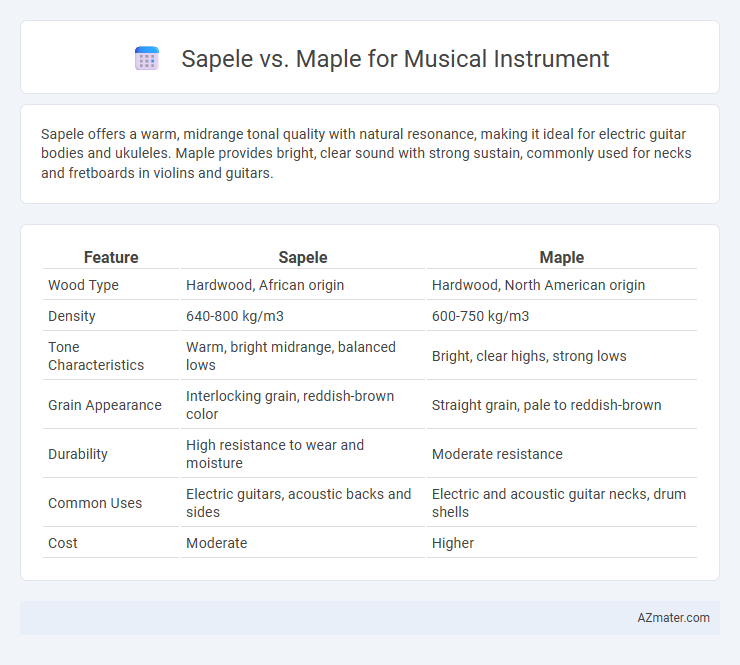
Sapele offers a warm, midrange tonal quality with natural resonance, making it ideal for electric guitar bodies and ukuleles. Maple provides bright, clear sound with strong sustain, commonly used for necks and fretboards in violins and guitars.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sapele | Maple |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood, African origin | Hardwood, North American origin |
| Density | 640-800 kg/m3 | 600-750 kg/m3 |
| Tone Characteristics | Warm, bright midrange, balanced lows | Bright, clear highs, strong lows |
| Grain Appearance | Interlocking grain, reddish-brown color | Straight grain, pale to reddish-brown |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and moisture | Moderate resistance |
| Common Uses | Electric guitars, acoustic backs and sides | Electric and acoustic guitar necks, drum shells |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction: Sapele vs Maple in Instrument Crafting
Sapele and maple are both prized tonewoods used in musical instrument crafting, each offering distinct acoustic properties. Sapele, a member of the mahogany family, provides a warm, rich sound with strong midrange frequencies, making it ideal for guitars and ukuleles focused on depth and resonance. Maple, known for its bright, clear tone and strong sustain, is often chosen for violins, guitars, and basses to enhance clarity and articulation in sound projection.
Wood Origins and Botanical Characteristics
Sapele, native to West Africa and classified as Entandrophragma cylindricum, features a fine interlocked grain with a naturally lustrous finish, prized for its tonal warmth and midrange clarity in musical instruments. Maple, primarily from temperate regions of Europe, Asia, and North America, belongs to the Acer genus and exhibits a tight, straight grain with excellent density, providing bright, articulate sound qualities favored in string instruments. The distinct botanical traits and geographic origins of Sapele and Maple influence their resonance, durability, and aesthetic appeal, guiding luthiers in selecting the ideal wood for specific tonal characteristics.
Grain Patterns and Visual Appeal
Sapele offers a striking interlocking grain pattern with a rich reddish-brown hue that deepens over time, making it a favored choice for visually impactful instruments. Maple features a tight, fine grain with a creamy, often wavy or flame-like figure that enhances light reflection and adds a luxurious aesthetic. Both woods provide distinct visual appeal: Sapele's dramatic texture suits warm, vintage-style finishes, while Maple's smooth, bright appearance is ideal for classic and modern instruments.
Density and Hardness Comparison
Sapele wood, with a density ranging from 640 to 720 kg/m3, offers a slightly higher hardness than maple, which typically has a density around 600 to 700 kg/m3 and a Janka hardness of 1450 lbf, while sapele's Janka hardness measures approximately 1680 lbf. The increased hardness of sapele provides enhanced durability and resistance to denting, making it suitable for instruments requiring robust construction. In contrast, maple's slightly lighter density and hardness contribute to a brighter tone and greater resonance favored in many acoustic and electric instruments.
Tonewood Properties: Sound and Resonance
Sapele offers a warm, balanced tone with pronounced midrange frequencies ideal for rich, full-bodied sound in musical instruments, while maple produces bright, clear, and articulate tones with strong high-frequency presence. The dense grain structure of sapele enhances sustain and provides a smooth resonance, making it popular for acoustic guitar backs and sides. In contrast, maple's hardness contributes to excellent projection and clarity, preferred for violin backs and electric guitar bodies seeking precise tonal definition.
Workability: Luthier and Builder Perspectives
Sapele is favored by luthiers for its medium density and consistent grain, offering excellent workability with minimal tool wear and smooth shaping, ideal for guitar backs and sides. Maple provides a harder, denser surface that requires sharper tools and more effort but delivers superior structural stability and a bright tonal response favored in necks and fingerboards. Both woods respond well to finishing, but Sapele's closed grain allows easier sanding and polishing, whereas Maple may need additional filler for a perfectly smooth finish.
Durability and Longevity in Musical Instruments
Sapele wood offers excellent durability and resistance to wear, making it a reliable choice for musical instruments exposed to frequent handling and environmental changes. Maple is renowned for its exceptional strength and stability, contributing to the longevity of instruments such as violins and guitars by withstanding tension and impacts over time. Both woods provide durability, but maple's denser grain structure often results in longer-lasting performance in high-stress musical applications.
Finishing Options and Aesthetic Customization
Sapele offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with a tight, interlocked grain pattern that responds well to oil and satin finishes, highlighting its natural luster while providing durability for musical instruments. Maple's lighter, creamy color and fine, even grain allow for versatile finishing options, including high-gloss and transparent lacquer, making it ideal for showcasing intricate aesthetic customizations such as figure patterns like flame or quilt maple. Both woods accept stains and dyes effectively, but maple's uniform texture affords superior consistency in color application and intricate detailing for personalized visual effects.
Price and Availability Worldwide
Sapele is generally more affordable and widely available than maple, especially in African and Asian markets, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers and musicians. Maple, prized for its tonal clarity and durability, tends to be more expensive due to limited supply from North American sources and higher demand in premium instrument production. Both woods are globally traded, but maple's higher price and availability constraints often influence its use in high-end guitars and violins compared to the more accessible sapele.
Best Applications: Which Wood for Which Instrument?
Sapele offers a warm, resonant tone with strong midrange frequencies, making it ideal for electric guitar bodies, ukuleles, and drum shells where durability and a rich, balanced sound are essential. Maple provides bright, clear articulation with excellent sustain and is preferred for violin backs and necks, acoustic guitar necks, and drum shells requiring sharp attack and projection. Both woods enhance tonal quality, but Sapele suits instruments needing warmth and robustness, while Maple excels in brightness and clarity.
Infographic: Sapele vs Maple for Musical Instrument
 azmater.com
azmater.com