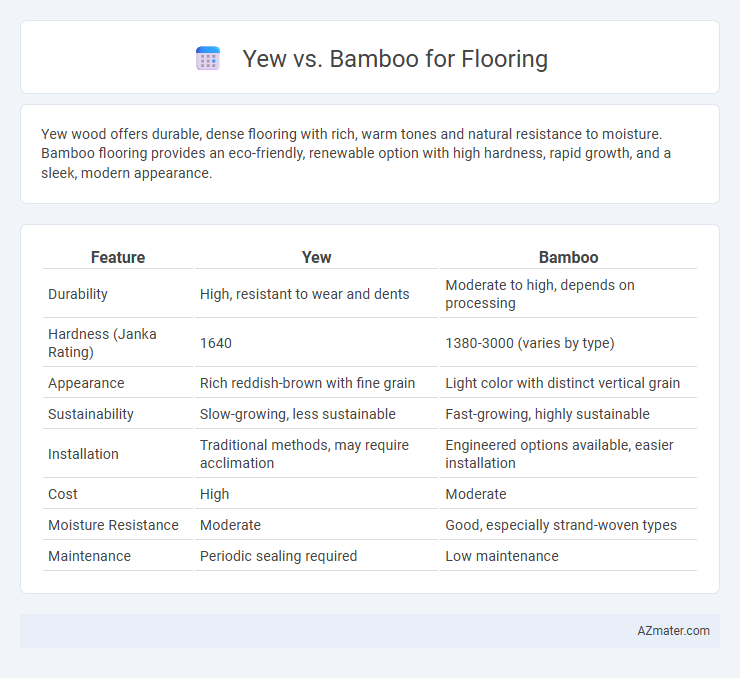
Yew wood offers durable, dense flooring with rich, warm tones and natural resistance to moisture. Bamboo flooring provides an eco-friendly, renewable option with high hardness, rapid growth, and a sleek, modern appearance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Yew | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, resistant to wear and dents | Moderate to high, depends on processing |
| Hardness (Janka Rating) | 1640 | 1380-3000 (varies by type) |
| Appearance | Rich reddish-brown with fine grain | Light color with distinct vertical grain |
| Sustainability | Slow-growing, less sustainable | Fast-growing, highly sustainable |
| Installation | Traditional methods, may require acclimation | Engineered options available, easier installation |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | Good, especially strand-woven types |
| Maintenance | Periodic sealing required | Low maintenance |
Introduction to Yew and Bamboo Flooring
Yew flooring is prized for its rich, warm tones and dense, fine grain, offering durability and a luxurious aesthetic ideal for traditional and high-end interiors. Bamboo flooring, derived from fast-growing grass, provides an eco-friendly alternative with remarkable hardness and resistance to moisture, suitable for modern, sustainable homes. Both materials exhibit unique structural properties that influence their longevity, maintenance needs, and overall performance in various indoor environments.
Material Origins and Sustainability
Yew flooring, derived from the slow-growing Taxus tree native to Europe and Asia, offers high durability and a rich, warm appearance but raises concerns due to its limited availability and longer regeneration period. Bamboo flooring, sourced from the fast-growing grass species predominantly found in Southeast Asia, stands out for its rapid renewability and eco-friendly harvesting process, making it a highly sustainable alternative. The sustainability of bamboo is enhanced by its ability to be harvested every 3-5 years without damaging the root system, while yew requires decades to mature, impacting its environmental footprint.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Yew wood exhibits moderate hardness with a Janka rating around 1180, offering a good balance of strength and flexibility ideal for residential flooring. Bamboo flooring, especially strand-woven varieties, achieves a much higher hardness rating, often exceeding 3000 on the Janka scale, making it exceptionally durable and resistant to dents and scratches. While yew provides a unique aesthetic and reasonable durability, bamboo surpasses yew in hardness and wear resistance, making it preferable for high-traffic areas.
Aesthetic Differences: Color and Grain
Yew flooring showcases a rich, warm reddish-brown hue with fine, straight grain patterns that create a smooth and elegant surface, offering a classic and luxurious ambiance. Bamboo flooring features a range of natural colors from pale tan to caramel, often with visible nodes and a linear grain that imparts a modern and casual look. The contrast between Yew's deep, consistent coloration and Bamboo's lighter, variegated tones allows designers to choose between traditional warmth and contemporary brightness in interior spaces.
Installation Methods and Ease
Yew flooring typically requires professional installation due to its dense grain and tendency to expand and contract, with methods such as glue-down or nail-down to secure the planks effectively. Bamboo flooring offers greater ease of installation, often available in click-lock or floating floor systems that allow for DIY-friendly setups without the need for adhesives or nails. The choice between yew and bamboo flooring installation largely depends on the skill level of the installer and the desired durability, with bamboo being more accessible for quick, straightforward installation projects.
Maintenance and Longevity
Yew flooring offers moderate maintenance with periodic sealing and refinishing required to protect its fine grain and natural oils, providing durability that can last several decades under proper care. Bamboo flooring is highly resilient and low-maintenance, needing only regular sweeping and occasional cleaning to maintain its hardness and resistance to moisture and wear, which can extend its lifespan to over 50 years. Both materials benefit from controlled indoor environments to prevent warping, but bamboo's rapid renewability and toughness generally result in longer-lasting floors with less upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Eco-Friendliness
Yew flooring, derived from slow-growing yew trees, often faces sustainability challenges due to limited tree availability and longer regrowth periods, increasing its environmental footprint compared to bamboo. Bamboo flooring boasts rapid renewability as bamboo can mature in 3-5 years, absorbing significant CO2 and releasing oxygen, making it a highly sustainable and eco-friendly choice. The cultivation of bamboo requires fewer pesticides and less water than yew, further enhancing its status as a green flooring material with a lower environmental impact.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Yew flooring typically commands a higher price per square foot compared to bamboo due to its rarity and labor-intensive harvesting process, often ranging from $8 to $15, while bamboo averages $3 to $7, making it a more budget-friendly option. Bamboo's rapid renewability and efficient manufacturing contribute to cost savings, appealing to both eco-conscious and price-sensitive homeowners. Long-term affordability also favors bamboo, as its durability and lower maintenance costs reduce overall investment despite initial price differences.
Pros and Cons of Yew Flooring
Yew flooring offers exceptional durability and a distinctive reddish-brown hue that deepens with age, making it a visually striking choice for interior spaces. Its natural resistance to decay and moderate hardness provide long-lasting performance, but it may be prone to denting compared to harder woods like bamboo. While yew requires regular maintenance to preserve its finish, its unique grain patterns and warmth contribute to a cozy, elegant aesthetic ideal for traditional and rustic design themes.
Pros and Cons of Bamboo Flooring
Bamboo flooring offers exceptional durability and sustainability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional hardwoods like yew. It resists moisture and insects better than yew, but can be prone to scratches and dents if not properly maintained. Despite its affordability and fast growth, bamboo's sensitivity to humidity changes may lead to expansion or warping over time.
Infographic: Yew vs Bamboo for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com