Buckeye plywood offers superior moisture resistance and stability, making it ideal for exterior applications, while birch plywood provides higher strength and a smoother finish, preferred for furniture and cabinetry. Both materials feature dense hardwood veneers, but buckeye's natural durability outperforms birch in humid environments.
Table of Comparison
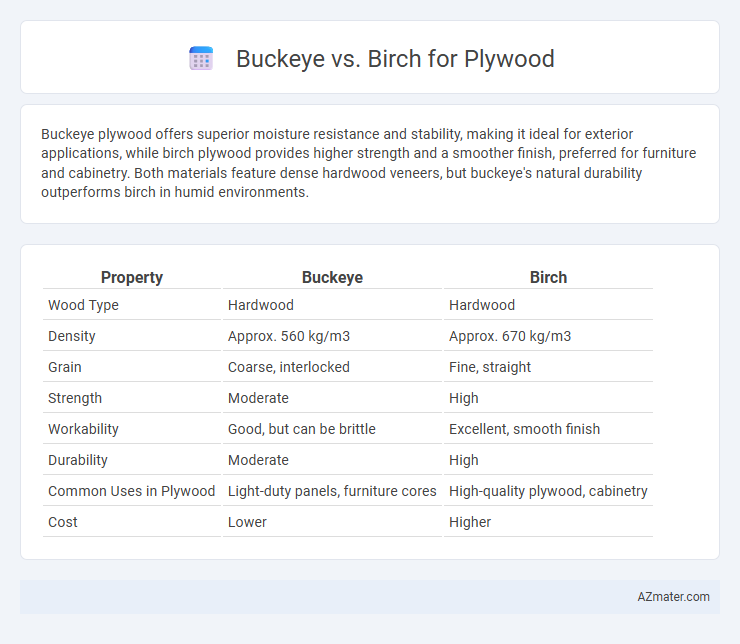
| Property | Buckeye | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Density | Approx. 560 kg/m3 | Approx. 670 kg/m3 |
| Grain | Coarse, interlocked | Fine, straight |
| Strength | Moderate | High |
| Workability | Good, but can be brittle | Excellent, smooth finish |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Common Uses in Plywood | Light-duty panels, furniture cores | High-quality plywood, cabinetry |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Buckeye and Birch Woods
Buckeye wood, characterized by its light color and soft texture, is known for its smooth finish and workability in plywood production. Birch wood, valued for its strength, durability, and fine grain, is a common choice for high-quality plywood applications requiring structural integrity. Both woods offer distinct advantages, with Buckeye preferred for aesthetic appeal and Birch favored for robust performance in plywood manufacturing.
Key Characteristics of Buckeye Plywood
Buckeye plywood is renowned for its exceptional strength, dimensional stability, and smooth surface finish, making it ideal for structural applications and high-quality furniture. Its tightly bonded layers resist warping and delamination, providing superior durability compared to birch plywood. Buckeye plywood also offers excellent screw-holding capacity and resistance to moisture, enhancing its performance in demanding environments.
Key Features of Birch Plywood
Birch plywood is renowned for its smooth, light-colored surface and consistent grain, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative projects that demand an attractive finish. It offers superior strength and durability compared to Buckeye plywood, with multiple layers of hardwood veneers that resist warping and provide excellent screw-holding capacity. Birch plywood also delivers enhanced stability and resistance to impact, ensuring reliable performance in both interior and exterior applications.
Appearance and Grain Comparison
Buckeye plywood exhibits a smooth, uniform grain with a light, creamy color that enhances modern interior aesthetics, while birch plywood features a fine, closed grain and a pale yellow to white tone, ideal for a clean, classic look. Buckeye's subtle grain pattern offers a sleek surface that resists visual clutter, contrasting with birch's more pronounced, consistent grain that adds natural warmth and texture. Both woods provide high-quality finishes, but buckeye stands out for minimal grain variation, whereas birch is preferred for its traditional, detailed grain appeal.
Strength and Durability Differences
Buckeye plywood offers superior strength due to its dense grain structure and tightly bonded veneers, making it ideal for heavy-duty construction projects. Birch plywood, known for its fine texture and uniform layers, provides excellent durability and resistance to impact, though it generally has slightly less load-bearing capacity than Buckeye. Both types boast high-quality performance, but Buckeye is often preferred where maximum strength and long-term structural integrity are crucial.
Workability and Machining
Buckeye plywood offers superior workability due to its fine grain and uniform texture, resulting in smooth cuts and easy sanding. Birch plywood, known for its consistent hardness and density, provides excellent machinability with minimal splintering and holds screws and nails securely. Both types maintain dimensional stability, but Birch is often preferred for projects requiring precision machining and durability.
Cost Comparison: Buckeye vs Birch Plywood
Buckeye plywood typically costs less than birch plywood, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale projects. Birch plywood offers higher durability and a smoother finish, which justifies its higher price point. When comparing cost-effectiveness, consider the long-term value of birch's strength against Buckeye's affordability.
Common Uses in Woodworking and Construction
Buckeye plywood offers excellent strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty construction projects such as subflooring and wall sheathing. Birch plywood is prized for its smooth finish and fine grain, commonly used in woodworking for cabinetry, furniture, and decorative paneling where aesthetic appeal is crucial. Both types provide reliable structural support, but birch suits interior applications requiring a high-quality appearance, while buckeye excels in robust, load-bearing construction tasks.
Sustainability and Sourcing
Buckeye plywood is often sourced from responsibly managed forests, emphasizing sustainability through certification programs like FSC that ensure reduced environmental impact and long-term forest health. Birch plywood, commonly harvested from fast-growing species in Northern Europe and Russia, benefits from renewable forestry practices and efficient replanting cycles, promoting sustainable material use. Both Buckeye and Birch plywood prioritize eco-friendly sourcing, but Birch's rapid growth and regeneration rates tend to offer enhanced sustainability advantages in plywood production.
Choosing the Right Plywood: Buckeye or Birch?
Choosing between Buckeye and Birch plywood hinges on durability, appearance, and cost-effectiveness. Birch plywood offers superior strength, consistent grain patterns, and smooth finish ideal for cabinetry and furniture, while Buckeye plywood is typically more affordable with moderate durability suited for general construction purposes. Evaluating the specific project requirements and budget will help determine whether the premium quality of Birch or the economical option of Buckeye aligns best with your woodworking needs.
Infographic: Buckeye vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com