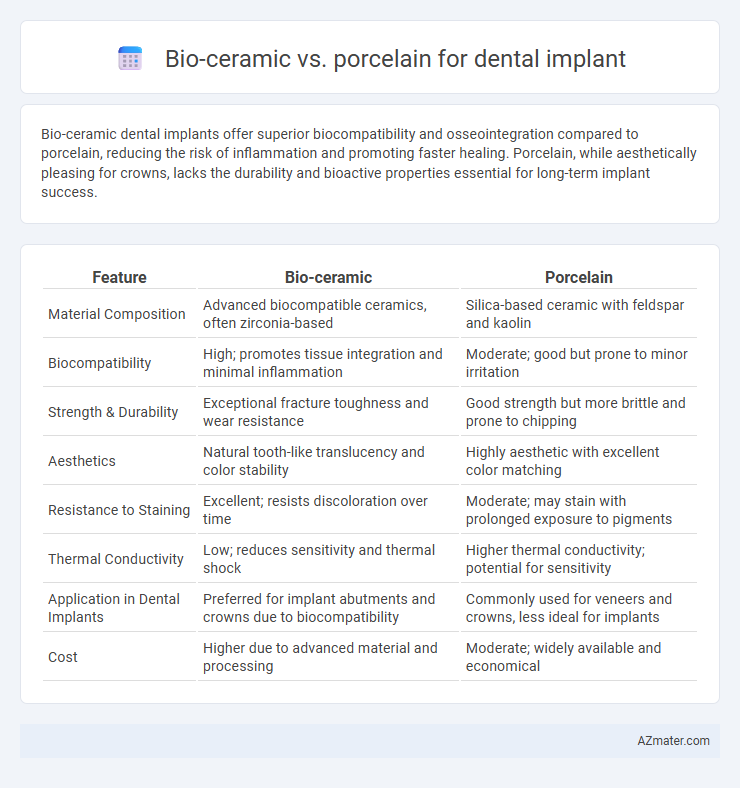
Bio-ceramic dental implants offer superior biocompatibility and osseointegration compared to porcelain, reducing the risk of inflammation and promoting faster healing. Porcelain, while aesthetically pleasing for crowns, lacks the durability and bioactive properties essential for long-term implant success.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bio-ceramic | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced biocompatible ceramics, often zirconia-based | Silica-based ceramic with feldspar and kaolin |
| Biocompatibility | High; promotes tissue integration and minimal inflammation | Moderate; good but prone to minor irritation |
| Strength & Durability | Exceptional fracture toughness and wear resistance | Good strength but more brittle and prone to chipping |
| Aesthetics | Natural tooth-like translucency and color stability | Highly aesthetic with excellent color matching |
| Resistance to Staining | Excellent; resists discoloration over time | Moderate; may stain with prolonged exposure to pigments |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low; reduces sensitivity and thermal shock | Higher thermal conductivity; potential for sensitivity |
| Application in Dental Implants | Preferred for implant abutments and crowns due to biocompatibility | Commonly used for veneers and crowns, less ideal for implants |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced material and processing | Moderate; widely available and economical |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Dental implant materials primarily include bio-ceramics and porcelain, each offering distinct advantages for biocompatibility and aesthetics. Bio-ceramics, such as zirconia, provide excellent osseointegration and resistance to wear, reducing the risk of inflammation and promoting long-term stability. Porcelain, commonly used for dental crowns, delivers superior esthetic qualities that mimic natural teeth but may exhibit less durability compared to bio-ceramics in implant abutments.
Understanding Bio-Ceramic Materials
Bio-ceramic materials, composed primarily of biocompatible compounds like zirconia and alumina, offer superior osseointegration and reduced risk of allergic reactions compared to traditional porcelain used in dental implants. Their enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to wear improve the longevity and stability of implants, making them ideal for patients seeking durable and aesthetic restorative solutions. Advanced bio-ceramic formulations promote bone regeneration, supporting faster healing and improved implant success rates.
Overview of Porcelain in Dentistry
Porcelain in dentistry is a highly durable ceramic material widely used for dental crowns, veneers, and implant restorations due to its excellent aesthetic qualities and biocompatibility. It closely mimics the natural translucency and color of tooth enamel, making it a preferred choice for achieving a natural appearance in dental implants. Porcelain's resistance to staining and wear also contributes to its long-term performance in restorative dental treatments.
Comparing Biocompatibility: Bio-Ceramic vs Porcelain
Bio-ceramic materials exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to porcelain due to their enhanced integration with surrounding tissues and reduced risk of inflammatory response. Bio-ceramics, such as zirconia, promote osseointegration and show excellent resistance to bacterial colonization, contributing to long-term implant success. Porcelain, while aesthetically favorable, may pose greater challenges in tissue compatibility and longevity when used for dental implants.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Bio-ceramic dental implants exhibit superior biocompatibility and enhanced resistance to wear and corrosion, contributing to their long-term durability in oral environments. Porcelain implants, while aesthetically favorable due to their natural tooth-like appearance, tend to be more brittle and less resistant to fracture under stress compared to bio-ceramic materials. Strength analysis indicates bio-ceramics maintain structural integrity under high masticatory forces, making them preferable for patients requiring durable, long-lasting dental restorations.
Aesthetics and Natural Appearance
Bio-ceramic dental implants offer superior biocompatibility and mimic the translucency and light reflection of natural teeth, enhancing overall aesthetics and providing a lifelike appearance. Porcelain crowns, commonly used in dental restorations, deliver excellent color matching and surface texture but may lack the same integration benefits as bio-ceramics. The choice between bio-ceramic and porcelain hinges on prioritizing natural translucency and gum compatibility versus traditional strength and color customization.
Resistance to Staining and Wear
Bio-ceramic dental implants exhibit superior resistance to staining and wear due to their high-density microstructure and biocompatible surface, maintaining aesthetic integrity over time. Porcelain, although durable and commonly used for dental restorations, is more prone to surface wear and discoloration from foods, beverages, and oral hygiene products. The inherent hardness and chemical stability of bio-ceramics contribute to long-term color retention and reduced abrasion compared to porcelain materials.
Clinical Performance and Longevity
Bio-ceramic dental implants exhibit superior biocompatibility and osseointegration, reducing inflammation and promoting faster healing compared to porcelain implants. Clinical studies highlight that bio-ceramic materials maintain structural integrity and resist wear better, contributing to enhanced longevity in dental applications. Porcelain, while aesthetic and commonly used for crowns, shows higher susceptibility to chipping and fracture under functional stress, affecting long-term performance.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility
Bio-ceramic dental implants often carry a higher upfront cost due to advanced material properties and biocompatibility advantages, while porcelain implants tend to be more affordable and widely available. Accessibility to bio-ceramic implants may be limited by geographic location and specialized dental providers, whereas porcelain options are commonly offered by most dental clinics worldwide. Cost considerations also include long-term durability and potential replacement expenses, where bio-ceramic implants may provide better value despite the initial investment.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Dental Implant
Bio-ceramic dental implants offer superior biocompatibility and promote faster osseointegration compared to traditional porcelain, reducing the risk of inflammation and implant rejection. Porcelain, while aesthetically appealing due to its natural tooth-like appearance, may lack the durability and bioactivity necessary for long-term implant success in certain patients. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as patient-specific bone density, allergy risk, and desired aesthetic outcome, with bio-ceramics often preferred for their strength and biological integration.
Infographic: Bio-ceramic vs Porcelain for Dental Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com