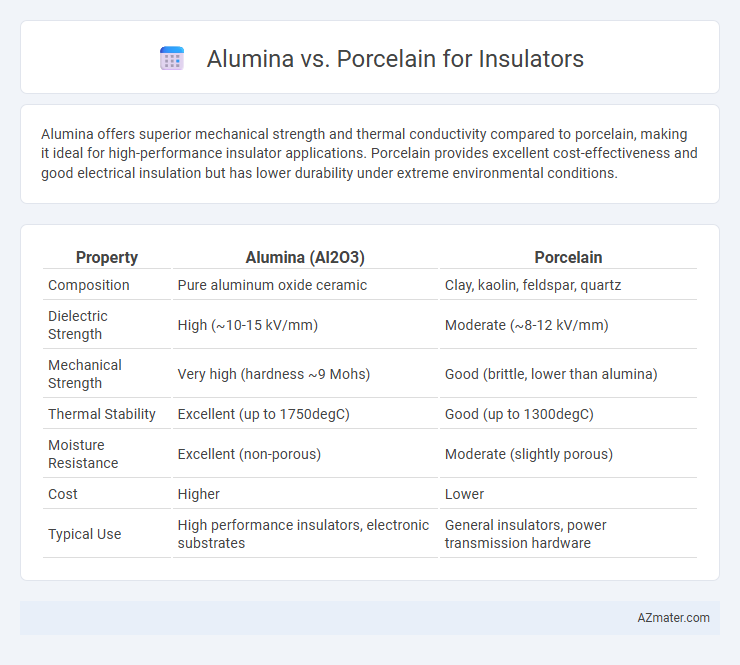
Alumina offers superior mechanical strength and thermal conductivity compared to porcelain, making it ideal for high-performance insulator applications. Porcelain provides excellent cost-effectiveness and good electrical insulation but has lower durability under extreme environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Al2O3) | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure aluminum oxide ceramic | Clay, kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Dielectric Strength | High (~10-15 kV/mm) | Moderate (~8-12 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high (hardness ~9 Mohs) | Good (brittle, lower than alumina) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (up to 1750degC) | Good (up to 1300degC) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent (non-porous) | Moderate (slightly porous) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Use | High performance insulators, electronic substrates | General insulators, power transmission hardware |
Introduction to Insulator Materials
Insulator materials such as alumina and porcelain are critical in electrical systems for preventing unwanted current flow and ensuring safety. Alumina offers superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-performance applications, while porcelain provides excellent dielectric properties and cost-effectiveness in traditional electrical insulators. The choice between alumina and porcelain depends on factors like operating voltage, environmental conditions, and mechanical stress requirements in power transmission and distribution infrastructure.
Overview of Alumina Insulators
Alumina insulators, composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), exhibit superior mechanical strength, high thermal conductivity, and excellent electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Their durability and resistance to chemical corrosion enable reliable performance in harsh industrial environments compared to porcelain insulators, which may be more susceptible to cracking and weathering. The dense microstructure of alumina ensures minimal moisture absorption, contributing to enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance in electrical systems.
Overview of Porcelain Insulators
Porcelain insulators, made from high-strength ceramic materials, provide excellent electrical insulation and mechanical stability, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Their microstructure offers superior resistance to weathering, chemical corrosion, and thermal stress, ensuring long-term durability in outdoor environments. Compared to alumina insulators, porcelain exhibits better hydrophobic properties and is often preferred for overhead transmission lines due to its reliable performance under varying environmental conditions.
Key Material Properties Compared
Alumina insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength and higher thermal conductivity compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-stress and high-temperature applications. Porcelain offers excellent electrical insulation and resistance to environmental degradation but has lower thermal shock resistance and mechanical durability than alumina. The choice depends on specific requirements like thermal management, mechanical load, and environmental exposure in electrical insulation systems.
Mechanical Strength: Alumina vs Porcelain
Alumina insulators exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength compared to porcelain, with tensile strength often exceeding 300 MPa, while porcelain ranges between 70-160 MPa. The superior hardness and fracture resistance of alumina make it ideal for high-stress electrical applications requiring durability against mechanical impacts. Porcelain, though mechanically weaker, offers excellent compressive strength and cost-effectiveness in less demanding environments.
Electrical Performance Analysis
Alumina insulators exhibit superior electrical performance due to their high dielectric strength and excellent thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat dissipation under high voltage conditions. Porcelain insulators, while offering good mechanical strength and moisture resistance, generally have lower dielectric strength compared to alumina, making them less effective in extreme electrical environments. The higher purity and density of alumina ceramics result in reduced electrical losses and enhanced insulation reliability in high-voltage applications.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Alumina insulators offer superior durability with high mechanical strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. Porcelain insulators provide good durability but are generally more susceptible to cracking under mechanical stress and less resistant to acidic or alkaline conditions. Both materials exhibit strong environmental resistance; however, alumina's dense microstructure enhances its performance against moisture penetration and chemical corrosion over prolonged usage.
Applications in Power Systems
Alumina insulators offer high mechanical strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-voltage power systems and switchgear components where durability and heat dissipation are critical. Porcelain insulators provide superior weather resistance and electrical insulation, widely used in overhead transmission lines and distribution networks to withstand environmental stresses. Both materials are essential in power systems, with alumina favored for demanding internal applications and porcelain dominating external, outdoor insulator usage.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Alumina insulators offer superior performance and durability but come at a higher cost and limited availability compared to porcelain insulators, which are more affordable and widely accessible in the market. Porcelain remains the preferred choice for cost-sensitive projects due to its extensive production and established supply chains. The trade-off between higher initial investment in alumina and the more economical porcelain depends on application-specific requirements and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Alumina insulators offer superior mechanical strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications. Porcelain insulators provide excellent dielectric strength and weather resistance, ensuring reliable performance in outdoor environments. Selecting the right insulator material depends on factors like electrical load, environmental conditions, and mechanical stress requirements.
Infographic: Alumina vs Porcelain for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com