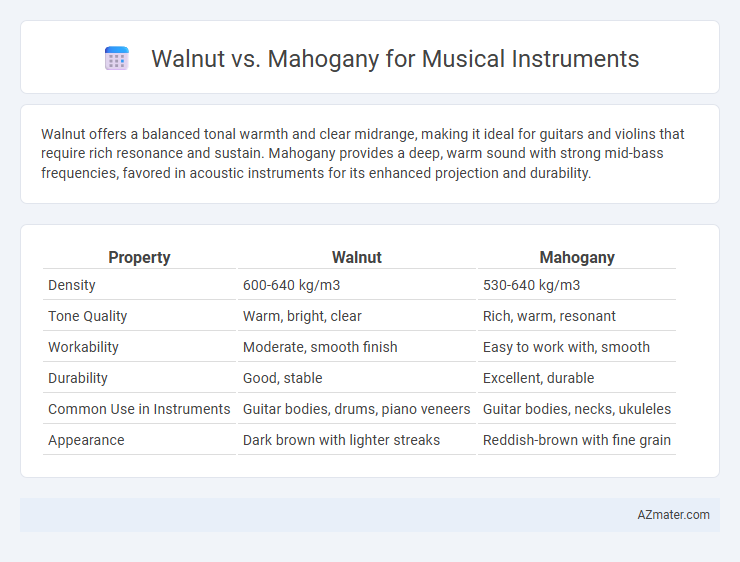
Walnut offers a balanced tonal warmth and clear midrange, making it ideal for guitars and violins that require rich resonance and sustain. Mahogany provides a deep, warm sound with strong mid-bass frequencies, favored in acoustic instruments for its enhanced projection and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Walnut | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 600-640 kg/m3 | 530-640 kg/m3 |
| Tone Quality | Warm, bright, clear | Rich, warm, resonant |
| Workability | Moderate, smooth finish | Easy to work with, smooth |
| Durability | Good, stable | Excellent, durable |
| Common Use in Instruments | Guitar bodies, drums, piano veneers | Guitar bodies, necks, ukuleles |
| Appearance | Dark brown with lighter streaks | Reddish-brown with fine grain |
Introduction: Why Wood Choice Matters in Musical Instruments
Wood choice in musical instruments directly influences sound quality, resonance, and durability, making it critical for musicians and luthiers. Walnut offers warm, balanced tones with moderate sustain, while mahogany provides rich, deep sound with pronounced midrange frequencies. Understanding each wood's acoustic properties helps optimize instrument performance and tonal character.
Overview of Walnut and Mahogany as Tonewoods
Walnut offers a balanced tonal profile with warm mids and clear highs, making it a versatile choice for musical instruments like guitars and violins. Mahogany is prized for its rich, resonant sound with strong midrange emphasis and excellent sustain, often used in acoustic guitars and basses to enhance depth and warmth. Both tonewoods provide distinct acoustic qualities, with walnut delivering brightness and clarity, while mahogany imparts warmth and a full-bodied tone.
Physical Properties: Hardness, Grain, and Weight
Walnut and mahogany differ notably in physical properties critical to musical instruments. Walnut exhibits a Janka hardness of approximately 1,010 lbf, offering moderate durability compared to mahogany's hardness, ranging from 800 to 900 lbf, which provides a softer, more resonant tonewood quality. Walnut features a fine, straight grain with occasional waves, contributing to clear, bright sound projection, while mahogany's interlocked grain yields warmer, mellower tones with greater weight, as walnut typically weighs around 38-41 lbs/ft3 and mahogany ranges from 35-40 lbs/ft3, affecting instrument resonance and playability.
Tonal Characteristics: Sound Differences Explained
Walnut produces a warm, balanced tone with clear midrange and smooth highs, making it ideal for acoustic guitars and percussion instruments that require a rich yet versatile sound. Mahogany delivers a pronounced midrange warmth and strong, resonant lows, often favored for its punchy, woody character that enhances the sustain and depth in guitars and string instruments. The choice between walnut and mahogany impacts tonal brightness and resonance, with walnut offering a slightly brighter, more articulate sound, while mahogany provides a fuller, warmer tone with greater emphasis on bass frequencies.
Popular Instruments Using Walnut and Mahogany
Walnut and mahogany are prized woods in musical instrument craftsmanship, with walnut commonly used for acoustic guitar bodies and snare drums due to its rich tonal warmth and attractive grain. Mahogany is favored for electric guitar necks, classical guitar backs, and violins for its strong midrange tones and durability. Both woods are essential in high-quality instruments, with walnut offering brighter sound characteristics and mahogany providing a deeper, resonant tone.
Durability and Longevity in Instrument Construction
Walnut offers moderate durability with a density of around 640 kg/m3, providing a balance between strength and resonance ideal for musical instruments. Mahogany, significantly denser at approximately 850 kg/m3, excels in longevity due to its natural resistance to wear and environmental factors, making it a preferred choice for instruments requiring long-term stability. The durability of mahogany contributes to sustained tonal quality over time, while walnut's lighter weight supports enhanced playability in instruments like guitars and violins.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color and Visual Texture
Walnut offers a rich, deep brown color with subtle grain patterns that create a warm, elegant visual texture, ideal for vintage-style instruments. Mahogany features a reddish-brown hue with a more consistent, fine grain that enhances the instrument's sleek and classic aesthetic appeal. Both woods provide distinct color profiles and textures, influencing the overall character and attractiveness of musical instruments.
Workability and Craftsmanship Challenges
Walnut offers excellent workability with its fine, straight grain and moderate hardness, allowing for precise carving and detailed craftsmanship in musical instruments. Mahogany, while denser and harder to shape, provides superior stability and rich tonal warmth, making it favored for bodies and necks despite increased effort in sanding and finishing. Both woods demand skilled craftsmanship to maximize acoustic properties and ensure durability, but walnut's ease of manipulation can reduce production time compared to mahogany's craftsmanship challenges.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Walnut is often favored for sustainable musical instrument production due to its faster growth rate and availability from managed forests, reducing ecological impact compared to Mahogany, which faces deforestation concerns and stricter regulations due to its slower maturation and endangered status. Mahogany offers rich tonal quality but comes with higher environmental costs linked to illegal logging and habitat destruction, prompting many luthiers to seek certified sustainable sources or alternatives. Choosing walnut aligns with eco-conscious practices by supporting renewable forestry and minimizing carbon footprints in instrument craftsmanship.
Choosing the Right Wood: Walnut vs Mahogany for Your Needs
Walnut offers bright tonal qualities and a balanced midrange, making it ideal for acoustic guitars and violins that require clarity and projection. Mahogany provides warm, rich tones with strong low-end support, favored in electric guitar bodies and drums for its resonance and sustain. Choosing between walnut and mahogany depends on the desired sound profile, instrument type, and durability needs.
Infographic: Walnut vs Mahogany for Musical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com