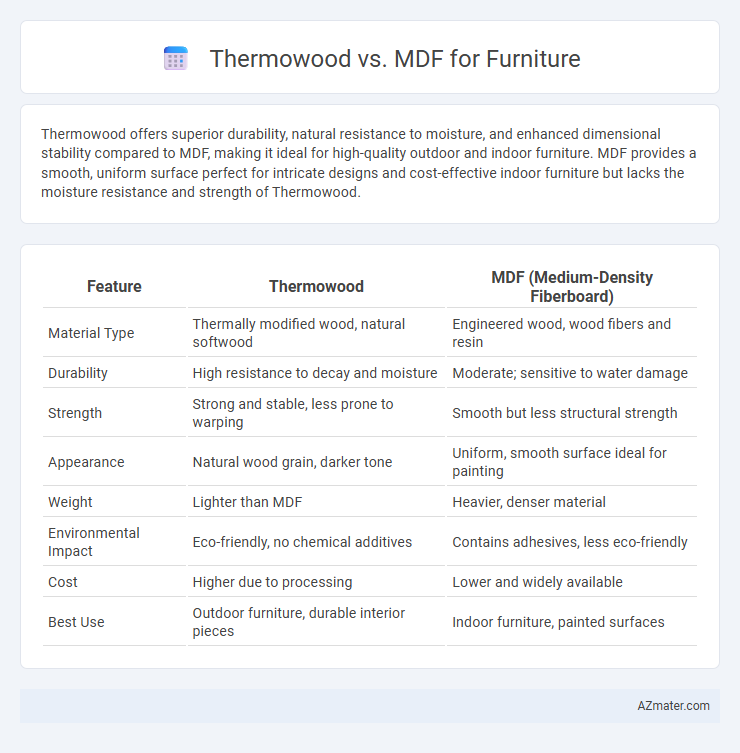
Thermowood offers superior durability, natural resistance to moisture, and enhanced dimensional stability compared to MDF, making it ideal for high-quality outdoor and indoor furniture. MDF provides a smooth, uniform surface perfect for intricate designs and cost-effective indoor furniture but lacks the moisture resistance and strength of Thermowood.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Thermowood | MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermally modified wood, natural softwood | Engineered wood, wood fibers and resin |
| Durability | High resistance to decay and moisture | Moderate; sensitive to water damage |
| Strength | Strong and stable, less prone to warping | Smooth but less structural strength |
| Appearance | Natural wood grain, darker tone | Uniform, smooth surface ideal for painting |
| Weight | Lighter than MDF | Heavier, denser material |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no chemical additives | Contains adhesives, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Lower and widely available |
| Best Use | Outdoor furniture, durable interior pieces | Indoor furniture, painted surfaces |
Introduction to Thermowood and MDF
Thermowood is a type of heat-treated timber known for its enhanced durability, stability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor and high-humidity furniture applications. MDF, or Medium-Density Fiberboard, is an engineered wood product made from wood fibers bonded with resin under heat and pressure, prized for its smooth surface and ease of machining in indoor furniture manufacturing. Choosing between Thermowood and MDF depends on factors like exposure to moisture, desired finish, and structural requirements.
Material Composition and Production Process
Thermowood is produced through a thermal modification process where timber is heated to high temperatures (160-220degC) in a controlled environment, altering its chemical and physical properties to enhance durability and moisture resistance without chemical additives. MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) consists of wood fibers combined with resin and wax, which are compressed under high pressure and heat to form a dense panel. The natural wood composition of Thermowood contrasts with the engineered, composite nature of MDF, influencing factors such as strength, moisture resistance, and environmental impact in furniture applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Thermowood offers superior durability compared to MDF due to its heat-treated wood structure, which enhances resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage, making it ideal for long-lasting furniture. MDF, composed of engineered wood fibers and resins, is more susceptible to swelling and deterioration when exposed to humidity or heavy use, reducing its overall longevity. Thermowood's enhanced dimensional stability and natural wood grain also contribute to a more durable and visually lasting furniture option than MDF.
Aesthetic Appeal and Finishing Options
Thermowood offers a natural, warm aesthetic with rich wood grain patterns that enhance the visual appeal of furniture, while MDF provides a smooth and uniform surface ideal for painted finishes and intricate detailing. The finishing options for Thermowood include staining and sealing, which highlight its texture and durability, whereas MDF excels with veneers, laminates, and diverse paint colors, allowing for versatile design customization. Choosing between Thermowood and MDF depends on the desired aesthetic effect and the level of finish refinement for the furniture piece.
Moisture Resistance and Stability
Thermowood offers superior moisture resistance compared to MDF, as it is heat-treated to reduce its hygroscopic properties, making it ideal for environments with high humidity. Unlike MDF, which tends to swell and degrade when exposed to moisture, Thermowood maintains dimensional stability and resists warping over time. This enhanced stability and durability make Thermowood a preferred material for furniture that requires longevity in variable climate conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Thermowood furniture utilizes sustainably sourced Nordic timber treated with heat to enhance durability without chemicals, resulting in a low environmental footprint and improved recyclability. MDF production involves gluing wood fibers with synthetic resins, often formaldehyde-based, raising concerns about VOC emissions and limited biodegradability. Choosing Thermowood supports eco-friendly furniture manufacturing through renewable resources and non-toxic processing methods.
Workability and Ease of Fabrication
Thermowood offers superior workability due to its stability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor and humid environments, while MDF excels in ease of fabrication with its smooth, uniform surface that allows for precise cutting, shaping, and veneering. MDF is more adaptable for intricate designs and detailed finishes but requires careful handling to avoid moisture damage. Thermowood's natural durability reduces the need for extensive treatments, streamlining the fabrication process for sturdy, long-lasting furniture pieces.
Cost Differences and Budget Considerations
Thermowood furniture typically costs more upfront due to the heat treatment process enhancing durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for long-term investment. MDF furniture, made from compressed wood fibers, offers a budget-friendly option with lower material and manufacturing expenses but may lack the longevity and outdoor suitability of Thermowood. When budgeting, consider Thermowood for premium, weather-resistant pieces and MDF for affordable, indoor use with sufficient care.
Ideal Applications for Furniture Design
Thermowood offers high durability and natural resistance to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and high-humidity environments such as kitchens or bathrooms. MDF provides a smooth, uniform surface perfect for intricate designs and painted finishes, best suited for indoor decorative furniture like cabinets and shelves. Choosing between Thermowood and MDF depends on application needs, balancing moisture resistance and aesthetic versatility in furniture design.
Choosing Between Thermowood and MDF
Choosing between Thermowood and MDF for furniture depends on durability, moisture resistance, and aesthetic preferences. Thermowood, a heat-treated softwood, offers enhanced resistance to decay and dimensional stability, making it ideal for outdoor and humid environments. MDF, made from wood fibers and resin, provides a smooth surface for painting and intricate designs but lacks natural moisture resistance and durability compared to Thermowood.
Infographic: Thermowood vs MDF for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com