Yew wood offers exceptional strength and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for durable rafter construction. Hemlock is lighter and more affordable but less resistant to moisture and insect damage compared to yew.
Table of Comparison
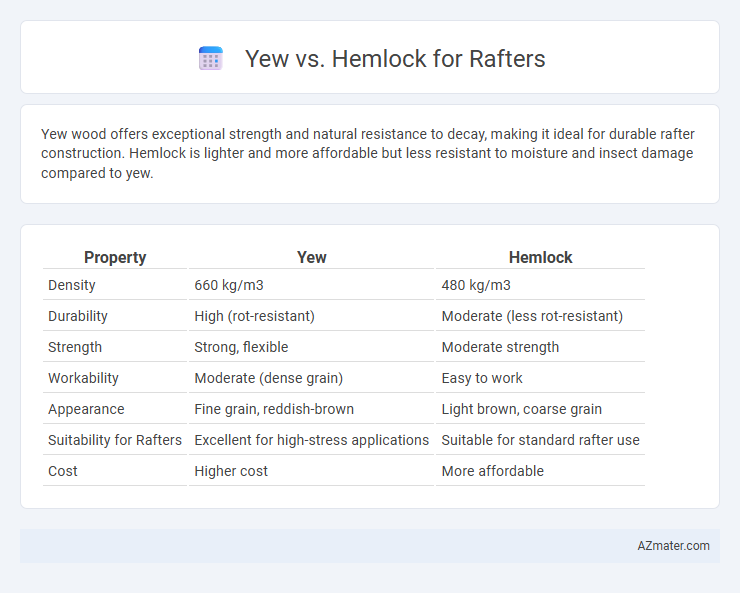
| Property | Yew | Hemlock |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 660 kg/m3 | 480 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High (rot-resistant) | Moderate (less rot-resistant) |
| Strength | Strong, flexible | Moderate strength |
| Workability | Moderate (dense grain) | Easy to work |
| Appearance | Fine grain, reddish-brown | Light brown, coarse grain |
| Suitability for Rafters | Excellent for high-stress applications | Suitable for standard rafter use |
| Cost | Higher cost | More affordable |
Introduction: Yew vs Hemlock for Rafters
Yew wood offers exceptional strength and durability, making it a valuable choice for rafters in construction due to its high resistance to decay and fine grain. Hemlock, known for its lightweight and moderate strength, provides ease of handling and cost-effectiveness but may require treatment to enhance its resistance to moisture and pests. Comparing Yew and Hemlock for rafters involves assessing factors such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and long-term maintenance needs.
Botanical Overview: Yew and Hemlock Trees
Yew (Taxus spp.) and Hemlock (Tsuga spp.) are both coniferous trees with distinct botanical characteristics important for rafters. Yew wood is dense, fine-grained, and highly durable due to its slow growth and resin content, making it ideal for structural uses requiring strength and resilience. Hemlock wood, derived from faster-growing needles with softer texture, offers moderate strength and excellent workability but is less resistant to decay compared to Yew.
Wood Strength and Durability Comparison
Yew wood offers moderate strength with a Janka hardness of approximately 1,130 psi, making it suitable for rafters that require flexibility and moderate load-bearing capacity. Hemlock presents higher durability and strength, with a Janka hardness around 810 psi but superior stiffness and resistance to decay, making it ideal for structural applications exposed to moisture. Both woods provide adequate durability, but Hemlock's enhanced resistance to decay and moisture makes it preferable for long-term rafter performance in outdoor or humid environments.
Weight and Workability Analysis
Yew wood is lighter, averaging around 30-35 lbs per cubic foot, providing easier handling during rafter installation compared to the denser hemlock, which weighs approximately 28-32 lbs per cubic foot but can be harder due to its firmer grain structure. In terms of workability, Yew offers excellent machinability and smooth finishing, making it ideal for detailed carpentry and refining rafter joints. Hemlock, while slightly heavier and less fine-grained, remains strong and moderately easy to work with, but may require more effort for precise cuts and finishing processes.
Moisture Resistance and Decay Performance
Yew wood exhibits superior moisture resistance and decay performance compared to Hemlock, making it a more durable choice for rafters exposed to varying weather conditions. Yew's dense grain and natural oils enhance its ability to repel water and resist fungal attacks, significantly reducing the risk of rot over time. Hemlock, while commonly used in construction, is more susceptible to moisture absorption and fungal decay, necessitating additional treatment or maintenance to ensure longevity in rafter applications.
Availability and Sourcing Factors
Yew wood is less commonly available and typically sourced from older, mature trees in specific regions such as Europe and parts of Asia, making it more expensive and harder to obtain for rafter construction. Hemlock, on the other hand, is widely distributed across North America and is harvested sustainably in large quantities, ensuring easier sourcing and lower costs. The abundant availability and consistent supply chain of Hemlock make it a practical choice for rafters compared to the limited and niche sourcing of Yew.
Cost Comparison: Yew vs Hemlock
Yew wood typically costs significantly more than hemlock due to its rarity and dense grain structure, making it a premium choice for rafters. Hemlock offers a budget-friendly alternative with adequate strength and workability, commonly used in construction projects that prioritize cost-efficiency. The price gap between yew and hemlock can influence project budgets, where yew's higher expense is justified by its durability and aesthetic appeal.
Common Applications in Construction
Yew is favored in rafter construction for its exceptional durability and resistance to decay, making it ideal for exposed structural elements in traditional timber framing and high-end woodworking projects. Hemlock, commonly used in residential and commercial building frameworks, offers a cost-effective alternative with good strength-to-weight ratio and ease of handling, although it is less resistant to moisture and insect damage compared to yew. Both woods are valued for their workability, but yew's dense grain makes it preferable for longevity in outdoor or load-bearing applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Yew wood offers moderate sustainability due to its slower growth rate and limited availability, making it less eco-friendly for rafters compared to faster-growing species. Hemlock, often sourced from sustainably managed forests and widely replanted, presents a more environmentally responsible option with lower carbon footprints and higher renewability. Both woods require careful sourcing to minimize ecological impact, but hemlock's greater abundance and regeneration potential make it preferable in sustainable construction contexts.
Final Recommendation: Choosing Between Yew and Hemlock for Rafters
Yew offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for rafters in environments exposed to moisture. Hemlock is more affordable and readily available, providing good strength and ease of workability but requires proper treatment to enhance longevity. For long-term structural integrity and minimal maintenance, yew is the preferred choice, while hemlock suits budget-conscious projects with appropriate protective finishes.
Infographic: Yew vs Hemlock for Rafter
 azmater.com
azmater.com