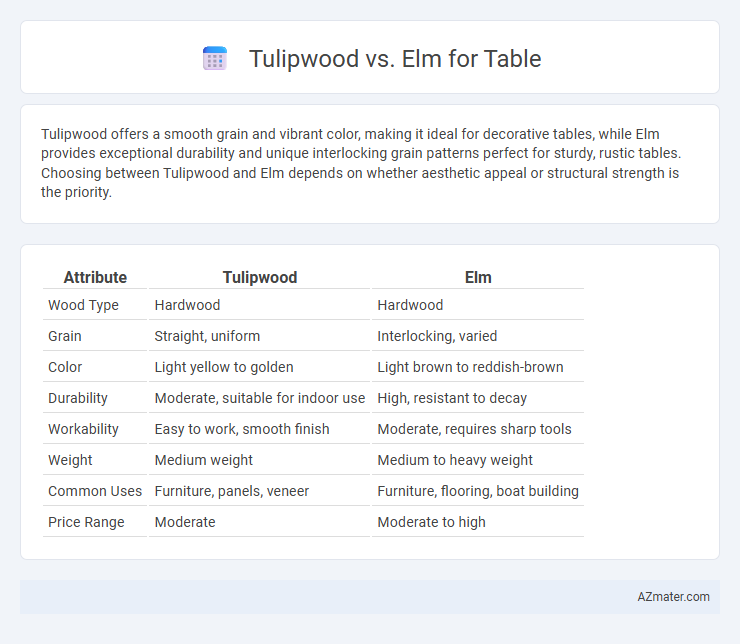
Tulipwood offers a smooth grain and vibrant color, making it ideal for decorative tables, while Elm provides exceptional durability and unique interlocking grain patterns perfect for sturdy, rustic tables. Choosing between Tulipwood and Elm depends on whether aesthetic appeal or structural strength is the priority.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Tulipwood | Elm |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Grain | Straight, uniform | Interlocking, varied |
| Color | Light yellow to golden | Light brown to reddish-brown |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for indoor use | High, resistant to decay |
| Workability | Easy to work, smooth finish | Moderate, requires sharp tools |
| Weight | Medium weight | Medium to heavy weight |
| Common Uses | Furniture, panels, veneer | Furniture, flooring, boat building |
| Price Range | Moderate | Moderate to high |
Introduction: Tulipwood vs Elm for Tables
Tulipwood offers a smooth, fine grain and a pale yellow to light brown color, making it ideal for sleek, modern tables with a consistent appearance. Elm features a characteristic interlocking grain with a coarse texture and warm reddish-brown hues, providing natural durability and resistance to splitting in traditional or rustic table designs. Both woods balance strength and aesthetic appeal, but tulipwood excels in fine finishing while elm is prized for its stability and unique grain patterns.
Overview of Tulipwood
Tulipwood features a smooth, fine grain and light yellow to pale orange color, making it an attractive choice for modern and contemporary table designs. Its moderate hardness and good workability ensure durability while allowing intricate shaping and finishing. Tulipwood resists warping and provides a stable surface, ideal for functional tabletops requiring both strength and aesthetic appeal.
Overview of Elm Wood
Elm wood is prized for its interlocking grain, which provides exceptional strength and resistance to splitting, making it an ideal choice for durable table construction. Its relatively high moisture resistance and attractive warm reddish-brown hues enhance the aesthetic appeal of table surfaces. Elm's coarse texture and natural luster offer a unique rustic charm, often preferred for traditional and farmhouse-style furniture designs.
Appearance and Grain Comparison
Tulipwood features a pale yellow to light brown color with uniform, straight grain that adds a smooth and refined appearance to tables. Elm showcases a wider color range from light brown to reddish-brown with an interlocking, wavy grain pattern that creates a more rustic and textured look. The consistent grain of Tulipwood offers a modern aesthetic, while Elm's distinct grain provides unique character and visual depth.
Durability and Strength
Tulipwood offers moderate durability with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 590, making it suitable for light to medium-use tables but less resistant to heavy wear and dents compared to elm. Elm boasts a higher durability due to its interlocked grain and density, with a Janka hardness around 830, providing superior strength and resistance to splitting, ideal for robust table construction. Both woods feature distinct grain patterns, but elm's resilience under stress makes it a preferred choice for long-lasting, sturdy dining and work tables.
Workability and Ease of Crafting
Tulipwood offers excellent workability due to its fine, even texture and straight grain, making it easy to cut, shape, and sand for detailed table designs. Elm, while slightly tougher, features interlocking grain that provides durability but may require sharper tools and more effort during carving and finishing. Both woods respond well to hand and machine tools, but tulipwood's softer nature grants smoother crafting experiences and faster project completion.
Sustainability and Sourcing
Tulipwood and Elm both offer sustainable options for table construction due to their rapid growth and availability in managed forests. Tulipwood, primarily sourced from North America, benefits from responsible forestry practices and regenerates quickly, minimizing environmental impact. Elm, often reclaimed or harvested from urban environments, promotes sustainability by reducing waste and utilizing an otherwise discarded resource for durable, long-lasting tables.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tulipwood offers moderate maintenance with occasional sealing to prevent moisture damage, while elm requires more frequent care due to its porous grain that can absorb stains and scratches. Elm's interlocked grain contributes to higher durability and resistance to warping, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting tables. Tulipwood, though visually appealing with its warm hues, may show wear faster without consistent upkeep compared to the robust nature of elm.
Cost Comparison
Tulipwood is generally more affordable than elm, making it a budget-friendly choice for table construction without sacrificing durability. Elm tends to be pricier due to its unique grain patterns and natural resistance to splitting, adding value to furniture pieces. Choosing between tulipwood and elm for a table depends on balancing cost efficiency with aesthetic preference and long-term wear.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Tulipwood offers a smooth texture and pale color ideal for fine furniture and interior cabinetry, making it suitable for indoor tables where aesthetics and a smooth finish are prioritized. Elm is known for its interlocking grain and superior resistance to splitting, making it a strong choice for rustic or handcrafted tables that require durability and visual character. For best results, choose tulipwood for delicate, polished tabletops and elm for sturdy, everyday tables exposed to moderate wear.
Infographic: Tulipwood vs Elm for Table
 azmater.com
azmater.com