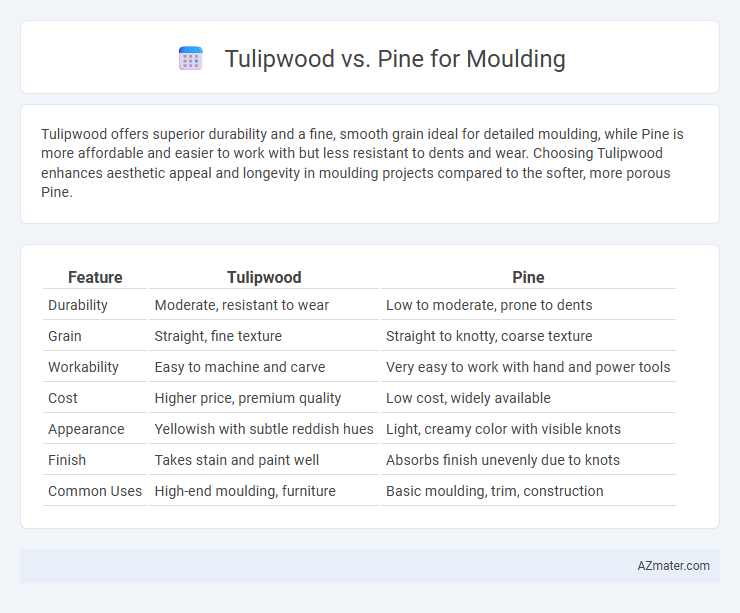
Tulipwood offers superior durability and a fine, smooth grain ideal for detailed moulding, while Pine is more affordable and easier to work with but less resistant to dents and wear. Choosing Tulipwood enhances aesthetic appeal and longevity in moulding projects compared to the softer, more porous Pine.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tulipwood | Pine |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to wear | Low to moderate, prone to dents |
| Grain | Straight, fine texture | Straight to knotty, coarse texture |
| Workability | Easy to machine and carve | Very easy to work with hand and power tools |
| Cost | Higher price, premium quality | Low cost, widely available |
| Appearance | Yellowish with subtle reddish hues | Light, creamy color with visible knots |
| Finish | Takes stain and paint well | Absorbs finish unevenly due to knots |
| Common Uses | High-end moulding, furniture | Basic moulding, trim, construction |
Introduction to Tulipwood and Pine for Moulding
Tulipwood, known for its fine grain and smooth texture, offers a durable and visually appealing option for moulding, often preferred in high-end interior finishes. Pine is a softwood characterized by its affordability, ease of workability, and lighter color, making it a popular choice for budget-friendly moulding projects. Both woods provide distinct aesthetic and functional qualities, with tulipwood excelling in hardness and paint adhesion, while pine is valued for its versatility and availability.
Wood Characteristics and Appearance
Tulipwood offers a smooth, fine grain with a light yellow to salmon pink hue, providing a more elegant and uniform appearance for moulding compared to the soft, pale yellow to white tones and prominent knots of pine. Pine's porous texture and tendency to dent easily make it less durable, while tulipwood's medium hardness and dense structure ensure greater resistance to wear and a more refined finish. The natural luster and consistent coloration of tulipwood enhance moulding aesthetics, making it a preferred choice for high-quality, visually appealing trim work.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tulipwood offers superior strength and durability compared to pine, making it ideal for moulding applications requiring long-lasting structural integrity. Pine is softer and more prone to dents and scratches, making it less resilient under heavy wear and tear. The high density and tight grain of tulipwood contribute to its enhanced resistance to warping and moisture damage, outperforming pine in demanding environments.
Workability and Machining Properties
Tulipwood offers superior workability with its fine, even grain and moderate hardness, allowing for smooth sanding and detailed carving in moulding applications. Pine, being softer and less dense, machines easily but tends to bruise or dent more readily, making it less ideal for intricate moulding work. Both woods hold nails and screws well, but tulipwood's stability and resistance to splitting enhance precision in moulding profiles and finishing.
Cost Differences: Tulipwood vs Pine
Tulipwood moulding typically costs more than pine due to its denser grain and durability, making it a premium choice. Pine is more affordable and widely available, ideal for budget-friendly projects without sacrificing versatility. The price gap between tulipwood and pine can vary based on regional availability and the quality of the lumber.
Finishing and Paintability
Tulipwood offers a smooth grain and dense texture, making it ideal for achieving a fine, even finish with minimal sanding for moulding projects. Pine, being a softer wood with prominent knots and grain patterns, often requires more surface preparation and a quality primer to prevent paint blotching or uneven absorption. The natural tight grain of tulipwood absorbs paint uniformly, providing a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish compared to the more porous and knotty nature of pine.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tulipwood offers a more sustainable option for moulding due to its fast growth rate and responsible harvesting practices, reducing deforestation pressures associated with slow-growing hardwoods. Pine, while also renewable and widely available, often comes from plantations that may require chemical treatments to prevent pests and decay, impacting environmental health. Both woods have lower carbon footprints compared to exotic hardwoods, but tulipwood's durability and minimal treatment needs make it a greener choice for eco-conscious moulding projects.
Ideal Applications for Each Wood Type
Tulipwood offers a smooth texture and rich grain ideal for decorative moulding in formal interiors, providing durability and a fine finish suitable for high-end millwork and detailed trim. Pine, being softer and more affordable, excels in rustic or casual moulding applications where ease of cutting and painting are prioritized, making it perfect for baseboards and crown moulding in budget-conscious or DIY projects. Selecting tulipwood or pine depends on the desired aesthetic, durability, and budget constraints specific to residential or commercial moulding installations.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tulipwood moulding offers higher durability and resistance to wear compared to pine, making it a longer-lasting option with less frequent maintenance requirements. Pine moulding, being softer and more prone to dents and scratches, demands regular upkeep such as sanding and refinishing to maintain its appearance. The natural hardness and density of tulipwood contribute to its superior longevity, reducing maintenance costs over time.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Moulding Project
Tulipwood offers a smooth surface and consistent grain, making it ideal for intricate moulding details and a high-quality finish. Pine is a cost-effective option with a softer texture, suitable for simpler designs and easy painting or staining. Assess project requirements such as budget, durability, and desired appearance to choose between tulipwood's fine grain or pine's affordability for moulding applications.
Infographic: Tulipwood vs Pine for Moulding
 azmater.com
azmater.com