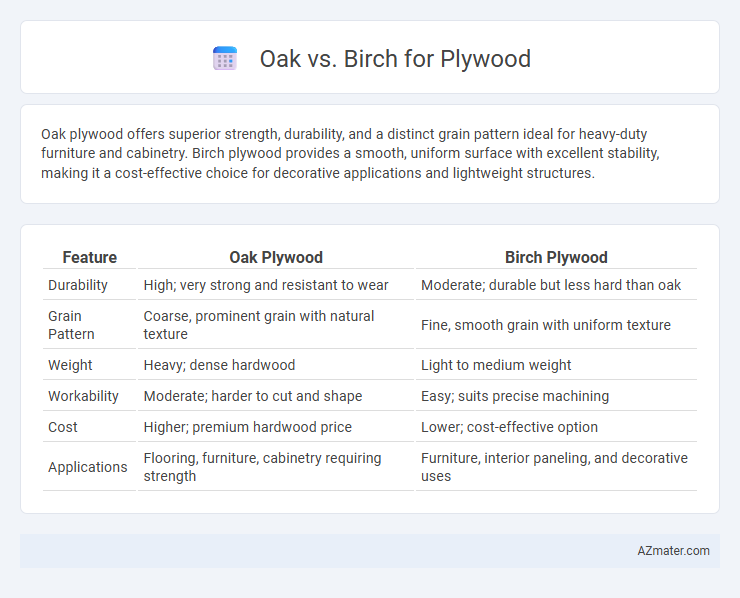
Oak plywood offers superior strength, durability, and a distinct grain pattern ideal for heavy-duty furniture and cabinetry. Birch plywood provides a smooth, uniform surface with excellent stability, making it a cost-effective choice for decorative applications and lightweight structures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oak Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High; very strong and resistant to wear | Moderate; durable but less hard than oak |
| Grain Pattern | Coarse, prominent grain with natural texture | Fine, smooth grain with uniform texture |
| Weight | Heavy; dense hardwood | Light to medium weight |
| Workability | Moderate; harder to cut and shape | Easy; suits precise machining |
| Cost | Higher; premium hardwood price | Lower; cost-effective option |
| Applications | Flooring, furniture, cabinetry requiring strength | Furniture, interior paneling, and decorative uses |
Introduction to Oak and Birch Plywood
Oak plywood offers exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and high-end furniture. Birch plywood provides a smooth, consistent surface with excellent machinability, favored for cabinetry and decorative projects. Both types feature distinct grain patterns, where oak displays pronounced texture and birch exhibits a fine, uniform appearance.
Wood Grain and Appearance Differences
Oak plywood features a prominent, coarse grain with a swirling pattern that adds a rustic and robust character, while birch plywood exhibits a subtle, fine, and uniform grain that creates a smooth and modern aesthetic. The color of oak ranges from light to medium brown with distinct growth rings, contrasting with birch's pale cream to light yellow tone that offers a cleaner, more consistent look. Oak's grain and appearance make it ideal for traditional and heavy-duty applications, whereas birch plywood suits projects requiring a sleek, minimalist finish.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Oak plywood exhibits superior durability and strength due to its dense hardwood fibers, making it highly resistant to wear and impact. Birch plywood, while slightly less robust, offers consistent strength with a fine grain structure that provides good stability and resistance to warping. For heavy-duty applications requiring maximum load-bearing capacity, oak plywood is generally preferred, whereas birch plywood is favored for balanced performance and cost-effectiveness.
Workability: Cutting and Finishing
Oak plywood is dense and hard, offering strong durability but requiring sharper tools and more effort during cutting, making it slightly less forgiving for complex cuts. Birch plywood provides superior workability with a smoother grain, allowing for easier cutting and a cleaner finish, which is ideal for detailed woodworking and fine sanding. Both woods accept stains and finishes well, but birch's consistent texture results in a more uniform appearance after finishing.
Cost and Availability
Oak plywood tends to have a higher cost due to its density and durability, making it a premium choice for furniture and cabinetry. Birch plywood is generally more affordable and widely available, favored for its smooth finish and ease of machining in construction projects. Both types offer strength, but birch's consistent supply and lower price point make it popular for budget-sensitive woodworking applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Oak plywood generally has a higher environmental impact than birch plywood due to slower growth rates and more intensive harvesting practices, resulting in less sustainable sourcing. Birch plywood is often considered more sustainable because birch trees grow faster and are widely replanted, reducing deforestation pressures and promoting responsible forest management. Both types should ideally come from certified sources like FSC to ensure minimal ecological disruption and support sustainable forestry.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Oak plywood offers superior resistance to moisture and decay due to its dense grain and natural tannins, making it ideal for environments with high humidity or occasional water exposure. Birch plywood, while generally durable and stable, is less resistant to moisture and can be more susceptible to swelling and fungal attack if not properly sealed. Choosing oak plywood enhances longevity in damp conditions, whereas birch plywood requires additional protective treatments to maintain structural integrity.
Common Applications in Construction and Furniture
Oak plywood, known for its durability and heavy load-bearing capacity, is commonly used in flooring, cabinetry, and structural elements requiring strength and resistance to wear. Birch plywood, prized for its smooth surface and fine grain, is preferred in furniture making, interior paneling, and decorative applications where aesthetics and ease of finishing are critical. Both materials offer stability, but oak's higher density suits heavy-duty construction, while birch's uniform texture enhances detailed craftsmanship in furniture.
Maintenance and Longevity
Oak plywood offers superior durability and resistance to wear, requiring minimal maintenance compared to birch plywood, which is softer and more prone to dents and scratches. Oak's dense grain structure enhances its longevity, maintaining structural integrity in high-moisture environments better than birch. Regular sealing and occasional refinishing can extend birch plywood's lifespan, but oak remains the preferred choice for long-term, low-maintenance applications.
Which is Better: Oak or Birch Plywood?
Oak plywood offers superior durability and a rich, attractive grain, making it ideal for cabinetry and furniture that require strength and aesthetic appeal. Birch plywood is valued for its smooth, uniform surface and affordability, often preferred for paint-grade projects and cost-effective applications. Choosing between oak and birch plywood depends on the desired balance between strength, appearance, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Oak vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com