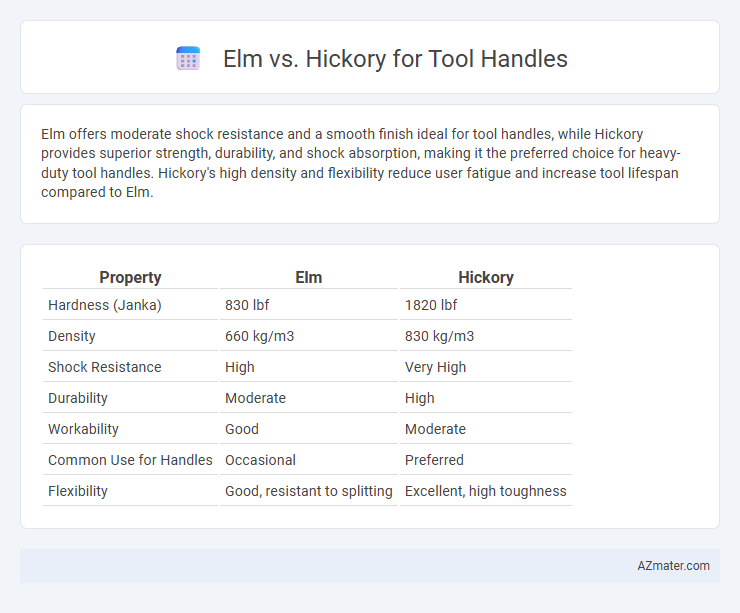
Elm offers moderate shock resistance and a smooth finish ideal for tool handles, while Hickory provides superior strength, durability, and shock absorption, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty tool handles. Hickory's high density and flexibility reduce user fatigue and increase tool lifespan compared to Elm.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elm | Hickory |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 830 lbf | 1820 lbf |
| Density | 660 kg/m3 | 830 kg/m3 |
| Shock Resistance | High | Very High |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Workability | Good | Moderate |
| Common Use for Handles | Occasional | Preferred |
| Flexibility | Good, resistant to splitting | Excellent, high toughness |
Overview: Elm vs Hickory for Tool Handles
Elm and Hickory are both popular choices for tool handles due to their strength and durability. Elm features an interlocking grain that offers excellent resistance to splitting and shock absorption, making it ideal for heavy-duty tools subjected to impact. Hickory is renowned for its exceptional toughness, flexibility, and wear resistance, providing superior shock resistance and a comfortable grip for prolonged use.
Wood Characteristics: Strength & Durability
Elm offers excellent strength and shock resistance due to its interlocking grain, making it highly durable for tool handles subjected to heavy impact. Hickory is renowned for its superior hardness, tensile strength, and flexibility, providing exceptional durability and resilience in demanding applications. While elm resists splitting and absorbs vibrations well, hickory withstands repeated stress better, making it the preferred choice for high-performance tool handles.
Shock Absorption Capabilities
Elm offers superior shock absorption capabilities for tool handles due to its interlocking grain structure, which effectively dampens vibrations and reduces hand fatigue during prolonged use. Hickory, known for its exceptional strength and toughness, also provides good shock absorption but tends to transmit more impact forces compared to elm. When optimizing for comfort and shock reduction, elm handles are often preferred in applications requiring frequent or intensive tool handling.
Flexibility and Toughness Compared
Elm offers exceptional toughness due to its interlocking grain, making it highly resistant to splitting under stress, which is ideal for tool handles enduring heavy impact. Hickory is renowned for its superior flexibility and shock absorption, allowing it to withstand bending and repeated force without cracking. Comparing both, Hickory provides greater flexibility, while Elm excels in toughness, making Hickory preferable for tools requiring resilience to flexural stress and Elm better suited for durability against impact.
Resistance to Splitting and Wear
Elm offers superior resistance to splitting due to its interlocking grain, making it highly durable under stress and impact conditions. Hickory excels in wear resistance because of its dense, hard fibers, which withstand abrasion and prolonged use effectively. Both woods provide excellent strength, but elm's fiber structure reduces the likelihood of handle fractures while hickory's toughness extends tool longevity.
Weight and Balance Considerations
Elm offers a moderate weight with excellent shock absorption, making it a popular choice for tool handles that require balance without excessive heft. Hickory is heavier and denser, providing superior strength and durability, which contributes to a well-balanced handle optimized for powerful, controlled use. Weight and balance considerations favor Elm for lighter tools and Hickory for those demanding more robust impact resistance and longevity.
Ease of Shaping and Working
Elm wood offers excellent toughness and shock resistance, making it relatively easy to shape and work with hand tools due to its interlocking grain, which reduces splitting. Hickory is prized for its exceptional hardness and strength, but its dense, fibrous texture can make it more challenging to shape and requires sharper tools and greater effort. For tool handles demanding durability and smooth shaping, elm provides a balance of workability and resilience, whereas hickory excels in strength but demands more skill during crafting.
Regional Availability and Sustainability
Elm is commonly available in the northeastern United States and parts of Europe, where elm trees grow abundantly, while hickory is predominantly found in the central and eastern regions of North America. Hickory is often regarded as more sustainable due to its faster growth rate and greater resilience to pests and diseases compared to elm, which has seen significant population declines from Dutch elm disease. Regional demand for hickory in tool handles is driven by both its durability and the more reliable supply resulting from sustainable forestry practices in those areas.
Cost Effectiveness and Value
Elm offers excellent durability and shock resistance at a lower cost, making it a highly cost-effective choice for tool handles. Hickory, known for its superior strength and impact resistance, tends to be more expensive but provides exceptional long-term value through durability and comfort. Choosing between elm and hickory hinges on balancing initial affordability with the need for longevity and performance in demanding tool applications.
Best Applications for Each Wood Type
Elm wood, known for its interlocking grain and shock resistance, is ideal for tool handles requiring strength and durability, such as axes and hammers that endure heavy impact. Hickory, prized for its exceptional hardness and flexibility, excels in applications like baseball bats, mauls, and hand tools where both toughness and shock absorption are critical. Selecting elm or hickory depends on whether impact resistance or a combination of toughness and flexibility is prioritized for the specific tool handle application.
Infographic: Elm vs Hickory for Tool handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com