Bone china offers superior chip resistance and a lightweight feel, making it ideal for elegant dinnerware, while porcelain enamel provides exceptional durability and heat retention, perfect for heavy-duty cookware. Porcelain enamel's non-reactive surface resists staining and corrosion, whereas bone china's delicate composition is less suited for direct cooking applications.
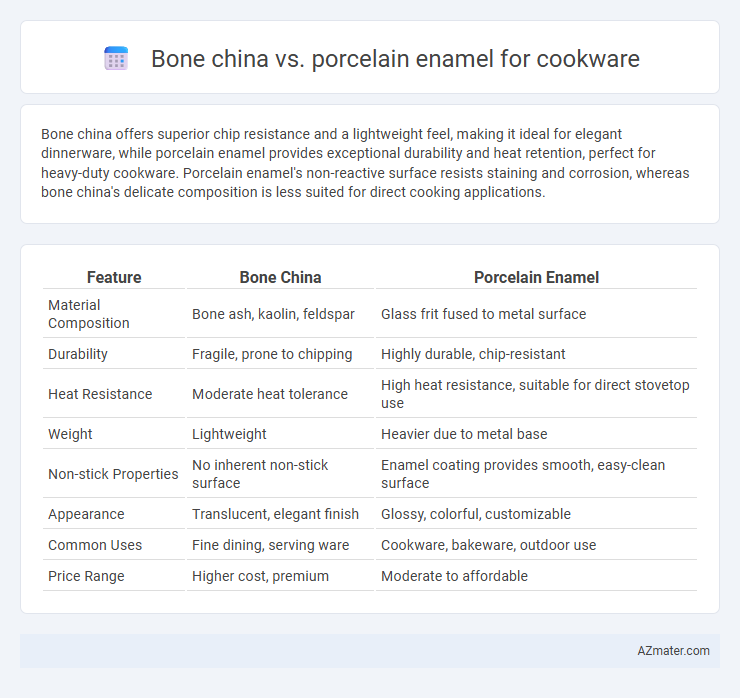
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone China | Porcelain Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Bone ash, kaolin, feldspar | Glass frit fused to metal surface |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping | Highly durable, chip-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat tolerance | High heat resistance, suitable for direct stovetop use |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to metal base |
| Non-stick Properties | No inherent non-stick surface | Enamel coating provides smooth, easy-clean surface |
| Appearance | Translucent, elegant finish | Glossy, colorful, customizable |
| Common Uses | Fine dining, serving ware | Cookware, bakeware, outdoor use |
| Price Range | Higher cost, premium | Moderate to affordable |
Introduction to Bone China and Porcelain Enamel Cookware
Bone china cookware combines refined feldspathic materials with bone ash, offering exceptional whiteness, translucency, and strength for elegant kitchen use. Porcelain enamel cookware features a durable vitreous enamel coating fused to metal, providing superior heat distribution and resistance to corrosion and chipping. Both materials enhance cooking performance through distinct structural properties, with bone china prized for aesthetic appeal and porcelain enamel favored for durability and heat retention.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Bone china cookware is composed primarily of bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, resulting in a lightweight, translucent material with high mechanical strength. Porcelain enamel cookware consists of a base metal, usually cast iron or steel, coated with a vitreous enamel layer made from powdered glass fused at high temperatures. The manufacturing of bone china requires firing at lower temperatures to preserve translucency, whereas porcelain enamel undergoes a high-temperature fusion process to create a durable, glossy coating resistant to corrosion and staining.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Bone china cookware offers moderate heat retention but excels in even distribution due to its fine, dense structure. Porcelain enamel cookware provides superior heat retention and uniform heat distribution because of its thick, glass-based coating fused to metal, typically cast iron or steel. For efficient cooking, porcelain enamel is preferred when consistent, sustained heat is essential, while bone china suits applications requiring precise temperature control but less heat storage.
Durability and Lifespan
Bone china cookware offers moderate durability with a lifespan suitable for light to medium use but is prone to chipping due to its delicate composition. Porcelain enamel cookware features a highly durable, non-porous coating fused to metal, providing excellent resistance to scratches, heat, and corrosion, resulting in a longer lifespan even under heavy daily use. The enamel's robust surface maintains its finish and performance over time, making it a preferred choice for longevity in cookware.
Weight and Handling Ease
Bone china cookware is significantly lighter than porcelain enamel, making it easier to handle during cooking and serving. Porcelain enamel, while durable and resistant to scratches, tends to be heavier due to its thick coating on metal bases, which can add extra weight and reduce maneuverability. The lightweight nature of bone china enhances user comfort and control, especially for prolonged cooking tasks or frequent movement.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Bone china cookware offers excellent safety with its non-toxic, lead-free composition, making it ideal for food use without chemical leaching risks. Porcelain enamel cookware features a durable, glass-like coating fused to metal that resists chipping and prevents harmful metals from seeping into food, ensuring food safety during cooking. Both materials are considered low-risk for toxicity, but porcelain enamel may occasionally chip, potentially exposing the metal base if damaged.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Bone china cookware offers a delicate, translucent aesthetic with smooth, elegant finishes that suit upscale kitchen settings, while porcelain enamel cookware provides a vibrant, glossy surface available in a wide range of colors and patterns. The design options for porcelain enamel are extensive, enabling bold, decorative styles that retain durability, compared to the subtle, classic look typical of bone china. Both materials enhance kitchen aesthetics, but porcelain enamel caters to those seeking versatile, striking visual designs, whereas bone china appeals to traditional, refined tastes.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Bone china cookware requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to preserve its delicate, translucent surface and prevent chipping. Porcelain enamel cookware demands careful maintenance to avoid scratching the enamel coating, using soft sponges and avoiding harsh chemicals to prevent dulling or cracking. Both materials benefit from hand washing and thorough drying to extend their lifespan and maintain optimal appearance.
Price Comparison and Value
Bone china cookware is generally more expensive due to its refined composition and delicate manufacturing process, often offering superior aesthetics but limited durability compared to porcelain enamel. Porcelain enamel cookware provides excellent value with its robust, chip-resistant surface and affordability, making it a practical choice for everyday use. While bone china may appeal to those prioritizing elegance, porcelain enamel delivers a more cost-effective and long-lasting option for versatile kitchen applications.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Bone china cookware offers excellent heat retention and is ideal for serving dishes due to its elegant appearance and durability, but it is less suitable for direct stovetop use. Porcelain enamel cookware provides superior resistance to high temperatures and scratch resistance, making it perfect for stovetop cooking and oven use, especially with cast iron bases for even heat distribution. For best results, choose bone china cookware for presentation and light baking, while porcelain enamel excels in everyday cooking and heavy-duty use.
Infographic: Bone china vs Porcelain enamel for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com