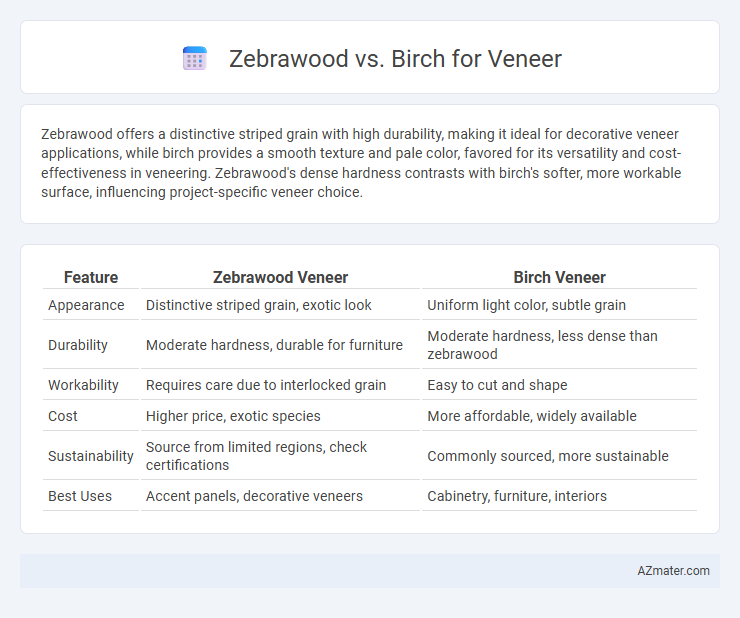
Zebrawood offers a distinctive striped grain with high durability, making it ideal for decorative veneer applications, while birch provides a smooth texture and pale color, favored for its versatility and cost-effectiveness in veneering. Zebrawood's dense hardness contrasts with birch's softer, more workable surface, influencing project-specific veneer choice.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zebrawood Veneer | Birch Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Distinctive striped grain, exotic look | Uniform light color, subtle grain |
| Durability | Moderate hardness, durable for furniture | Moderate hardness, less dense than zebrawood |
| Workability | Requires care due to interlocked grain | Easy to cut and shape |
| Cost | Higher price, exotic species | More affordable, widely available |
| Sustainability | Source from limited regions, check certifications | Commonly sourced, more sustainable |
| Best Uses | Accent panels, decorative veneers | Cabinetry, furniture, interiors |
Introduction to Zebrawood and Birch Veneer
Zebrawood veneer, known for its distinctive striped grain pattern and rich golden-brown hues, provides a bold and exotic aesthetic, making it a popular choice for high-end furniture and decorative panels. Birch veneer offers a smooth, pale surface with subtle grain patterns, favored for its versatility and modern appeal in cabinetry and interior design. Both veneers present durable, workable options, but Zebrawood is often selected for dramatic visual impact, while Birch supports clean, minimalist looks.
Botanical Origins and Overview
Zebrawood (Microberlinia brazzavillensis) is a tropical hardwood native to Central Africa, recognized for its striking dark stripes on a pale yellow to golden background, making it visually distinctive in veneer applications. Birch (Betula spp.), originating from temperate regions in the Northern Hemisphere, features a tight, uniform grain with a light cream to reddish-brown hue, offering a smooth and clean aesthetic in veneers. The contrasting botanical origins influence their density, texture, and coloration, with Zebrawood providing exotic boldness and Birch delivering subtle warmth and versatility for woodworking projects.
Visual Appearance and Grain Pattern
Zebrawood veneer features bold, contrasting dark and light stripes creating a dramatic, exotic appearance ideal for statement pieces. Birch veneer offers a more subtle, uniform grain pattern with light, creamy tones that provide a clean, contemporary look. The distinct, irregular grain of Zebrawood contrasts sharply with the smooth, consistent grain of Birch, influencing the overall aesthetic impact in cabinetry or furniture design.
Color Variations and Aging
Zebrawood veneer exhibits bold, contrasting dark brown and creamy yellow stripes that deepen and develop a richer, amber tone with age, enhancing its exotic appearance. Birch veneer offers a more subtle range of colors, typically presenting a pale cream to light reddish-brown hue that gently darkens and acquires a warm, honeyed patina over time. The dynamic color evolution of Zebrawood makes it ideal for statement pieces, while Birch maintains a consistent, understated elegance suited for classic and modern designs.
Durability and Hardness
Zebrawood veneer boasts a Janka hardness of approximately 1575, making it significantly harder and more durable than birch veneer, which has a Janka hardness around 1260. Its dense grain structure enhances resistance to dents and wear, ideal for high-traffic furniture surfaces. Birch veneer, while softer, offers moderate durability suitable for decorative applications but may show signs of wear faster in heavy-use environments.
Workability and Machining
Zebrawood offers moderate workability with a coarse texture that can cause challenges during machining, requiring sharp tools and careful handling to avoid tear-out. Birch veneer is known for its excellent workability, featuring a smooth, uniform grain that machines cleanly and consistently, making it ideal for detailed veneer applications. Both woods respond well to finishing, but birch provides superior ease in cutting, sanding, and gluing processes.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Zebrawood veneer commands a higher price due to its exotic status and limited availability, often sourced from West Africa, making it a premium choice for luxury projects. Birch veneer, widely grown in North America and Europe, is more readily available and significantly more affordable, offering excellent value for budget-conscious designs. The cost disparity reflects Zebrawood's unique grain pattern and rarity, contrasting with Birch's widespread supply and consistent quality.
Environmental Sustainability
Zebrawood veneer, sourced primarily from West African trees, faces sustainability challenges due to slow growth and deforestation concerns, leading to stricter harvesting regulations. Birch veneer, commonly harvested from fast-growing North American and European species, offers a more renewable option with managed forest practices promoting regrowth and reducing environmental impact. Choosing birch veneer supports sustainability efforts through responsible forestry certification programs like FSC, whereas zebrawood veneer requires careful consideration of its ecological footprint and sourcing transparency.
Common Applications in Veneering
Zebrawood veneer is commonly used in high-end furniture, cabinetry, and decorative wall panels due to its distinctive dark stripes and exotic appearance. Birch veneer, valued for its light color and fine grain, is frequently applied in modern interiors, plywood fabrication, and lightweight furniture. Both woods offer durability and aesthetic versatility, but Zebrawood is preferred for striking visual impact while Birch suits minimalist and Scandinavian-style designs.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Factors to Consider
Zebrawood veneer offers striking, bold grain patterns ideal for statement pieces, while birch veneer provides a smooth, light-toned surface suitable for modern, minimalist designs. Consider the project's aesthetic goals, wood hardness, and durability; zebrawood is harder and more wear-resistant, whereas birch is softer but easier to work with and finish. Cost and availability also influence choice, with birch typically more affordable and widely accessible compared to the exotic and pricier zebrawood.
Infographic: Zebrawood vs Birch for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com