Mahogany offers a rich, deep color with excellent durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-end tables. Birch provides a lighter tone, smooth grain, and cost-effective strength, perfect for modern and budget-friendly furniture designs.
Table of Comparison
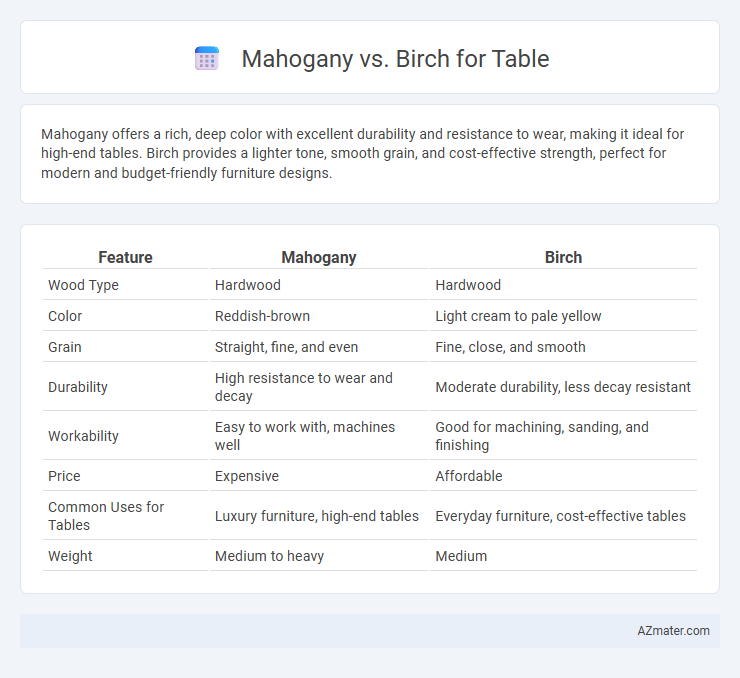
| Feature | Mahogany | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Light cream to pale yellow |
| Grain | Straight, fine, and even | Fine, close, and smooth |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and decay | Moderate durability, less decay resistant |
| Workability | Easy to work with, machines well | Good for machining, sanding, and finishing |
| Price | Expensive | Affordable |
| Common Uses for Tables | Luxury furniture, high-end tables | Everyday furniture, cost-effective tables |
| Weight | Medium to heavy | Medium |
Introduction to Mahogany and Birch Wood
Mahogany is a dense, durable hardwood prized for its rich reddish-brown color and fine, straight grain, making it a popular choice for high-end furniture and tables. Birch wood is known for its pale cream color and smooth, even texture, offering excellent strength and resistance to wear while providing a more affordable option compared to mahogany. Both woods are valued for their unique aesthetic qualities and durability, but mahogany typically commands a higher price due to its luxurious appearance and longer aging potential.
Appearance and Color Differences
Mahogany exhibits a rich, reddish-brown hue with a smooth, straight grain that deepens over time, creating a warm and luxurious appearance ideal for elegant tables. Birch offers a lighter, creamy pale yellow to white color with a fine, even grain pattern, providing a clean and modern look suited for minimalist or Scandinavian-style furniture. The distinct color contrast between mahogany's deep, warm tones and birch's light, neutral shades significantly influences the overall aesthetic and ambiance of the table.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Mahogany offers exceptional durability and superior strength due to its dense grain structure, making it highly resistant to warping and decay, ideal for long-lasting tables. Birch, while also strong and relatively hard, tends to be less dense than mahogany and may show wear more quickly under heavy use. Choosing mahogany ensures robust, durable tables with excellent resistance to scratches and dents, whereas birch provides a cost-effective, moderately strong alternative.
Grain Patterns and Texture
Mahogany features a straight, fine grain with a smooth texture, offering a rich, deep reddish-brown appearance ideal for elegant tables. Birch displays a uniform, subtle grain with a fine, even texture, providing a lighter, creamy tone that enhances modern and minimalist furniture styles. Both woods are prized for their durability, but mahogany's pronounced grain adds warmth and character, while birch's subtle pattern delivers a clean, refined look.
Workability and Ease of Crafting
Mahogany offers excellent workability with its fine, straight grain and consistent texture, making it easy to shape, sand, and finish, ideal for detailed woodworking projects. Birch is also highly workable but tends to be harder and slightly more prone to splintering, requiring sharp tools and careful handling for precise crafting. Both woods are popular for table-making, but mahogany's smoother finish and ease of staining often give it an advantage in detailed furniture construction.
Cost and Affordability
Mahogany tables often come with a higher price tag due to their dense grain, durability, and rich reddish-brown color, making them a premium choice for luxury furniture. Birch tables offer a more affordable alternative, boasting a lighter color and a smooth texture that easily adapts to various stains and finishes. The cost difference makes birch a practical option for budget-conscious buyers seeking quality without sacrificing aesthetics.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Mahogany and birch differ significantly in sustainability and environmental impact when used for tables. Mahogany, often sourced from tropical rainforests, faces criticism due to illegal logging and slower growth rates, raising concerns about deforestation and habitat loss. Birch, native to temperate regions and more abundant, tends to have a lower environmental footprint, benefiting from faster growth cycles and more sustainable harvesting practices.
Maintenance and Longevity
Mahogany offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting tables with minimal maintenance requirements, often needing only occasional polishing to maintain its rich color. Birch is more affordable and easier to work with but requires regular sealing and protection from moisture to prevent warping and prolong its lifespan. Choosing mahogany ensures a table that withstands heavy use and environmental stress better than birch, enhancing both maintenance ease and longevity.
Best Uses for Dining and Work Tables
Mahogany's dense grain and rich reddish-brown color make it ideal for dining tables, offering durability and an elegant appearance that resists warping over time. Birch, with its lighter tone and fine grain, is preferred for work tables due to its strong shock resistance and ability to withstand heavy use without denting. Both woods provide excellent stability, but mahogany suits formal dining settings while birch excels in functional, high-traffic workspace environments.
Verdict: Choosing the Right Wood for Your Table
Mahogany offers exceptional durability and rich reddish-brown tones, ideal for elegant, long-lasting tables, while birch provides a lighter, more affordable option with a fine grain and pale color perfect for modern or casual designs. The choice depends on your budget, desired aesthetic, and maintenance preferences, as mahogany typically requires more care but ages gracefully. For a balance of strength and cost-effectiveness, birch suits everyday use, whereas mahogany is best for heirloom-quality furniture and statement pieces.
Infographic: Mahogany vs Birch for Table
 azmater.com
azmater.com