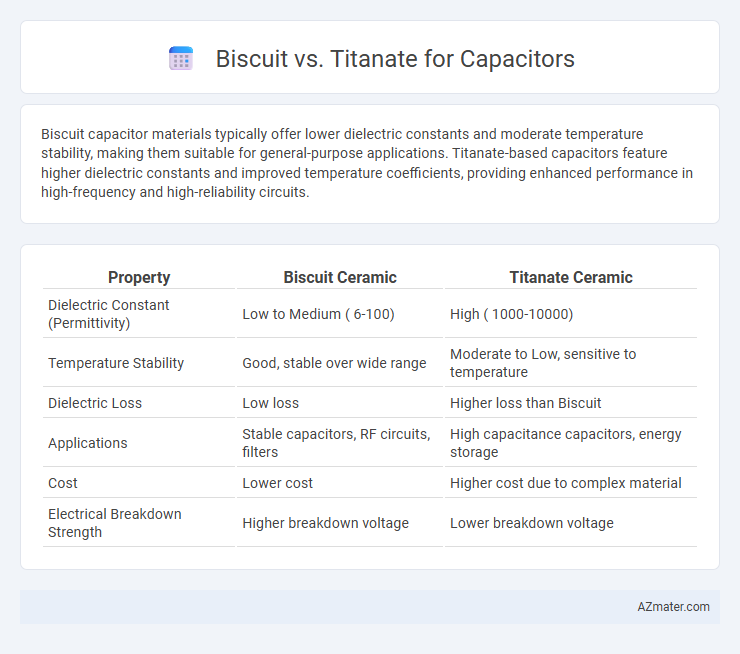
Biscuit capacitor materials typically offer lower dielectric constants and moderate temperature stability, making them suitable for general-purpose applications. Titanate-based capacitors feature higher dielectric constants and improved temperature coefficients, providing enhanced performance in high-frequency and high-reliability circuits.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biscuit Ceramic | Titanate Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (Permittivity) | Low to Medium ( 6-100) | High ( 1000-10000) |
| Temperature Stability | Good, stable over wide range | Moderate to Low, sensitive to temperature |
| Dielectric Loss | Low loss | Higher loss than Biscuit |
| Applications | Stable capacitors, RF circuits, filters | High capacitance capacitors, energy storage |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to complex material |
| Electrical Breakdown Strength | Higher breakdown voltage | Lower breakdown voltage |
Introduction: Understanding Biscuit and Titanate Capacitors
Biscuit capacitors, known for their compact, rectangular shape, utilize a thin ceramic dielectric material to achieve high capacitance in a small form factor, making them ideal for high-frequency and precision applications. Titanate capacitors incorporate barium titanate-based ceramics, providing stable dielectric properties and enhanced temperature tolerance, which are crucial for automotive and industrial electronics. Both capacitor types offer distinct advantages depending on performance requirements, with biscuit capacitors favored for miniaturization and titanate capacitors excelling in reliability under thermal stress.
Material Composition: Biscuit vs Titanate
Biscuit capacitors utilize ceramic materials primarily based on mixed metal oxides, often including barium or calcium titanate, providing stability and moderate dielectric constants. Titanate capacitors specifically employ pure or doped barium titanate as their dielectric material, yielding higher dielectric constants and enhanced capacitance values compared to biscuit variants. The distinct differences in ceramic composition directly impact their electrical characteristics, such as dielectric loss, insulation resistance, and temperature stability.
Dielectric Properties and Performance
Biscuit capacitors exhibit moderate dielectric constants and low dielectric losses, making them suitable for general-purpose applications requiring stable capacitance over a wide temperature range. Titanate capacitors, composed of complex titanium oxide ceramics, offer higher dielectric constants and improved temperature stability, resulting in greater energy storage capacity and enhanced performance in high-frequency applications. The superior dielectric properties of titanate materials translate to increased capacitance density and reduced leakage current compared to biscuit-type dielectrics, optimizing overall capacitor efficiency.
Capacitance Range and Tolerance
Biscuit capacitors typically offer capacitance ranges from a few picofarads up to several microfarads with tight tolerances around +-5% to +-10%, making them suitable for precision applications. Titanate capacitors usually provide broader capacitance values, from nanofarads to several microfarads, but with wider tolerances spanning +-10% to +-20%, prioritizing stability over precision. The choice between biscuit and titanate capacitors depends on the required capacitance accuracy and the specific tolerance needed for the electronic design.
Temperature Stability Comparison
Titanate capacitors exhibit superior temperature stability compared to biscuit capacitors, maintaining consistent capacitance across a wide temperature range from -55degC to 125degC. Biscuit capacitors often show greater capacitance variation and increased dielectric losses at elevated temperatures, limiting their performance in high-temperature environments. The robust temperature coefficient of titanate dielectric materials makes them ideal for applications requiring reliable operation under thermal stress.
Size, Shape, and Design Differences
Biscuit capacitors typically feature a rectangular or flat oval shape, optimized for compact circuit board layouts, while Titanate capacitors often have a cylindrical form that suits high-voltage applications. In terms of size, Biscuit capacitors are generally smaller and thinner, enabling higher component density, whereas Titanate capacitors tend to be bulkier due to their robust construction and enhanced dielectric properties. Design differences include Biscuit types favoring surface-mount technology with ease of integration, while Titanate capacitors leverage their unique ceramic composition for thermal stability and longer lifespan in demanding environments.
Reliability and Lifespan
Biscuit capacitors, typically made from ceramic or polymer materials, offer superior reliability with lower failure rates under thermal and mechanical stress compared to titanate-based capacitors. Titanate capacitors, while providing higher capacitance density and better performance at high frequencies, tend to have shorter lifespans due to their susceptibility to aging and dielectric degradation. In applications demanding long-term durability and stable performance, biscuit capacitors are generally preferred for their enhanced lifespan and consistent reliability.
Common Applications for Each Type
Biscuit capacitors are commonly used in high-frequency circuits, RF applications, and precision analog signal processing due to their stable capacitance and low loss characteristics. Titanate capacitors excel in power electronics, motor run applications, and energy storage systems, offering high dielectric constant and robust temperature stability. Both types serve distinct roles in electronic systems, with biscuits favored for signal integrity and titanates for power handling and durability.
Cost Analysis: Biscuit vs Titanate
Biscuit capacitors are generally more cost-effective due to their simpler manufacturing process and use of readily available materials, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications. Titanate capacitors, while offering superior performance in terms of temperature stability and dielectric constant, come with higher production costs driven by complex raw materials and processing techniques. Cost analysis reveals biscuit capacitors provide a low-cost solution with acceptable performance, whereas titanate capacitors justify their premium price through enhanced durability and electrical characteristics in demanding environments.
Future Trends in Capacitor Technologies
Biscuit and Titanate capacitors both contribute uniquely to future capacitor technologies, with Biscuit capacitors offering enhanced high-frequency performance and miniaturization suitable for next-generation electronics. Titanate capacitors leverage their superior dielectric properties and thermal stability, making them ideal for electric vehicles and renewable energy systems demanding long lifespan and reliability. Emerging trends indicate a convergence of these materials with nanotechnology and advanced ceramics to achieve higher energy density, faster charge-discharge cycles, and improved environmental sustainability in capacitor development.
Infographic: Biscuit vs Titanate for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com