high dielectric strength and resistance to electrical degradation, critical for preventing flashovers. The combination of thermal stability and electrical insulation properties makes these ceramics indispensable for reliable power line insulation under fluctuating thermal and electrical loads.
Moisture Resistance and Environmental Durability
Structural ceramics for power line insulators typically exhibit superior mechanical strength but may have limited moisture resistance compared to insulator ceramics specifically engineered for electrical insulation. Insulator ceramics, such as alumina and silicon nitride composites, offer enhanced environmental durability with hydrophobic surfaces that reduce moisture accumulation and prevent electrical tracking. These specialized ceramics maintain high dielectric strength and resist degradation from UV exposure, pollution, and varying weather conditions, ensuring long-term performance in harsh outdoor environments.
Manufacturing Processes: Differences and Implications
Structural ceramics for power line insulators undergo high-temperature sintering processes to achieve enhanced mechanical strength and fracture toughness, ensuring durability under mechanical stresses. Insulator ceramics prioritize electrical insulation properties through precise control of microstructure during processes like slip casting and glaze application, reducing electrical conductivity and enhancing dielectric performance. Variations in manufacturing techniques directly influence the material's performance, with structural ceramics optimized for load-bearing capacity and insulator ceramics tailored for electrical isolation and weather resistance.
Longevity and Reliability in Power Line Applications
Structural ceramics used in power line insulators exhibit exceptional mechanical strength and resistance to thermal stress, enhancing longevity under harsh environmental conditions. Insulator ceramics, specifically designed with high dielectric strength and low conductivity, ensure reliable electrical insulation and minimize power loss over extended periods. Both ceramic types contribute to the durability and efficiency of power line insulators, but structural ceramics offer superior robustness against physical wear, while insulator ceramics provide optimized electrical performance.
Choosing the Right Ceramic: Structural vs Insulator for Power Lines
Structural ceramics for power line insulators provide mechanical strength and durability under high stress and environmental conditions, making them ideal for supporting electrical conductors. Insulator ceramics primarily offer excellent electrical insulation and resistance to high voltage, preventing current leakage and maintaining safety. Selecting the right ceramic depends on balancing mechanical load requirements with electrical insulation performance to ensure reliable, long-lasting power line operation.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Insulator ceramic for Power line insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com