Ramin offers a dense, fine-grained texture ideal for detailed carving in model crafts, while Balsa is lighter and softer, providing exceptional ease of shaping and faster assembly. Model builders prefer Ramin for structural strength and Balsa for lightweight framework and rapid prototyping.
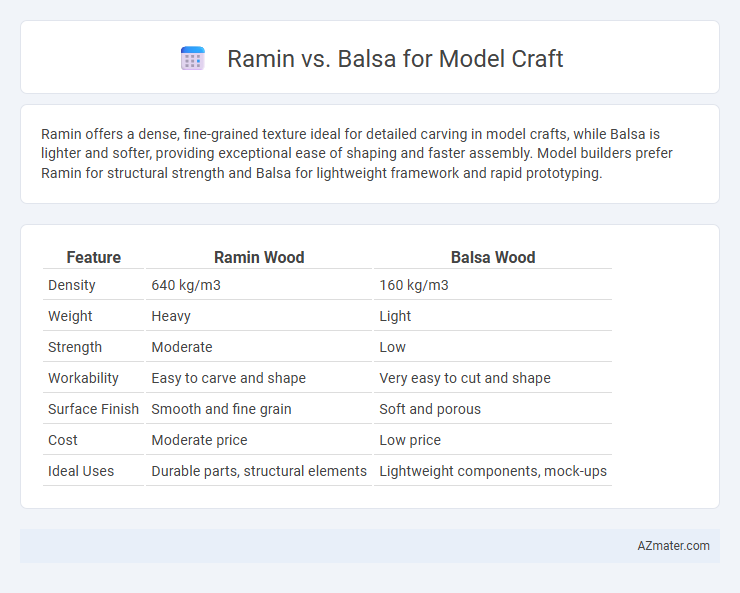
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ramin Wood | Balsa Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 640 kg/m3 | 160 kg/m3 |
| Weight | Heavy | Light |
| Strength | Moderate | Low |
| Workability | Easy to carve and shape | Very easy to cut and shape |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and fine grain | Soft and porous |
| Cost | Moderate price | Low price |
| Ideal Uses | Durable parts, structural elements | Lightweight components, mock-ups |
Introduction to Ramin and Balsa Wood
Ramin wood, sourced from Southeast Asia, is valued for its fine grain, light color, and strength, making it an excellent choice for detailed model craft requiring durability and smooth finishing. Balsa wood, originating from Central and South America, is renowned for its exceptional lightness and ease of cutting, ideal for model builders prioritizing weight reduction and quick shaping. Both woods cater to different modeling needs, with Ramin offering structural integrity and Balsa providing lightweight versatility.
Key Properties of Ramin Wood
Ramin wood, derived from the Shorea genus, is prized in model craft for its light weight, fine grain, and smooth texture, enabling intricate detailing and ease of carving. Compared to balsa, ramin offers greater density and strength, providing enhanced durability without significant weight increase, ideal for structural components. Its pale, uniform color simplifies finishing processes, making ramin a versatile choice for precision model building where stability and aesthetics are critical.
Key Properties of Balsa Wood
Balsa wood is renowned for its exceptional lightness and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it the preferred choice for model craft where weight reduction is crucial. Its cellular, porous structure allows for easy shaping and cutting, providing superior workability compared to ramin wood. Balsa's low density and good stiffness ensure effortless assembly and durability in intricate model constructions.
Weight Comparison: Ramin vs Balsa
Ramin wood typically weighs around 550 to 700 kg/m3, making it denser and heavier than balsa, which ranges between 100 to 300 kg/m3. This significant weight difference impacts model craft durability and buoyancy, with balsa preferred for lightweight requirements and Ramin favored for sturdier construction. Selecting between Ramin and balsa depends on balancing weight constraints with structural strength in model building.
Strength and Durability Differences
Ramin wood offers moderate strength with a fine, uniform texture, making it suitable for lightweight model craft components that require smooth finishes. Balsa wood stands out for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior durability, providing resilience against impact while maintaining lightness, ideal for more structural model parts. The key difference lies in Balsa's enhanced durability combined with lighter weight, whereas Ramin offers a balance of strength and smoothness but with less impact resistance.
Workability for Model Crafting
Ramin wood offers superior workability for model crafting due to its fine, even texture and smooth grain, allowing for precise cuts and detailed carvings without splintering. Balsa, known for its exceptional lightness, is easier to sand and shape but can be prone to dents and less durable under intricate handling. Both woods serve model crafters well, but Ramin provides a more stable and resilient material for detailed and long-lasting projects.
Cost and Availability
Ramin wood offers a cost-effective option for model craft due to its widespread availability and moderate price range, making it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike. Balsa wood, renowned for its lightweight and ease of shaping, often comes at a higher price point and can be less readily available depending on the region. Both materials serve distinct purposes in model crafting, but for budget-conscious projects, Ramin provides better value without compromising quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ramin wood, sourced mainly from Southeast Asia, faces significant sustainability challenges due to overharvesting and habitat loss, leading to increased regulation and scarcity concerns. Balsa wood, native to South America, offers a more environmentally friendly option because of its rapid growth rate and renewable plantation sources, reducing deforestation pressure. Model craft enthusiasts prioritize balsa for its lightweight properties combined with a lower ecological footprint compared to ramin.
Best Uses for Each Wood in Model Craft
Ramin wood, known for its fine grain and smooth texture, excels in detailed model crafting where precision and a clean finish are essential, making it ideal for intricate architectural models and delicate carvings. Balsa wood stands out for its lightweight and softness, which allows easy cutting and shaping, making it the preferred choice for aerodynamic model airplanes and prototypes requiring minimal weight. Selecting Ramin provides durability and a polished appearance, while Balsa offers flexibility and ease of manipulation for varied model craft applications.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Wood
Ramin wood offers excellent durability and smooth finish, making it ideal for detailed model craft projects requiring fine sanding and paint adherence. Balsa wood, known for its lightweight and ease of cutting, is preferred for larger models needing quick assembly and structural flexibility. The final verdict depends on project priorities: select Ramin for strength and fine detail, or Balsa for lightweight and rapid construction.
Infographic: Ramin vs Balsa for Model Craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com