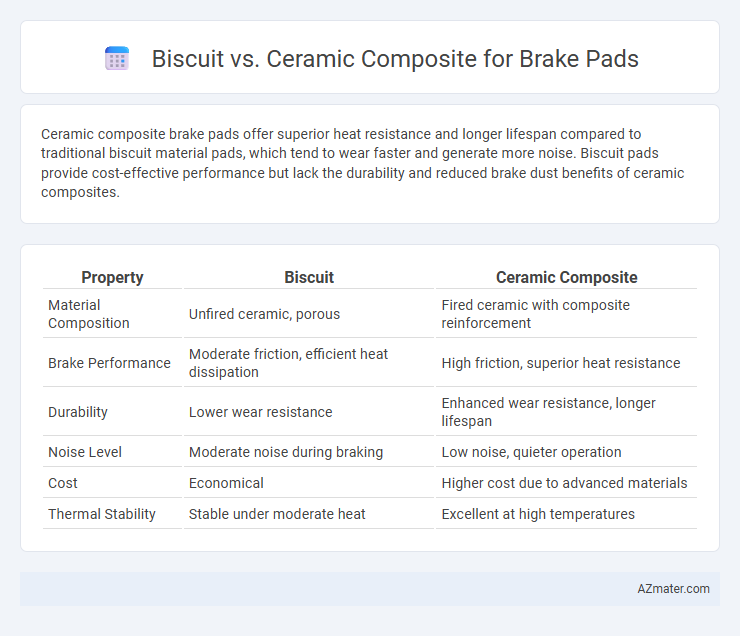
Ceramic composite brake pads offer superior heat resistance and longer lifespan compared to traditional biscuit material pads, which tend to wear faster and generate more noise. Biscuit pads provide cost-effective performance but lack the durability and reduced brake dust benefits of ceramic composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biscuit | Ceramic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Unfired ceramic, porous | Fired ceramic with composite reinforcement |
| Brake Performance | Moderate friction, efficient heat dissipation | High friction, superior heat resistance |
| Durability | Lower wear resistance | Enhanced wear resistance, longer lifespan |
| Noise Level | Moderate noise during braking | Low noise, quieter operation |
| Cost | Economical | Higher cost due to advanced materials |
| Thermal Stability | Stable under moderate heat | Excellent at high temperatures |
Introduction to Brake Pad Materials
Brake pads commonly use biscuit and ceramic composite materials, each offering distinct performance characteristics for braking systems. Biscuit brake pads typically consist of organic compounds mixed with metals, providing good friction and heat dissipation but often wearing faster and generating more dust. Ceramic composite pads integrate ceramic fibers and bonding agents, delivering quieter operation, reduced dust, and enhanced durability under high temperatures.
What is Biscuit Composite?
Biscuit composite brake pads consist of a metal backing plate bonded with a friction material made from organic fibers, resins, and fillers, designed for effective heat dissipation and wear resistance. This type of composite balances performance and noise control, making it suitable for everyday driving conditions. Biscuit composites offer moderate durability and cost-efficiency compared to ceramic composites, which typically provide superior heat tolerance and longer lifespan.
What is Ceramic Composite?
Ceramic composite brake pads consist of dense ceramic fibers, bonding agents, and small amounts of metal fibers, providing excellent heat dissipation and reduced brake dust compared to traditional organic or semi-metallic pads. These materials offer quieter braking performance and longer lifespan due to their resistance to wear and high temperatures. Ceramic composites are preferred in passenger vehicles for their enhanced comfort, minimal rotor wear, and consistent stopping power under various driving conditions.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Biscuit brake pads are typically manufactured through a stamping or molding process using friction materials bonded to a metal backing plate, allowing for efficient mass production with consistent thickness and shape. Ceramic composite brake pads involve a more complex manufacturing process where ceramic fibers, bonding agents, and other fillers are mixed and cured under high pressure and temperature to achieve enhanced heat resistance and durability. The ceramic composite process results in quieter performance and less brake dust, whereas biscuit pads prioritize cost-effectiveness and straightforward production methods.
Performance Characteristics
Biscuit brake pads exhibit superior initial bite and consistent friction levels, making them ideal for everyday driving with balanced braking performance. Ceramic composite brake pads offer enhanced heat dissipation and reduced brake dust production, contributing to longer pad life and improved performance during high-temperature conditions. Both materials provide reliable stopping power, but ceramic composites excel in maintaining performance under extreme braking scenarios.
Heat Resistance and Fade
Ceramic composite brake pads exhibit superior heat resistance, maintaining performance at temperatures exceeding 1200degF, compared to biscuit pads which typically begin to fade around 700degF. The enhanced thermal stability of ceramic composites reduces brake fade, ensuring consistent stopping power under high-stress braking conditions. This makes ceramic composite pads ideal for performance vehicles requiring reliable heat dissipation and minimal fade during extended use.
Noise and Dust Generation
Biscuit brake pads typically generate higher noise levels due to their metallic content, which can cause squealing under heavy braking. Ceramic composite brake pads produce significantly less dust, resulting in cleaner wheels and reduced brake system wear. Noise reduction and minimal dust generation are key advantages of ceramic composites over biscuit brake pads in automotive braking systems.
Longevity and Durability
Ceramic composite brake pads offer superior longevity compared to biscuit-style pads due to their enhanced resistance to heat and wear, extending their service life significantly under high-stress conditions. The composite materials in ceramic pads maintain structural integrity and reduce rotor wear, making them more durable for heavy-duty and performance driving. Biscuit brake pads, while often more affordable, tend to wear out faster and are less effective at withstanding extreme temperatures, which can compromise overall brake system durability.
Cost Effectiveness
Biscuit brake pads typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to ceramic composite options, making them more budget-friendly for routine maintenance. Ceramic composite brake pads provide longer lifespan and enhanced performance, which can reduce overall replacement frequency and labor costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, ceramic composites often prove more cost-effective despite higher initial prices due to durability and reduced wear on rotors.
Choosing the Right Brake Pad Material
Choosing the right brake pad material depends on driving habits and vehicle requirements, where biscuit (organic) brake pads offer quieter operation and better initial bite but wear faster and produce more dust. Ceramic composite brake pads provide superior durability, consistent performance under high temperatures, and reduced brake dust, making them ideal for performance and daily use. Balancing cost, driving style, and maintenance needs ensures optimal braking performance and longevity.
Infographic: Biscuit vs Ceramic Composite for Brake Pad
 azmater.com
azmater.com