Wenge offers a dense, durable hardwood with a dark, rich grain ideal for high-end panels, while pine provides a softer, lightweight option with a pale color and prominent knots suited for budget-friendly or rustic panels. Wenge panels excel in durability and aesthetic luxury; pine panels prioritize cost-effectiveness and ease of workability.
Table of Comparison
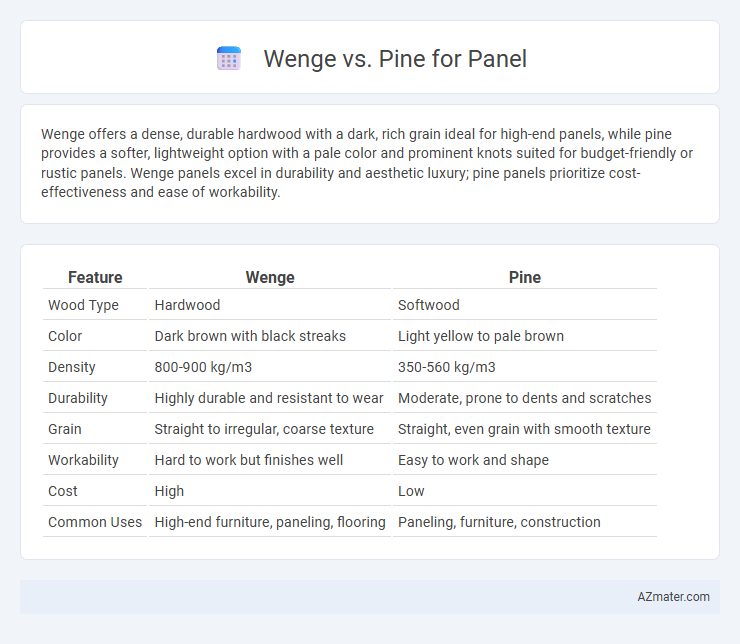
| Feature | Wenge | Pine |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Softwood |
| Color | Dark brown with black streaks | Light yellow to pale brown |
| Density | 800-900 kg/m3 | 350-560 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to wear | Moderate, prone to dents and scratches |
| Grain | Straight to irregular, coarse texture | Straight, even grain with smooth texture |
| Workability | Hard to work but finishes well | Easy to work and shape |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Common Uses | High-end furniture, paneling, flooring | Paneling, furniture, construction |
Introduction to Wenge and Pine Panels
Wenge panels, derived from the dark, dense wood of the Millettia laurentii tree native to Central Africa, are prized for their rich, deep brown color with striking black streaks, offering an elegant, luxurious finish ideal for high-end interiors. Pine panels, sourced from fast-growing pine trees primarily found in North America and Europe, feature a lighter, soft texture with prominent knots and a warm yellowish tone, making them versatile and cost-effective for rustic or casual design aesthetics. Both wood types offer distinct visual and structural characteristics, influencing their selection based on durability requirements and stylistic preferences in paneling applications.
Wenge vs Pine: Wood Characteristics
Wenge wood features a dark brown to black color with a straight grain and coarse texture, offering high durability and natural resistance to wear and insects, making it ideal for premium panels. Pine wood is light in color with a soft texture and pronounced grain patterns, known for its ease of workability but lower hardness and susceptibility to dents and scratches. The dense, heavier Wenge provides superior strength and longevity, while Pine is more affordable and versatile but requires protective finishes for enhanced durability.
Visual Appeal and Color Differences
Wenge wood panels showcase a rich, deep brown color with striking dark streaks, offering a sophisticated and exotic visual appeal ideal for modern and upscale interiors. Pine panels feature a lighter, natural yellowish tone with prominent knots and grain patterns that provide a rustic, warm, and cozy aesthetic. The striking contrast between wenge's dark, smooth finish and pine's light, textured appearance makes each suitable for different design atmospheres, emphasizing bold luxury versus natural simplicity.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Wenge wood, known for its exceptional hardness and density, offers superior durability and strength compared to pine, making it ideal for high-traffic or heavy-use panel applications. Pine, while more affordable and lighter, is softer and more prone to dents, scratches, and wear over time, limiting its longevity in demanding environments. For long-term resilience, wenge provides greater resistance to impact and structural deformation, ensuring panels maintain their integrity under stress.
Workability: Machining and Finishing
Wenge wood offers excellent workability with smooth machining due to its dense, fine grain, allowing for precise cuts and detailed finishes, though its hardness can cause increased tool wear. Pine, being a softwood, is easier to machine, shape, and sand, making it ideal for intricate panel designs and quicker finishing processes. When considering finishing, Wenge absorbs stains evenly, providing a rich, dark appearance, while Pine's open grain often requires sealing or multiple coats for a uniform finish.
Cost and Availability of Wenge and Pine
Wenge is a premium hardwood known for its rich dark color and durability, but its cost is significantly higher due to limited supply and slower growth rates. Pine is widely available and costs considerably less, making it a budget-friendly option for paneling, especially in large projects. The availability of Pine is robust in most regions, while Wenge is often sourced from Africa and may have longer lead times and higher shipping expenses.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wenge wood, derived from the Millettia laurentii tree native to Central Africa, is prized for its durability and rich dark color but faces sustainability challenges due to overharvesting and slow growth rates, leading to increased deforestation concerns. Pine, commonly sourced from fast-growing species like Scots Pine or Eastern White Pine, typically offers a more sustainable option with faster replenishment cycles and certified forestry practices such as FSC, which help minimize environmental impact. Choosing pine panels can significantly reduce ecological footprint compared to wenge, as pine forests regenerate quicker, sequester carbon efficiently, and support biodiversity maintenance.
Common Applications in Paneling
Wenge and Pine are popular choices for paneling, with Wenge commonly used in high-end interior applications such as luxury wall panels, cabinetry, and decorative features due to its dark color and dense grain. Pine is favored in residential paneling, offering affordability and ease of installation for walls, ceilings, and furniture backs. Both woods are chosen based on desired aesthetics and performance, with Wenge providing durability and a rich appearance while Pine suits budget-friendly and rustic designs.
Maintenance and Longevity
Wenge panels offer exceptional durability and resistance to wear, requiring minimal maintenance compared to pine, which is softer and more prone to dents and scratches. Pine panels often need regular sealing or varnishing to protect against moisture and wear, while wenge's dense grain naturally repels moisture and resists decay. For long-term use, wenge provides superior longevity and maintains its aesthetic integrity with less frequent upkeep.
Which is Better for Panels: Wenge or Pine?
Wenge, a dense hardwood known for its rich dark brown color with black streaks, offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-quality panels that require strength and longevity. Pine, a softwood, is lighter and more affordable, with a pale yellow tone and prominent grain patterns, but it is more prone to dents and scratches, which may reduce its suitability for heavy-duty paneling. For panels needing robust structural integrity and a luxurious finish, wenge is better, while pine suits budget-conscious projects and applications where softness and ease of workability are prioritized.
Infographic: Wenge vs Pine for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com