Balsa plywood offers exceptional lightweight strength ideal for model making and aerospace, while birch plywood provides superior durability and hardness suited for furniture and construction. Birch plywood's tight grain structure enhances resistance to wear and impact compared to the softer, more flexible balsa layers.
Table of Comparison
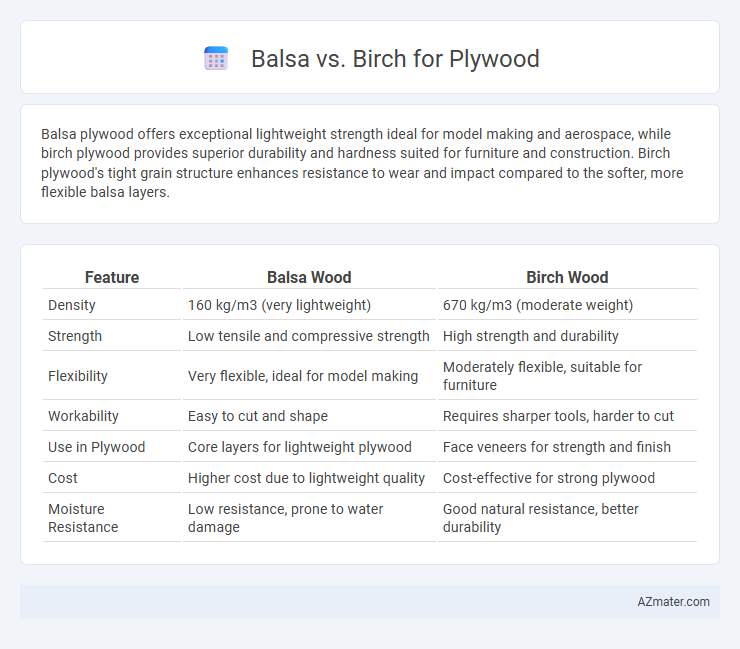
| Feature | Balsa Wood | Birch Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 160 kg/m3 (very lightweight) | 670 kg/m3 (moderate weight) |
| Strength | Low tensile and compressive strength | High strength and durability |
| Flexibility | Very flexible, ideal for model making | Moderately flexible, suitable for furniture |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Requires sharper tools, harder to cut |
| Use in Plywood | Core layers for lightweight plywood | Face veneers for strength and finish |
| Cost | Higher cost due to lightweight quality | Cost-effective for strong plywood |
| Moisture Resistance | Low resistance, prone to water damage | Good natural resistance, better durability |
Introduction to Balsa and Birch in Plywood
Balsa and birch are two popular wood species used in plywood fabrication, each offering distinct properties. Balsa plywood is prized for its exceptional lightness and buoyancy, making it ideal for lightweight construction, model building, and marine applications. Birch plywood is valued for its strength, durability, and fine grain, commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and architectural projects where structural integrity is crucial.
Physical Properties Comparison
Balsa plywood is significantly lighter with a density ranging from 100 to 200 kg/m3, offering excellent strength-to-weight ratio, whereas birch plywood is denser at approximately 600 to 700 kg/m3, providing superior hardness and durability. Balsa exhibits higher compressive strength but lower bending strength compared to birch, making it ideal for lightweight structural applications but less resistant to impact and wear. Birch plywood features tighter grain structure and greater resistance to moisture and deformation, enhancing its suitability for furniture and flooring where rigidity and longevity are critical.
Density and Weight Differences
Balsa plywood is significantly lighter than birch plywood due to its extremely low density, typically around 160 kg/m3 compared to birch's much higher density of approximately 700 kg/m3. This density difference makes balsa ideal for applications requiring lightweight materials, such as model building and aviation, whereas birch plywood offers superior strength and durability suitable for furniture and flooring. The weight advantage of balsa reduces overall project mass but compromises load-bearing capacity compared to the much denser and sturdier birch plywood.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Birch plywood offers significantly higher strength and durability compared to balsa plywood, making it ideal for structural applications and heavy-duty use. Balsa plywood, while lightweight and easy to work with, lacks the density and resilience required for load-bearing projects and deteriorates faster under stress or environmental exposure. The dense grain structure of birch provides superior resistance to impact, wear, and moisture, ensuring longer lifespan and reliable performance in demanding conditions.
Workability and Ease of Machining
Balsa plywood is exceptionally lightweight and soft, making it easy to cut, shape, and sand with minimal effort, ideal for fine detail work and model building. Birch plywood, though denser and harder, offers greater durability and resistance to wear while still maintaining good machinability with standard woodworking tools. Both materials suit different applications: balsa for projects requiring ease of machining and low weight, and birch for sturdier constructions demanding smooth finishes and structural strength.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Balsa plywood is significantly more expensive due to its lightweight properties and limited commercial availability, making it ideal for specialized applications like model building and aircraft components. Birch plywood, on the other hand, offers a more cost-effective alternative with widespread commercial availability, commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and general construction. The price difference reflects balsa's rarity and unique characteristics compared to birch's durability and abundant supply in the market.
Common Applications in Industry
Balsa plywood is widely used in aerospace and model-making industries due to its exceptional lightweight properties and high strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for crafting prototypes and lightweight structures. Birch plywood dominates in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and flooring applications because of its durability, smooth finish, and resistance to warping and cracking under stress. Both materials serve critical roles where specific strength, weight, and surface qualities align with industry demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Balsa plywood is highly renewable due to the rapid growth rate of balsa trees, allowing for quicker regrowth and reduced carbon footprint compared to birch. Birch plywood, while denser and stronger, typically comes from slower-growing hardwood forests, which can lead to greater environmental strain and less sustainable logging practices. Choosing balsa plywood supports sustainable forestry initiatives and reduces deforestation impacts associated with birch harvesting.
Moisture Resistance and Stability
Balsa plywood offers exceptional moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, making it less prone to water absorption and swelling compared to birch plywood. Birch plywood excels in dimensional stability and strength but tends to absorb more moisture, which can lead to warping or delamination in humid conditions. Selecting balsa plywood is ideal for applications requiring lightweight, moisture-resistant materials, while birch plywood suits projects needing durable, stable panels with moderate moisture exposure.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Balsa plywood offers exceptional lightweight properties and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for model building and applications requiring minimal weight. Birch plywood provides superior strength, durability, and a smooth finish, well-suited for furniture, cabinetry, and structural uses. Selecting the right wood depends on project demands: choose balsa for lightweight needs and birch for robustness and aesthetic appeal.
Infographic: Balsa vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com