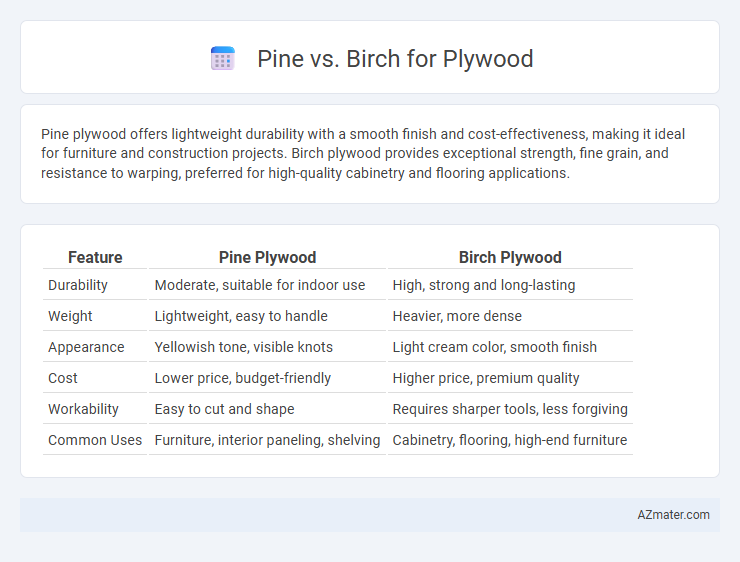
Pine plywood offers lightweight durability with a smooth finish and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for furniture and construction projects. Birch plywood provides exceptional strength, fine grain, and resistance to warping, preferred for high-quality cabinetry and flooring applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pine Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for indoor use | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier, more dense |
| Appearance | Yellowish tone, visible knots | Light cream color, smooth finish |
| Cost | Lower price, budget-friendly | Higher price, premium quality |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Requires sharper tools, less forgiving |
| Common Uses | Furniture, interior paneling, shelving | Cabinetry, flooring, high-end furniture |
Introduction to Pine and Birch Plywood
Pine plywood is crafted from softwood pine layers, known for its lightweight structure and affordability, making it ideal for general construction and furniture applications. Birch plywood, derived from hardwood birch veneers, offers superior strength, durability, and a smooth surface that excels in cabinetry, flooring, and decorative projects. Both types vary in density and grain pattern, influencing their suitability for different plywood uses based on project requirements.
Botanical Differences: Pine vs Birch Trees
Pine trees belong to the Pinaceae family and are coniferous evergreens characterized by needle-like leaves and seed-bearing cones, while Birch trees are deciduous hardwoods from the Betulaceae family, known for their broad leaves and distinctive bark. Pine wood is softwood, generally lighter and resinous, whereas Birch wood is hardwood, denser and harder, influencing the strength and finish of plywood made from each. These botanical differences impact plywood durability, grain texture, and suitability for various construction or furniture applications.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Pine plywood offers moderate strength with a softer wood grain, making it easier to work but less resistant to dents and wear compared to birch. Birch plywood features a denser and harder wood grain, resulting in superior strength, higher resistance to impact, and enhanced durability for heavy-duty applications. The enhanced hardness and stability of birch plywood make it a preferred choice for furniture and cabinetry requiring long-lasting structural integrity.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Pine plywood features a light, warm tone with pronounced knots and a rustic, natural grain pattern ideal for casual or country-style interiors. Birch plywood offers a smoother, more uniform grain and a pale, creamy color that creates a sleek and modern aesthetic. The distinct grain patterns in birch provide a subtle elegance, while pine's varied texture adds character and visual interest.
Workability and Ease of Use
Pine plywood offers superior workability due to its softwood nature, allowing for easier cutting, shaping, and sanding, making it ideal for DIY projects and intricate woodworking. Birch plywood, a hardwood, provides a smoother, denser surface but can be more challenging to work with, requiring sharper tools and more effort during cutting and sanding. Pine's lightweight and flexibility make it more user-friendly, while birch delivers enhanced durability and a fine finish, balancing ease of use with premium quality.
Cost Comparison: Pine vs Birch Plywood
Pine plywood is generally more affordable than birch plywood due to the faster growth rate and wider availability of pine trees, making it a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious projects. Birch plywood offers higher structural strength and a smoother surface finish, resulting in a higher price point but better durability and aesthetic appeal for premium applications. When comparing cost, pine plywood ranges from $20 to $30 per 4x8 sheet, while birch plywood typically costs between $40 and $60 per 4x8 sheet, reflecting the quality and longevity differences.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pine plywood generally has a lower environmental impact due to faster growth rates and widespread availability, enabling more efficient carbon sequestration and reduced deforestation pressure compared to birch. Birch plywood, often sourced from slower-growing trees in northern forests, can contribute to higher ecological costs and longer regeneration times, impacting forest biodiversity. Sustainable forestry certifications such as FSC and PEFC are crucial for both woods to ensure responsible harvesting and minimal environmental footprint in plywood production.
Common Applications for Each Type
Pine plywood is widely used in construction, cabinetry, and furniture-making due to its affordability, lightweight nature, and ease of staining or painting. Birch plywood, valued for its smooth finish, strength, and resistance to warping, is commonly employed in high-quality furniture, cabinetry, shelving, and decorative applications requiring a refined appearance. Both types serve distinct purposes, with pine favored for cost-effective projects and birch chosen for durability and aesthetic appeal in premium products.
Pros and Cons Summary
Pine plywood offers affordability, lightweight properties, and ease of staining, making it ideal for furniture and interior projects but is prone to dents and scratches due to its softness. Birch plywood provides superior strength, durability, and a smooth, consistent grain that resists warping, suitable for cabinetry and structural applications, though it comes at a higher cost and is heavier than pine. Choosing between pine and birch plywood depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for durability and visual finish quality.
Choosing the Right Plywood for Your Project
Pine plywood offers a lightweight and cost-effective option with a smooth surface ideal for indoor applications, while birch plywood provides superior strength, durability, and a fine grain pattern preferred for furniture and cabinetry. Choosing the right plywood depends on the project's structural requirements and aesthetic preferences, with pine suited for budget-friendly and decorative uses and birch favored for load-bearing and high-quality finishes. Evaluating factors like moisture resistance, ease of staining, and intended environment ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Pine vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com