Larch offers superior durability and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for long-lasting molding applications. Poplar provides a smooth finish and is easier to machine, suitable for intricate molding details in interior settings.
Table of Comparison
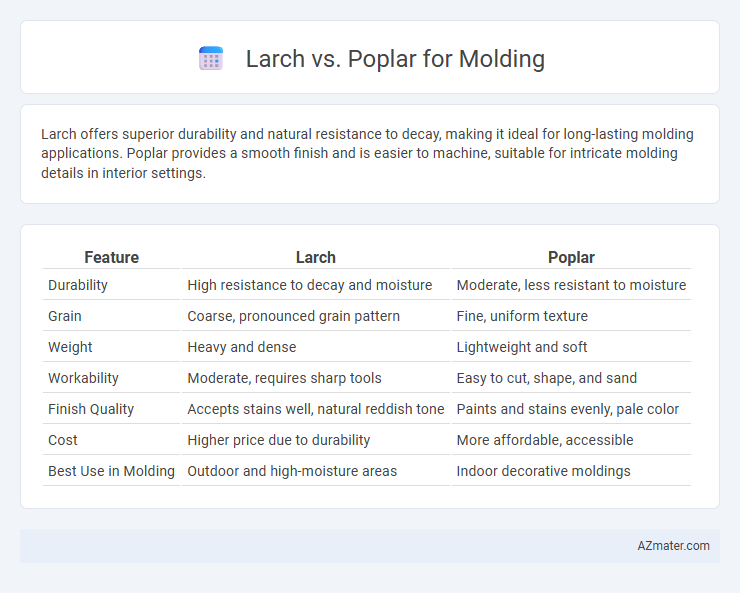
| Feature | Larch | Poplar |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to decay and moisture | Moderate, less resistant to moisture |
| Grain | Coarse, pronounced grain pattern | Fine, uniform texture |
| Weight | Heavy and dense | Lightweight and soft |
| Workability | Moderate, requires sharp tools | Easy to cut, shape, and sand |
| Finish Quality | Accepts stains well, natural reddish tone | Paints and stains evenly, pale color |
| Cost | Higher price due to durability | More affordable, accessible |
| Best Use in Molding | Outdoor and high-moisture areas | Indoor decorative moldings |
Introduction to Larch and Poplar for Molding
Larch wood is valued in molding for its durability, natural resistance to decay, and tight grain that allows for precise shaping and smooth finishes. Poplar, a lightweight hardwood, is favored for its ease of machining, uniform texture, and excellent paint adhesion, making it ideal for decorative and intricate moldings. Both species offer unique benefits: larch excels in outdoor and high-moisture environments, while poplar is preferred for cost-effective interior applications.
Physical Characteristics of Larch vs Poplar
Larch wood features a dense, hard texture with a natural resistance to rot and moisture, making it ideal for durable moldings in exterior or high-humidity environments. Poplar is a softer, lightweight wood with a fine, even grain that allows for smooth finishes and easy machining, preferred for interior moldings requiring detailed shaping and painting. Larch's distinctive reddish-brown color contrasts with Poplar's pale, cream-to-yellow tones, influencing aesthetic choices in molding applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Larch wood offers superior durability and strength compared to poplar, making it a preferred choice for molding in high-traffic or moisture-prone areas due to its dense grain and resistance to decay. Poplar, while easier to work with and more affordable, has a softer texture and lower resistance to wear, which may result in faster deterioration over time. For molding applications requiring long-lasting performance and structural integrity, larch provides a more robust and resilient option than poplar.
Workability and Machining Properties
Larch wood offers moderate workability with good resistance to machining, making it suitable for detailed molding projects that require durability and fine finishes. Poplar, known for its excellent workability, machines smoothly with minimal blunting of tools and produces clean, sharp edges, ideal for intricate molding profiles. Poplar's softer grain compared to larch allows for easier shaping and sanding, while larch provides higher strength and weather resistance in finished moldings.
Grain Pattern and Aesthetic Appeal
Larch wood features a tight, straight grain pattern with occasional knots, offering a warm, amber hue that enhances molding's classic and rustic appeal. Poplar exhibits a fine, uniform grain with a smooth texture and pale, creamy color, making it ideal for painted molding or modern, minimalist designs. The choice between Larch and Poplar for molding depends on whether a natural wood look with rich grain character or a smooth, paint-ready surface is desired.
Cost and Availability Factors
Larch and poplar differ significantly in cost and availability for molding applications, with poplar generally being more affordable due to its fast growth and widespread availability in North America. Larch, a denser and more durable wood primarily sourced from Europe and parts of Asia, tends to be pricier and less readily available in many markets. Choosing poplar can reduce material expenses and ensure consistent supply, whereas larch offers superior durability but at a higher cost and potential procurement challenges.
Finishing and Staining Capabilities
Larch wood's dense grain structure offers superior stain absorption, resulting in a smooth and rich finish ideal for detailed molding work. Poplar, with its fine and even texture, accepts paint and stains uniformly but may require a wood conditioner for consistent results. Both woods are commonly used in molding, but Larch provides enhanced finishing durability and color depth compared to Poplar's versatility and ease of staining.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Larch offers greater environmental benefits for molding due to its fast growth rate and natural durability, reducing the need for chemical treatments and frequent replacement. Poplar is a lightweight, renewable resource but typically requires more processing and chemical finishes to enhance durability, impacting its sustainability profile. Choosing larch supports longer-lasting moldings with a lower carbon footprint, aligning better with eco-friendly construction practices.
Popular Applications in Molding Projects
Larch wood's natural durability and moisture resistance make it a preferred choice for exterior molding applications such as window casings and door frames, especially in coastal and humid environments. Poplar, being lightweight and easy to machine, is widely used for interior molding projects, including baseboards and decorative trim, where smooth finishes and paint adherence are essential. Both woods offer versatility, but poplar is favored for intricate designs due to its fine grain, while larch excels in robust, weather-exposed moldings.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Molding Needs
Larch offers exceptional durability and a tight grain structure, making it ideal for molding that requires strength and resistance to wear. Poplar, known for its smooth texture and ease of painting, suits interior molding where a fine finish and versatility are essential. Selecting between larch and poplar depends on whether you prioritize longevity and natural aesthetics or cost-effectiveness and paintability for your molding project.
Infographic: Larch vs Poplar for Molding
 azmater.com
azmater.com