Larch decking offers high durability and natural resistance to rot with a dense grain, making it ideal for outdoor use. Cedar decking provides superior decay resistance and a smooth finish, valued for its aromatic properties and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
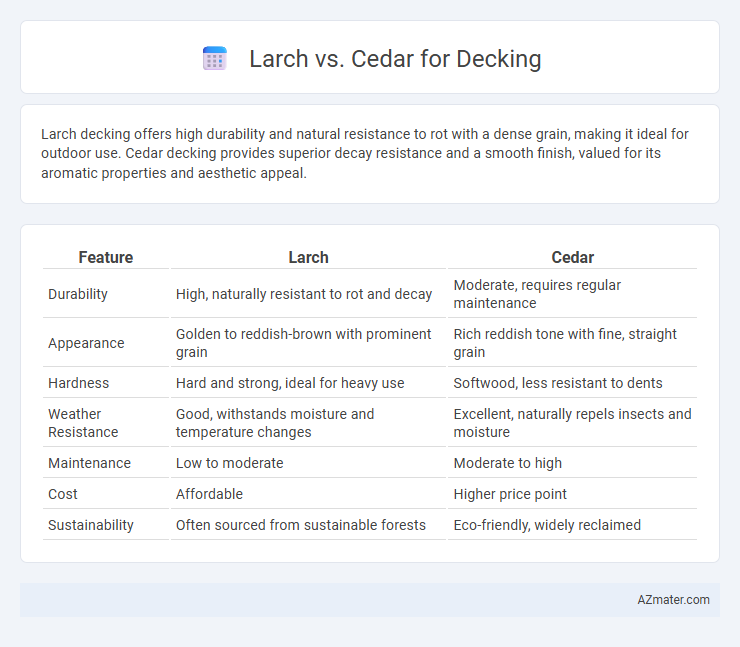
| Feature | Larch | Cedar |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, naturally resistant to rot and decay | Moderate, requires regular maintenance |
| Appearance | Golden to reddish-brown with prominent grain | Rich reddish tone with fine, straight grain |
| Hardness | Hard and strong, ideal for heavy use | Softwood, less resistant to dents |
| Weather Resistance | Good, withstands moisture and temperature changes | Excellent, naturally repels insects and moisture |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Cost | Affordable | Higher price point |
| Sustainability | Often sourced from sustainable forests | Eco-friendly, widely reclaimed |
Introduction to Larch and Cedar Decking
Larch decking offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to rot and insects, making it a popular choice for outdoor applications. Cedar decking is praised for its rich color, smooth texture, and natural oils that protect against decay and moisture damage. Both woods provide excellent structural strength and aesthetic appeal, but larch tends to be harder and more weather-resistant, while cedar is valued for its aromatic properties and ease of workability.
Key Differences Between Larch and Cedar Wood
Larch wood is known for its exceptional durability and natural resistance to decay, making it highly suitable for outdoor decking where moisture exposure is common. Cedar offers superior dimensional stability and a rich, aromatic scent that naturally repels insects, enhancing comfort and longevity in decking applications. Key differences include larch's higher density and strength compared to cedar's softer texture and better resistance to warping and cracking over time.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Larch wood offers excellent durability for decking due to its natural resistance to rot and insects, with a typical lifespan of 20 to 30 years when properly maintained. Cedar, known for its natural oils that repel moisture and pests, provides moderate durability and can last around 15 to 25 years in outdoor conditions. Both woods require regular treatment to maximize lifespan, but larch generally outperforms cedar in terms of long-term resistance to harsh weather elements.
Appearance and Color Characteristics
Larch decking features a warm, golden-yellow hue with distinctive reddish undertones that deepen over time, offering a natural rustic charm. Cedar exhibits a more uniform reddish-brown color with subtle pinkish and amber tones, known for its rich, smooth grain that ages gracefully to a silvery patina. Both woods retain their color well but larch tends to darken with exposure, while cedar maintains a softer, consistent appearance, making each ideal for different aesthetic preferences in deck design.
Resistance to Rot, Insects, and Weather
Larch wood offers excellent resistance to rot and insect infestation due to its natural resin content, making it a durable choice for decking exposed to harsh weather conditions. Cedar is also highly resistant to moisture, decay, and insect damage, attributable to its natural oils that act as preservatives. Both larch and cedar perform well outdoors, but cedar typically requires less maintenance to preserve its resistance against rot, insects, and weathering over time.
Maintenance Requirements for Larch vs Cedar
Larch decking requires moderate maintenance, including annual sealing or staining to prevent weathering and decay due to its higher resin content and natural durability. Cedar decking demands more frequent maintenance with biannual sealing or staining, as it is softer and more prone to surface damage and moisture absorption. Both woods benefit from regular cleaning, but cedar's susceptibility to fading and cracking necessitates more attentive upkeep to maintain its appearance and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Larch wood offers a high level of sustainability due to its rapid growth and natural resistance to decay, reducing the need for chemical treatments. Cedar, while slower growing, is prized for its longevity and natural insect repellence, which also minimizes environmental impact over its lifecycle. Both woods are renewable resources, but larch's faster growth rate and wide availability make it a more environmentally sustainable choice for decking.
Cost and Availability of Materials
Larch wood offers a cost-effective option for decking due to its widespread availability in Europe and North America, often priced lower than cedar. Cedar, particularly Western Red Cedar, commands a higher price point because of its natural resistance to decay and limited regional supply. Availability varies regionally; larch is easier to source in northern climates, while cedar is more prevalent in Pacific Northwest markets, influencing material costs and accessibility.
Installation Ease and Workability
Larch wood offers moderate ease of installation due to its medium density and natural durability, allowing straightforward cutting and fastening without excessive wear on tools. Cedar's lightweight and stable grain enhance workability, making it easier to saw, drill, and fasten while minimizing splitting during decking installation. Both woods provide good dimensional stability, but cedar's softness often results in quicker, less strenuous installation compared to the denser larch.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Larch offers superior durability and resistance to rot, making it ideal for outdoor decking exposed to harsh weather, especially in colder climates. Cedar provides excellent natural insect resistance and a smooth finish, best suited for shaded or less exposed deck areas where aesthetic appeal is prioritized. For long-lasting performance, choose larch in high-moisture environments and cedar for projects emphasizing ease of maintenance and visual warmth.
Infographic: Larch vs Cedar for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com