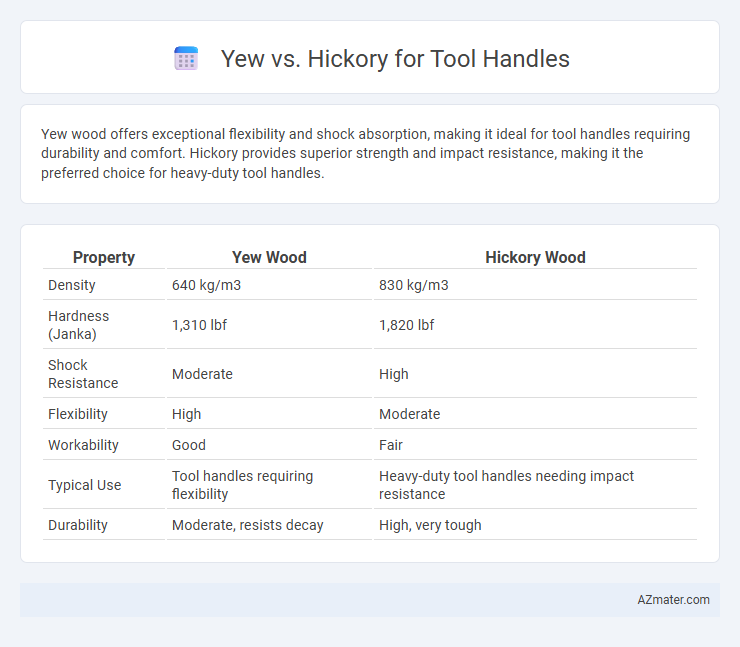
Yew wood offers exceptional flexibility and shock absorption, making it ideal for tool handles requiring durability and comfort. Hickory provides superior strength and impact resistance, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty tool handles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Yew Wood | Hickory Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 640 kg/m3 | 830 kg/m3 |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1,310 lbf | 1,820 lbf |
| Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Workability | Good | Fair |
| Typical Use | Tool handles requiring flexibility | Heavy-duty tool handles needing impact resistance |
| Durability | Moderate, resists decay | High, very tough |
Overview: Yew vs Hickory for Tool Handles
Yew wood offers a dense, smooth grain with natural flexibility, making it suitable for tool handles requiring shock absorption and fine control, such as carving tools and small hand tools. Hickory is renowned for its exceptional strength, toughness, and resistance to impact, often preferred for heavy-duty tool handles like hammers, axes, and mauls, where durability and endurance are critical. Both woods provide durability, but yew excels in elasticity and aesthetic grain patterns, while hickory leads in strength and wear resistance.
Wood Grain and Texture Comparison
Yew wood features a fine, straight grain with a smooth texture, providing excellent shock resistance and flexibility ideal for tool handles. Hickory exhibits a coarse, interlocked grain pattern coupled with a dense, tough texture, making it highly durable and resistant to impact stress. Both woods offer distinct tactile qualities, with yew delivering a more refined finish while hickory provides superior strength and wear resistance for heavy-duty applications.
Strength and Durability of Yew and Hickory
Yew offers exceptional strength and moderate durability, characterized by its dense grain and natural flexibility, making it resistant to impact and less prone to cracking under stress. Hickory is renowned for its superior toughness, high shock resistance, and outstanding durability, often preferred for tool handles that require sustained heavy use and maximum resilience. The choice between yew and hickory depends on balancing yew's flexibility and hardness with hickory's exceptional strength and long-lasting wear resistance.
Flexibility and Shock Absorption Properties
Yew wood offers superior flexibility compared to hickory, making it ideal for tool handles that require a degree of bending without breaking. Hickory is renowned for its exceptional shock absorption, effectively reducing user fatigue and impact stress during heavy-duty tasks. The combination of yew's flexibility and hickory's shock resistance highlights their unique advantages for ergonomic and durable tool handle design.
Weight and Handling Comfort
Yew wood is lightweight and offers excellent flexibility, making it a popular choice for tool handles that require precision and ease of movement. Hickory, on the other hand, is significantly denser and heavier, providing superior shock absorption and durability but potentially causing quicker hand fatigue during prolonged use. Choosing between Yew and Hickory for tool handles depends on whether the priority is lightweight maneuverability or robust impact resistance and comfort over extended tasks.
Resistance to Wear and Environmental Factors
Yew wood offers moderate resistance to wear and maintains durability under variable moisture conditions, making it suitable for tool handles exposed to light to moderate use. Hickory stands out with superior wear resistance and exceptional toughness, providing excellent shock absorption and lasting performance in harsh environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. For tool handles requiring high resilience and sustained durability, hickory is the preferred choice due to its outstanding strength and environmental stability.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Yew wood offers excellent workability and ease of shaping due to its fine grain and moderate hardness, making it ideal for detailed tool handles. Hickory, while tougher and denser, requires more effort to shape but provides superior shock resistance and durability for heavy-duty tool use. Choosing between Yew and Hickory depends on balancing the priority of ease of craftsmanship against the need for strength and impact absorption.
Cost and Availability
Yew is generally more expensive and less readily available than hickory due to its limited supply and slower growth rate, making it a higher-cost option for tool handles. Hickory offers greater affordability and widespread availability, as it grows abundantly in North America and is commonly used in commercial tool manufacturing. Cost-conscious consumers prioritize hickory for its balance of strength and economic value, while yew is chosen for premium, specialty applications despite its higher price point.
Traditional and Modern Applications
Yew wood, prized for its elasticity and fine grain, has been traditionally used in tool handles where precision and a smooth finish are crucial, such as woodworking chisels and archery bows, reflecting its historical significance in craftsmanship. Hickory, known for exceptional toughness and shock resistance, dominates modern tool handles in applications like hammers, axes, and mauls, where durability and impact absorption are paramount. Both woods offer unique advantages: Yew provides flexibility and aesthetic appeal for specialized, traditional tools, while Hickory delivers rugged performance in contemporary, heavy-duty hand tools.
Which Wood is Best: Yew or Hickory?
Hickory is widely regarded as the superior wood for tool handles due to its exceptional strength, shock resistance, and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty use and impact tools. Yew, while visually appealing with its fine grain and flexibility, lacks the same level of toughness and may not withstand repeated stress as effectively as hickory. For optimal performance and longevity, hickory remains the preferred choice among professionals and craftsmen for tool handles.
Infographic: Yew vs Hickory for Tool Handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com