Walnut doors offer rich, dark hues with natural grain patterns, providing a luxurious and durable finish ideal for premium interiors. Alder doors feature a lighter, softer tone with a smoother grain, making them cost-effective and versatile for both traditional and modern door designs.
Table of Comparison
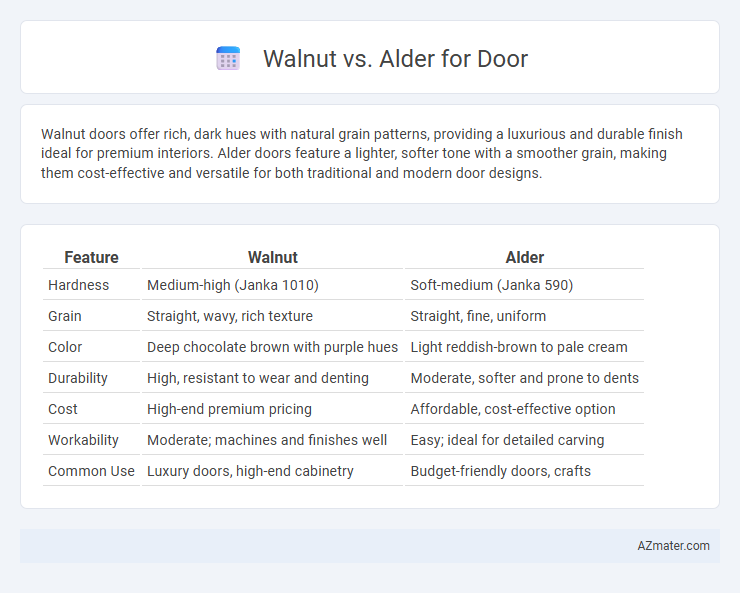
| Feature | Walnut | Alder |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Medium-high (Janka 1010) | Soft-medium (Janka 590) |
| Grain | Straight, wavy, rich texture | Straight, fine, uniform |
| Color | Deep chocolate brown with purple hues | Light reddish-brown to pale cream |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear and denting | Moderate, softer and prone to dents |
| Cost | High-end premium pricing | Affordable, cost-effective option |
| Workability | Moderate; machines and finishes well | Easy; ideal for detailed carving |
| Common Use | Luxury doors, high-end cabinetry | Budget-friendly doors, crafts |
Introduction to Walnut and Alder Doors
Walnut doors feature rich, dark brown hues with intricate grain patterns that enhance the elegance of any interior space. Alder doors offer a lighter, warm tone with smooth texture and subtle knots, providing a rustic and inviting aesthetic. Both hardwood options deliver durability and a distinct visual appeal, making them popular choices for custom and high-end door designs.
Key Differences Between Walnut and Alder Wood
Walnut wood features a rich, dark brown hue with distinct grain patterns, offering superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-end door applications. Alder wood is lighter in color, ranging from pale yellow to reddish-brown, with a softer texture and less density, which allows for easier carving but lower impact resistance. The choice between walnut and alder for doors hinges on desired aesthetics, hardness level, and budget, with walnut commanding a premium price due to its luxury appearance and strength.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Walnut doors offer superior durability and strength due to their dense hardwood structure, providing excellent resistance to wear and impact over time. Alder doors, while moderately strong, are softer and more prone to dents and scratches, making them less ideal for high-traffic areas. Choosing walnut ensures enhanced longevity and structural integrity for doors exposed to frequent use and environmental stress.
Aesthetic Appeal: Grain and Color Variations
Walnut doors showcase rich, deep brown tones with intricate, swirling grain patterns that add warmth and sophistication to any interior. Alder offers a lighter, reddish-brown hue with a more uniform and subtle grain, creating a rustic yet refined look. The choice between the two depends on the desired ambiance, with walnut providing a dramatic elegance and alder delivering a natural, inviting charm.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Walnut doors typically cost between $50 to $150 per square foot, making them a premium option due to their rich color and durability. Alder doors, priced around $30 to $70 per square foot, offer a more budget-friendly alternative while still providing good strength and a light, warm appearance. Choosing alder over walnut can reduce upfront expenses by up to 50%, making it ideal for cost-conscious homeowners seeking aesthetic appeal without compromising quality.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Walnut offers superior workability due to its fine, straight grain and consistent texture, making it easier to shape and finish smoothly for door applications. Alder is softer and less dense, which simplifies cutting and machining but can be more prone to dents and scratches during installation. Choosing between Walnut and Alder depends on whether ease of precise shaping or straightforward handling during installation is prioritized.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Wood
Walnut doors require moderate maintenance, needing periodic cleaning and occasional refinishing to preserve their rich, dark color and natural grain patterns. Alder doors demand more frequent upkeep due to their softer nature, including regular sealing or varnishing to protect against dents, scratches, and moisture damage. Both woods benefit from stable humidity levels and gentle cleaning to prolong their lifespan and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Walnut offers moderate sustainability due to its slower growth rate and limited availability, resulting in higher environmental impact from deforestation and transportation. Alder, a fast-growing hardwood, is more eco-friendly, often sourced from sustainably managed forests, reducing carbon footprint and promoting regeneration. Choosing alder for doors supports sustainable forestry practices and minimizes ecological harm compared to walnut.
Best Applications for Walnut vs Alder Doors
Walnut doors excel in high-end residential and commercial settings where rich, dark tones and intricate grain patterns are desired, offering durability and a luxurious appearance ideal for entry doors and interior panels. Alder doors are best suited for rustic or casual styles, providing a softer, lighter wood with a uniform grain that takes stains and paints well, perfect for kitchen cabinets, interior doors, and furniture where cost-effectiveness and versatility are priorities. Choosing walnut enhances spaces requiring elegance and strength, while alder is preferred for affordability and adaptability in various architectural designs.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Door
Choosing between walnut and alder for your door depends on desired aesthetics and durability; walnut offers a rich, dark brown hue with a smooth grain texture ideal for upscale, modern designs, while alder provides a lighter, warm tone with subtle grain patterns suited for rustic or traditional styles. Walnut's density and resistance to wear make it a long-lasting option for high-traffic areas, whereas alder, being softer, requires more maintenance but is easier to work with for custom designs. Consider environmental conditions and maintenance preferences to ensure your door material aligns with both functional needs and stylistic goals.
Infographic: Walnut vs Alder for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com