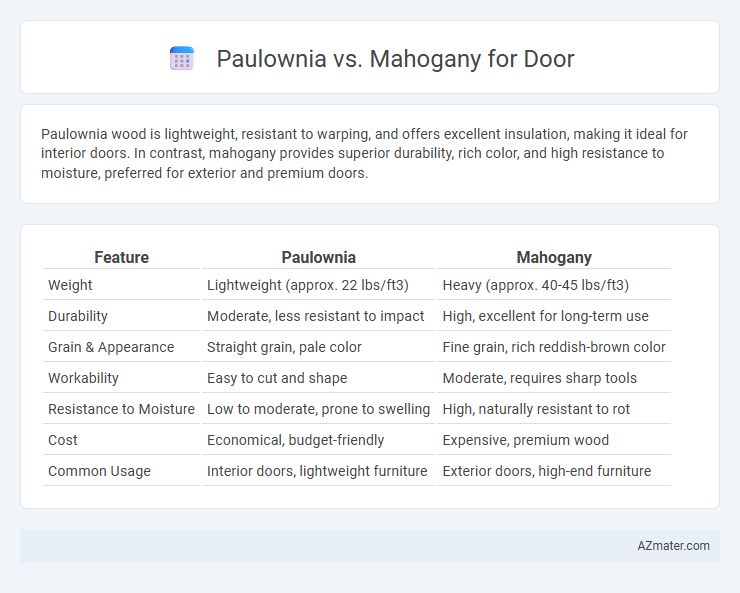
Paulownia wood is lightweight, resistant to warping, and offers excellent insulation, making it ideal for interior doors. In contrast, mahogany provides superior durability, rich color, and high resistance to moisture, preferred for exterior and premium doors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Paulownia | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight (approx. 22 lbs/ft3) | Heavy (approx. 40-45 lbs/ft3) |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to impact | High, excellent for long-term use |
| Grain & Appearance | Straight grain, pale color | Fine grain, rich reddish-brown color |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Moderate, requires sharp tools |
| Resistance to Moisture | Low to moderate, prone to swelling | High, naturally resistant to rot |
| Cost | Economical, budget-friendly | Expensive, premium wood |
| Common Usage | Interior doors, lightweight furniture | Exterior doors, high-end furniture |
Overview of Paulownia and Mahogany Wood
Paulownia wood is lightweight, fast-growing, and moisture-resistant, making it ideal for doors requiring durability and ease of installation. Mahogany is a dense, hardwood renowned for its rich, reddish-brown color, exceptional strength, and natural resistance to decay, often preferred for high-end, traditional doors. Both woods offer distinct benefits for door construction, with Paulownia excelling in weight and weather resistance, and Mahogany valued for its longevity and classic aesthetic.
Physical Properties and Appearance
Paulownia wood is lightweight and has a low density of approximately 0.31 g/cm3, making it easier to handle and resistant to warping, while mahogany is denser, around 0.60 g/cm3, offering greater strength and durability for doors. Paulownia features a pale, creamy color with a fine, straight grain, providing a smooth finish that can be stained or painted, whereas mahogany displays a rich reddish-brown hue with a pronounced, interlocking grain pattern that enhances its luxurious appearance. Both woods have moderate hardness, but mahogany's superior hardness rating (approximately 900 on the Janka scale) ensures better resistance to dents and scratches compared to paulownia's softer profile.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Paulownia wood offers lightweight properties and moderate durability, making it less resistant to impact and moisture compared to mahogany. Mahogany is renowned for its exceptional durability and longevity, with natural resistance to decay, insects, and warping, often lasting decades in door applications. For doors requiring long-term strength and minimal maintenance, mahogany outperforms paulownia in terms of durability and lifespan.
Weight and Workability Factors
Paulownia wood is significantly lighter than mahogany, making it ideal for doors where weight reduction is crucial without compromising strength. Mahogany offers superior workability due to its fine grain and uniform texture, allowing for easier carving and finishing in custom door designs. The lightweight nature of paulownia enhances energy efficiency in door installation, while mahogany's durability ensures longer lifespan and resistance to swelling or warping.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Paulownia doors offer superior insulation properties due to their lightweight and low-density cellular structure, effectively reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in homes. Mahogany, while denser and more durable, has comparatively lower insulating capabilities, making it less effective at maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Choosing Paulownia wood for doors can lead to improved thermal performance and reduced energy costs in residential applications.
Resistance to Pests and Decay
Paulownia wood exhibits excellent resistance to pests and decay due to its natural oils and lightweight structure, making it a durable choice for doors in humid or insect-prone environments. Mahogany, while prized for its rich color and strength, is moderately resistant to pests but may require chemical treatment to enhance decay resistance in outdoor applications. Choosing Paulownia provides a longer-lasting door option with less maintenance in areas vulnerable to termites and fungal attacks.
Environmental Sustainability
Paulownia wood, known for its rapid growth rate of up to 20 feet per year, offers a highly renewable resource compared to the slow-growing mahogany, which takes decades to mature. Harvesting paulownia significantly reduces deforestation pressure and carbon footprint due to its efficient oxygen production and soil-enhancing properties. Mahogany's slower regeneration often leads to overharvesting and habitat loss, making paulownia a more environmentally sustainable choice for door manufacturing.
Cost and Availability
Paulownia doors are often more cost-effective due to the wood's rapid growth and widespread plantation availability, making it a budget-friendly option for interior and exterior doors. Mahogany, prized for its durability and rich aesthetic, commands a higher price and can be less readily available, with supply often limited to sustainable sources or imports. Choosing between Paulownia and Mahogany largely depends on budget constraints and the desired balance between cost efficiency and premium quality.
Best Applications for Each Wood Type
Paulownia wood, known for its lightweight and moisture resistance, is ideal for interior doors requiring easy handling and stability in humid environments such as bathrooms or kitchens. Mahogany, prized for its durability, rich grain, and resistance to decay, excels in exterior doors and high-traffic entryways where strength and aesthetic elegance are essential. Choosing mahogany enhances security and longevity, while paulownia offers affordability and flexibility for decorative interior use.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Door
Choosing the right wood for your door involves balancing durability, aesthetics, and cost. Paulownia wood offers lightweight properties, resistance to warping, and a smooth finish ideal for intricate door designs, while Mahogany provides superior strength, rich deep color, and excellent resistance to pests and decay, making it a premium choice for high-end doors. Consider environmental factors and maintenance needs, as Mahogany requires more upkeep but ensures long-term durability, whereas Paulownia is easier to handle and eco-friendly due to its rapid growth.
Infographic: Paulownia vs Mahogany for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com