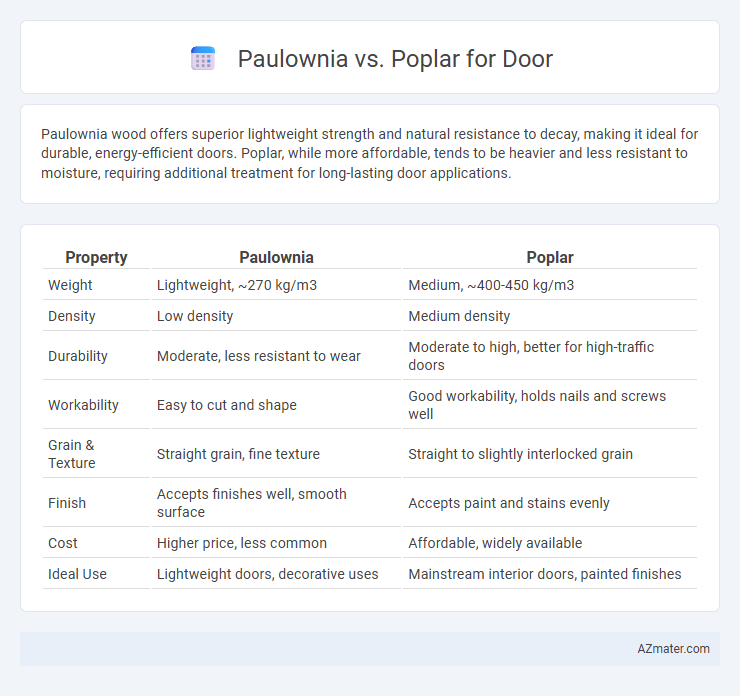
Paulownia wood offers superior lightweight strength and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for durable, energy-efficient doors. Poplar, while more affordable, tends to be heavier and less resistant to moisture, requiring additional treatment for long-lasting door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Paulownia | Poplar |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, ~270 kg/m3 | Medium, ~400-450 kg/m3 |
| Density | Low density | Medium density |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to wear | Moderate to high, better for high-traffic doors |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Good workability, holds nails and screws well |
| Grain & Texture | Straight grain, fine texture | Straight to slightly interlocked grain |
| Finish | Accepts finishes well, smooth surface | Accepts paint and stains evenly |
| Cost | Higher price, less common | Affordable, widely available |
| Ideal Use | Lightweight doors, decorative uses | Mainstream interior doors, painted finishes |
Introduction to Paulownia and Poplar Woods
Paulownia wood is known for its lightweight, durability, and natural resistance to warping and insects, making it ideal for door construction where stability and longevity are essential. Poplar wood offers a more affordable, moderately dense option with a smooth texture that takes paint well, but it is less resistant to moisture and damage compared to Paulownia. Choosing between Paulownia and Poplar depends on the desired balance of strength, weight, and finishing properties for door applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Paulownia wood is significantly lighter and more dimensionally stable than Poplar, making it ideal for lightweight door applications with reduced warping risks. Poplar has a higher density and hardness, offering better impact resistance but adding more weight to doors. Both woods have moderate resistance to moisture, but Paulownia's low shrinkage rate enhances durability in varying humidity conditions.
Durability for Door Applications
Paulownia wood offers superior durability for door applications due to its natural resistance to warping, cracking, and insect damage, making it ideal for long-lasting exterior and interior doors. Poplar, while affordable and easy to work with, tends to be less durable and more prone to dents and moisture damage, which can limit its lifespan in high-traffic or exterior door use. For doors requiring high durability and low maintenance, Paulownia is generally the better choice, especially in environments exposed to varying weather conditions.
Weight and Handling Differences
Paulownia wood is significantly lighter than poplar, with a density around 0.25 g/cm3 compared to poplar's 0.4-0.5 g/cm3, making it easier to handle during door manufacturing and installation. This lightweight nature reduces strain on hinges and frames, improving door durability and ease of use. In contrast, poplar's heavier weight provides greater rigidity but may require stronger support structures for doors, impacting overall handling and installation complexity.
Aesthetic Appeal and Grain Patterns
Paulownia wood displays a light, creamy color with subtle, straight grain patterns, offering a smooth and refined aesthetic ideal for modern door designs. Poplar features a more varied palette with streaks of green, yellow, and brown, providing unique and rustic grain patterns that enhance doors with a natural, textured appearance. Both woods offer distinct visual appeals, with Paulownia favoring minimalism and Poplar delivering character through its dynamic grain.
Insulation and Soundproofing Qualities
Paulownia wood offers superior insulation due to its low density and cellular structure, making it highly effective in maintaining indoor temperatures and reducing energy costs for doors. Poplar, while moderately insulating, lacks the same soundproofing capabilities because it is denser and transmits vibrations more readily. For soundproof doors, poplar tends to perform less effectively than paulownia, which provides better noise reduction properties and thermal efficiency.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Paulownia wood offers superior sustainability compared to poplar due to its rapid growth rate and ability to sequester carbon efficiently, making it a highly renewable resource. Poplar, while also fast-growing, typically requires more water and pesticides, impacting its environmental footprint negatively. Choosing paulownia for door manufacturing supports eco-friendly practices through responsible forestry and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost Analysis: Paulownia vs Poplar Doors
Paulownia doors typically cost more upfront due to the wood's lightweight properties, fast growth rate, and superior durability, making it a cost-effective choice over time despite higher initial investment. Poplar doors are generally less expensive initially but may incur higher maintenance and replacement costs due to lower resistance to moisture and wear. When analyzing long-term value, Paulownia offers better cost efficiency through its combination of durability, ease of workability, and lower susceptibility to warping compared to poplar.
Workability and Finishing Options
Paulownia offers excellent workability due to its lightweight nature and fine, even grain, making it easy to cut, shape, and sand for door applications. Poplar is similarly easy to work with but tends to be denser and can exhibit more grain variations, affecting its finishing uniformity. Finishing options for Paulownia include staining and painting with good absorption, while Poplar's smooth surface takes paint well but can require sealing to avoid blotchy finishes.
Best Use Cases for Each Wood Type
Paulownia is ideal for lightweight doors requiring dimensional stability and resistance to warping, making it perfect for interior applications and areas with fluctuating humidity. Poplar excels in painted doors due to its smooth grain and affordability, suited for decorative or budget-conscious projects where strength is moderate. Both woods offer unique benefits: Paulownia's low density supports ease of handling, while Poplar provides a solid surface ideal for finishing options.
Infographic: Paulownia vs Poplar for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com