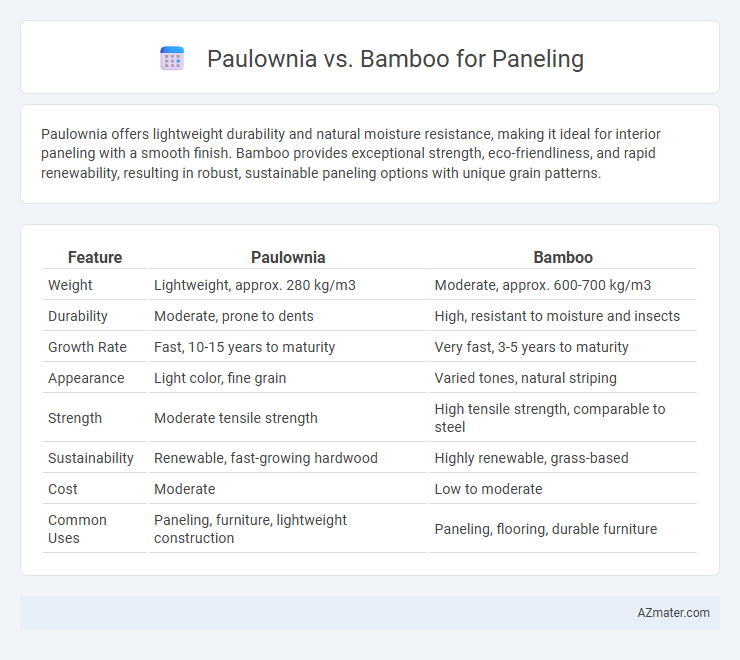
Paulownia offers lightweight durability and natural moisture resistance, making it ideal for interior paneling with a smooth finish. Bamboo provides exceptional strength, eco-friendliness, and rapid renewability, resulting in robust, sustainable paneling options with unique grain patterns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Paulownia | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, approx. 280 kg/m3 | Moderate, approx. 600-700 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to dents | High, resistant to moisture and insects |
| Growth Rate | Fast, 10-15 years to maturity | Very fast, 3-5 years to maturity |
| Appearance | Light color, fine grain | Varied tones, natural striping |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, comparable to steel |
| Sustainability | Renewable, fast-growing hardwood | Highly renewable, grass-based |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Common Uses | Paneling, furniture, lightweight construction | Paneling, flooring, durable furniture |
Introduction to Paulownia and Bamboo Paneling
Paulownia paneling is renowned for its lightweight yet strong characteristics, offering excellent thermal insulation and a smooth, fine-grained finish ideal for interior wall applications. Bamboo paneling, derived from fast-growing grass species, provides exceptional durability, moisture resistance, and a unique natural texture that enhances aesthetic appeal. Both materials are eco-friendly alternatives to traditional wood panels, with Paulownia emphasizing lightweight versatility and Bamboo excelling in robustness and sustainability.
Botanical and Material Origins
Paulownia, a fast-growing hardwood tree native to East Asia, produces lightweight, fine-grained timber with excellent insulation properties ideal for paneling. Bamboo, a rapidly renewable grass species, offers high tensile strength and natural moisture resistance, making it a durable and eco-friendly paneling material. Both materials originate from distinctly different botanical classifications, impacting their texture, durability, and environmental benefits in interior design.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Paulownia and bamboo are both fast-growing, renewable resources ideal for sustainable paneling, with bamboo recognized for its rapid growth cycle of 3-5 years and high carbon sequestration capacity. Paulownia offers lightweight, strong panels with a growth cycle of about 10 years, making it suitable for eco-friendly construction while requiring less water and pesticides. Bamboo's extensive root system prevents soil erosion and promotes biodiversity, whereas paulownia improves soil quality through nitrogen fixation, both contributing positively to environmental conservation.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Paulownia wood offers moderate durability with resistance to rot and insects but is softer and more prone to dents than bamboo, which boasts exceptional hardness and resilience ideal for high-traffic paneling. Bamboo's natural silica content enhances its longevity, making it less susceptible to moisture damage and warping compared to Paulownia, which requires proper sealing for extended lifespan. For long-term paneling applications, bamboo generally outperforms Paulownia in durability and maintenance demands.
Weight and Density Differences
Paulownia wood is significantly lighter than bamboo, with a density ranging from 0.25 to 0.32 g/cm3 compared to bamboo's 0.60 to 0.90 g/cm3, making Paulownia ideal for lightweight paneling applications. The lower density of Paulownia provides ease of handling and installation, while bamboo's higher density offers greater durability and impact resistance. Choosing between Paulownia and bamboo paneling depends on the balance between weight requirements and desired strength for the specific interior or exterior project.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Paulownia offers a light, smooth grain with a pale finish that enhances modern, minimalist paneling designs, while bamboo presents a rich texture and natural variations ideal for creating warm, organic aesthetics. The uniformity of Paulownia allows for sleek, consistent patterns in large panels, whereas bamboo's strip-based structure provides versatility in creating intricate geometric or linear designs. Both materials are sustainable choices but differ significantly in visual impact and adaptability, influencing design decisions based on desired ambiance and creative expression.
Ease of Installation
Paulownia panels are lightweight and dimensionally stable, making them easier to cut and fasten, which significantly reduces installation time compared to bamboo. Bamboo paneling often requires meticulous preparation due to its hardness and natural variability, potentially complicating alignment and fastening processes. The uniformity and lower density of Paulownia enhance ease of handling, resulting in quicker and more efficient panel installation for interior surfaces.
Cost Analysis
Paulownia wood typically costs more upfront than bamboo due to its slower growth rate and limited supply, but offers superior durability and lightweight properties that can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Bamboo is generally more economical, growing rapidly and widely available, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious paneling projects. Cost analysis should consider not only initial material prices but also installation ease, lifespan, and potential replacement frequency to determine overall value.
Maintenance Requirements
Paulownia paneling requires minimal maintenance due to its natural resistance to moisture, pests, and decay, making it ideal for indoor and outdoor applications where durability is crucial. Bamboo paneling, while also resilient, demands more frequent sealing and treatment to prevent mold, warping, and insect damage, especially in humid environments. Proper maintenance of bamboo includes routine cleaning and protective coatings to maintain its appearance and longevity, whereas paulownia's low-maintenance nature significantly reduces upkeep efforts.
Best Applications for Paulownia and Bamboo Paneling
Paulownia paneling excels in lightweight, moisture-resistant applications, making it ideal for interior walls, ceilings, and furniture where easy handling and dimensional stability are crucial. Bamboo paneling offers superior hardness and durability, perfect for high-traffic areas, accent walls, and eco-friendly projects requiring strong, sustainable materials. Both materials enhance aesthetics and sustainability, but Paulownia suits environments demanding lightweight and moisture resistance, while bamboo thrives in tough, wear-prone spaces.
Infographic: Paulownia vs Bamboo for Paneling
 azmater.com
azmater.com