Tulipwood plywood offers a unique grain pattern and superior durability compared to birch plywood, which is known for its smooth surface and consistent strength. Tulipwood is ideal for decorative applications, while birch is preferred for structural projects due to its stability and ease of finishing.
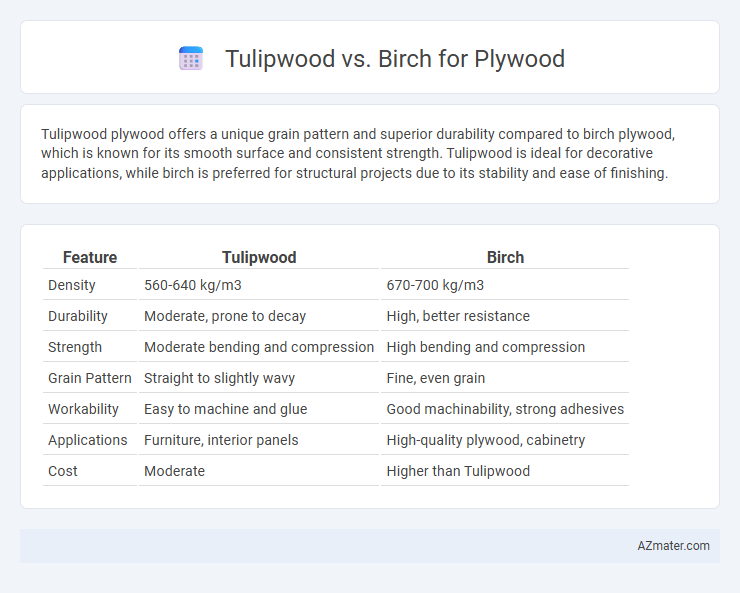
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tulipwood | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 560-640 kg/m3 | 670-700 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to decay | High, better resistance |
| Strength | Moderate bending and compression | High bending and compression |
| Grain Pattern | Straight to slightly wavy | Fine, even grain |
| Workability | Easy to machine and glue | Good machinability, strong adhesives |
| Applications | Furniture, interior panels | High-quality plywood, cabinetry |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than Tulipwood |
Introduction to Tulipwood and Birch Plywood
Tulipwood plywood is valued for its pale yellow to light brown color and smooth grain, offering excellent strength and durability for furniture and cabinetry. Birch plywood is known for its fine grain and uniform texture, providing high stability and resistance to warping, making it a popular choice for interior applications and structural uses. Both materials are prized in woodworking for their workability and finish quality, with tulipwood slightly softer than birch but still highly durable.
Botanical Origins and Species Overview
Tulipwood plywood is derived from the Liriodendron tulipifera tree, commonly found in eastern North America, known for its light color and fine grain ideal for cabinetry and furniture. Birch plywood originates from Betula species, primarily Betula pendula and Betula pubescens in the Northern Hemisphere, prized for its strength, uniform texture, and smooth finish suitable for structural and decorative applications. Both woods offer distinct botanical origins influencing their grain patterns, durability, and suitability for various plywood uses.
Physical Appearance and Color Differences
Tulipwood plywood presents a light cream to pale yellow hue with subtle pinkish or reddish undertones that enhance its warm and inviting aesthetic. Birch plywood offers a more consistent pale white to light beige color with a smooth, fine grain that provides a clean, modern look often preferred for minimalist designs. The natural grain patterns in tulipwood tend to be slightly more pronounced and varied, adding unique character compared to birch's uniform and subtle texture.
Grain Patterns and Texture Comparison
Tulipwood plywood features a fine, straight grain with a smooth texture, often exhibiting subtle waves that create an elegant, consistent appearance. Birch plywood displays a tight, even grain pattern with a slightly more uniform texture, providing a clean and classic look ideal for cabinetry and furniture. Both woods offer durability, but tulipwood's softer grain imparts a warmer aesthetic compared to birch's more neutral tone.
Strength and Durability Factors
Tulipwood plywood offers moderate strength and good durability, making it suitable for furniture and interior applications where a smooth finish is desired. Birch plywood is known for its superior hardness, strength, and resistance to warping, making it ideal for structural and high-stress uses. When comparing both, birch plywood generally outperforms tulipwood in durability and load-bearing capacity, providing a longer lifespan under heavy use.
Workability and Machining Properties
Tulipwood plywood offers excellent workability due to its fine, uniform texture and consistent grain, allowing for smooth cutting, shaping, and sanding. Birch plywood is highly regarded for its superior machining properties, including precise cutting and minimal splintering, making it ideal for complex joinery and detailed woodworking. Both woods provide strong bonding surfaces, but birch plywood's hardness often results in better screw holding and durability in finished products.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Tulipwood plywood typically costs more than birch plywood due to its relative rarity and limited supply, making it less available in general markets. Birch plywood is widely available and more budget-friendly, favored for its consistent quality and ease of sourcing. Market trends show birch as the preferred choice for cost-conscious projects without compromising strength and appearance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tulipwood plywood, sourced from fast-growing Liriodendron trees, offers a more sustainable option due to its rapid renewability and lower carbon footprint compared to birch plywood, which typically involves harvesting slower-growing Betula species. Birch plywood, although durable, often requires more intensive forestry management and longer regeneration periods, increasing its environmental impact. Choosing tulipwood plywood supports sustainable forestry practices and reduces deforestation pressure, aligning with eco-friendly construction goals.
Common Applications and Best Uses
Tulipwood plywood is commonly used in high-end furniture and cabinetry due to its smooth finish and attractive grain, making it ideal for decorative interior applications. Birch plywood, known for its superior strength and durability, is frequently utilized in structural projects, flooring, and industrial-grade furniture where toughness and resistance to wear are essential. For precise woodworking tasks requiring fine detailing, tulipwood offers better workability, while birch is preferred in applications demanding robust load-bearing capacity.
Summary: Choosing Between Tulipwood and Birch Plywood
Tulipwood plywood offers a lightweight, attractive grain with moderate durability, making it ideal for decorative applications and furniture where aesthetics matter. Birch plywood provides superior strength and stability, with a fine, uniform texture suitable for structural uses and high-quality cabinetry. Selecting between tulipwood and birch plywood depends on balancing the need for visual appeal versus robustness and long-term performance.
Infographic: Tulipwood vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com