Ramin veneer offers a light, creamy color with a fine, uniform texture, making it ideal for smooth finishes and contemporary designs. Cherry veneer features a rich, reddish-brown hue that darkens over time, providing warmth and a classic look for traditional woodworking projects.
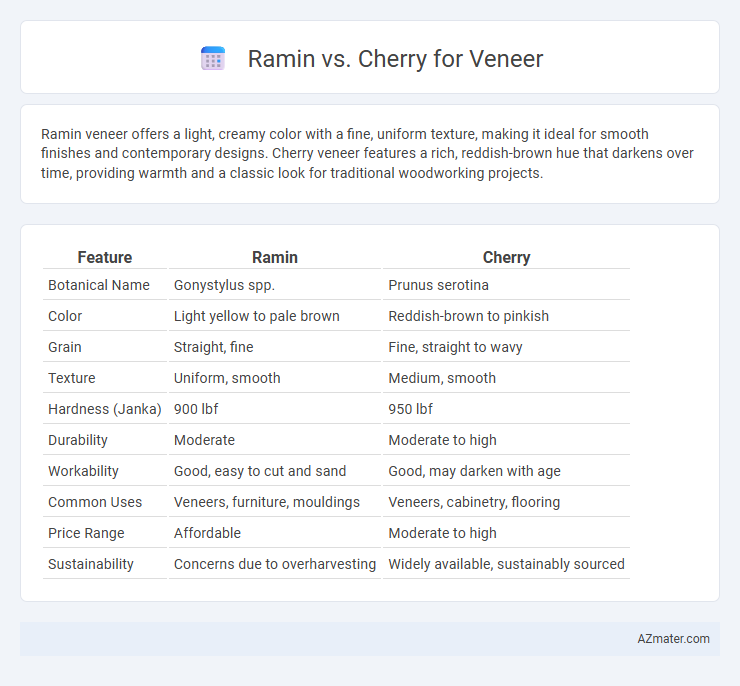
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ramin | Cherry |
|---|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Gonystylus spp. | Prunus serotina |
| Color | Light yellow to pale brown | Reddish-brown to pinkish |
| Grain | Straight, fine | Fine, straight to wavy |
| Texture | Uniform, smooth | Medium, smooth |
| Hardness (Janka) | 900 lbf | 950 lbf |
| Durability | Moderate | Moderate to high |
| Workability | Good, easy to cut and sand | Good, may darken with age |
| Common Uses | Veneers, furniture, mouldings | Veneers, cabinetry, flooring |
| Price Range | Affordable | Moderate to high |
| Sustainability | Concerns due to overharvesting | Widely available, sustainably sourced |
Introduction to Veneer Wood Choices
Veneer wood choices such as Ramin and Cherry offer distinct characteristics suited for different design aesthetics and functional needs. Ramin veneer is known for its light, creamy color and fine, uniform grain, making it ideal for contemporary interiors seeking a clean and airy look. Cherry veneer, valued for its rich reddish-brown hue and smooth texture, enhances traditional and elegant furniture pieces, gaining depth and warmth over time through natural oxidation.
Overview of Ramin and Cherry Woods
Ramin wood, derived from the genus Gonystylus, is a lightweight, pale hardwood commonly used in veneer production for its fine grain and smooth texture. Cherry wood, sourced from Prunus species, features a rich reddish-brown color and a fine, straight grain that darkens with age, making it highly prized for decorative veneers. Both woods offer durability and aesthetic appeal, with Ramin favored for lighter finishes and Cherry preferred for warm, elegant surfaces.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Ramin veneer features a fine, even texture with a pale cream to light yellow color, showcasing subtle grain patterns that provide a smooth, uniform appearance ideal for modern and minimalist designs. Cherry veneer displays rich reddish-brown hues that deepen over time, with prominent, flowing grain patterns creating a warm, elegant, and dynamic look often favored in traditional and luxury furniture. The choice between Ramin and Cherry veneers largely depends on the desired aesthetic, with Ramin offering a lighter, consistent appearance and Cherry providing a vibrant, striking grain character.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Ramin veneer exhibits superior durability due to its dense grain structure, making it highly resistant to wear and impact compared to Cherry veneer, which tends to be softer and more susceptible to dents. Strength-wise, Ramin wood's consistent hardness provides enhanced load-bearing capacity, ideal for high-traffic applications, whereas Cherry veneer offers moderate strength with a balance of flexibility and hardness. The inherent toughness of Ramin makes it a preferred choice for durable interior finishes, while Cherry's aesthetic appeal suits less demanding environments.
Workability and Ease of Application
Ramin veneer exhibits excellent workability due to its fine, uniform texture and straight grain, making it easy to cut, shape, and apply without excessive sanding or finishing. Cherry veneer, while slightly harder, offers good workability with a smoother surface but requires more attention during application to prevent cracking or chipping. In terms of ease of application, Ramin's consistent density allows for predictable adhesion and less risk of warping, whereas Cherry's natural oils may necessitate specialized adhesives for optimal bonding.
Cost and Availability
Ramin veneer generally costs less than cherry veneer, making it a more budget-friendly option for large projects. Cherry veneer, prized for its rich color and fine grain, is often more expensive due to its higher demand and slower growth rate. Ramin is widely available in Southeast Asia, while cherry veneer availability can be limited and more variable, especially outside North America.
Suitability for Different Applications
Ramin veneer, with its light color and fine, uniform grain, is highly suitable for interior applications such as furniture, cabinetry, and decorative paneling, offering a smooth finish and ease of staining or painting. Cherry veneer is prized for its rich reddish-brown hue and natural luster, making it ideal for high-end furniture, flooring, and musical instruments where warmth and elegance are desired. Both veneers perform well in indoor environments, but ramin's hardness and resistance to wear make it preferable for more utilitarian uses, while cherry's aesthetic appeal suits premium, visible surfaces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ramin veneer is sourced primarily from Southeast Asian forests, where overharvesting has led to significant deforestation and habitat loss, raising sustainability concerns. Cherry veneer, often harvested from North American hardwoods, benefits from more regulated forestry practices and sustainable management, resulting in a lower environmental impact. Choosing cherry veneer typically supports better forest conservation efforts and reduces carbon footprint compared to ramin due to stricter legal protections and reforestation programs.
Maintenance and Longevity
Ramin veneer offers high durability and resistance to wear, requiring minimal maintenance such as regular dusting and occasional polishing to maintain its smooth finish. Cherry veneer, while aesthetically rich with its warm tones, demands more careful upkeep to prevent scratches and fading, often necessitating the use of specialized wood cleaners and protective finishes. Both veneers can last decades with proper care, but Ramin's natural hardness typically grants it a slight edge in longevity under everyday use.
Choosing Between Ramin and Cherry Veneer
Choosing between Ramin and Cherry veneer depends on desired aesthetic and durability, as Cherry veneer offers warm reddish tones with fine grain patterns that enhance traditional and elegant designs, while Ramin veneer provides a lighter, creamy appearance with subtle texture suited for modern or minimalist interiors. Cherry veneer is valued for its aging process, developing richer hues over time, making it ideal for high-end furniture, whereas Ramin's stability and resistance to warping make it practical for cabinetry and paneling in humid environments. Cost considerations also favor Ramin as a more budget-friendly option compared to the premium pricing of Cherry veneer.
Infographic: Ramin vs Cherry for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com