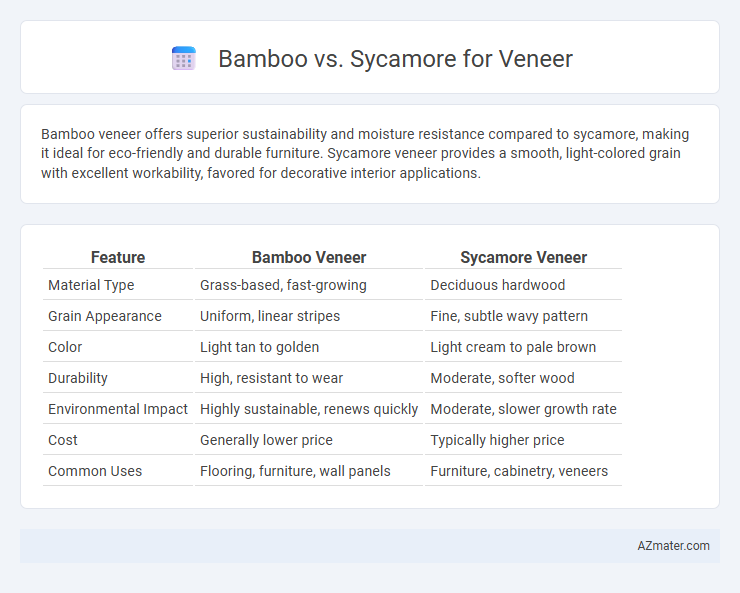
Bamboo veneer offers superior sustainability and moisture resistance compared to sycamore, making it ideal for eco-friendly and durable furniture. Sycamore veneer provides a smooth, light-colored grain with excellent workability, favored for decorative interior applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Veneer | Sycamore Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Grass-based, fast-growing | Deciduous hardwood |
| Grain Appearance | Uniform, linear stripes | Fine, subtle wavy pattern |
| Color | Light tan to golden | Light cream to pale brown |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear | Moderate, softer wood |
| Environmental Impact | Highly sustainable, renews quickly | Moderate, slower growth rate |
| Cost | Generally lower price | Typically higher price |
| Common Uses | Flooring, furniture, wall panels | Furniture, cabinetry, veneers |
Introduction to Bamboo and Sycamore Veneer
Bamboo veneer, derived from the fast-growing bamboo plant, offers exceptional strength, sustainability, and a distinctive linear grain pattern ideal for modern interior applications. Sycamore veneer, sourced from the sycamore tree, features a fine, consistent texture with light coloration, providing a classic and versatile appearance for cabinetry and furniture. Both veneers deliver unique aesthetic and performance qualities, making them popular choices in eco-friendly and stylish woodworking projects.
Botanical Origins and Growth Habits
Bamboo, a fast-growing grass native to Asia, thrives in diverse climates and regenerates quickly after harvesting, making it a sustainable veneer source. Sycamore, a deciduous hardwood from the genus Platanus primarily found in North America and Europe, grows slower and develops a dense, tight grain ideal for fine veneers. The contrasting growth habits of bamboo's rapid, segmented culms versus sycamore's slow-maturing, broad trunks significantly influence veneer texture and durability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bamboo veneer offers superior sustainability due to its rapid growth rate and ability to regenerate without replanting, reducing deforestation and soil erosion compared to sycamore. Sycamore veneer, while durable and visually appealing, requires longer growth cycles and intensive resource use, contributing to higher carbon emissions and habitat disruption. Choosing bamboo veneer supports eco-friendly production with lower carbon footprints and sustainable harvesting practices.
Physical Properties and Appearance
Bamboo veneer offers exceptional strength and flexibility with a uniform grain pattern, showcasing a natural light golden hue that enhances modern interiors. Sycamore veneer features a fine, even texture with subtle wavy grain, providing a pale, creamy coloration ideal for classic and contemporary furniture designs. Both materials provide durability, but bamboo's higher hardness rating makes it preferable for high-traffic applications, while sycamore's smooth surface excels in detailed craftsmanship.
Workability and Machining Characteristics
Bamboo veneer offers superior workability due to its consistent grain and density, allowing for smooth cutting and sanding with minimal chipping. Sycamore veneer, while attractive with its fine, even texture, tends to be more prone to splintering during machining and requires sharper tools and slower feed rates. Both materials respond well to gluing and finishing, but bamboo's uniform fiber structure provides greater ease when shaping and pressing.
Durability and Dimensional Stability
Bamboo veneer offers superior durability due to its dense fiber composition and natural resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Sycamore veneer, while aesthetically appealing with its fine grain, has moderate durability and is more prone to dimensional changes when exposed to humidity fluctuations. Bamboo's exceptional dimensional stability ensures minimal warping and swelling, outperforming sycamore in environments with varying moisture levels.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Bamboo veneer offers a cost-effective alternative with rapidly renewable sourcing, often priced lower due to its fast growth and widespread cultivation, making it highly available in markets focused on sustainable materials. Sycamore veneer, while generally more expensive because of slower tree growth and limited regional distribution, provides a fine, uniform grain favored for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Availability of sycamore is typically restricted to temperate zones, causing fluctuations in supply and cost compared to the consistently accessible bamboo veneer.
Common Applications in Veneering
Bamboo veneer is widely used in eco-friendly furniture, wall panels, and cabinetry due to its sustainability and uniform grain pattern, providing a modern and clean aesthetic. Sycamore veneer, valued for its fine texture and light color variations, is commonly applied in high-end cabinetry, musical instruments, and decorative plywood to achieve an elegant and warm finish. Both veneers offer versatility, with bamboo favored for contemporary designs and sycamore preferred in traditional or refined interior applications.
Maintenance and Longevity
Bamboo veneer offers high durability and requires minimal maintenance, benefiting from its natural resistance to moisture and pests, making it ideal for humid environments. Sycamore veneer, while visually appealing with its fine grain, demands more frequent sealing and careful upkeep to prevent warping and discoloration over time. Bamboo's faster growth cycle also contributes to its sustainability, supporting long-term use with consistent performance.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Bamboo vs Sycamore
Bamboo veneer offers exceptional durability, sustainability, and a unique linear grain pattern ideal for modern, eco-friendly designs, while sycamore veneer provides a fine, even texture with a light, creamy color suitable for classic and elegant interiors. Bamboo grows rapidly, making it a renewable resource, whereas sycamore, a hardwood, delivers stability and subtle grain variations that enhance its aesthetic appeal. Selecting the right veneer depends on the desired look, environmental impact, and application, with bamboo favored for contemporary, sustainable projects and sycamore preferred for timeless, refined finishes.
Infographic: Bamboo vs Sycamore for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com