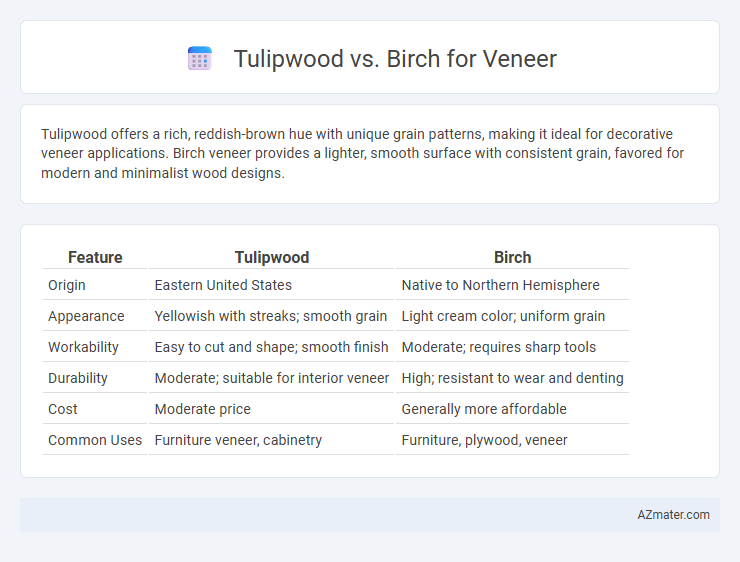
Tulipwood offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with unique grain patterns, making it ideal for decorative veneer applications. Birch veneer provides a lighter, smooth surface with consistent grain, favored for modern and minimalist wood designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tulipwood | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Eastern United States | Native to Northern Hemisphere |
| Appearance | Yellowish with streaks; smooth grain | Light cream color; uniform grain |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape; smooth finish | Moderate; requires sharp tools |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for interior veneer | High; resistant to wear and denting |
| Cost | Moderate price | Generally more affordable |
| Common Uses | Furniture veneer, cabinetry | Furniture, plywood, veneer |
Introduction to Tulipwood and Birch Veneer
Tulipwood veneer offers a distinctive warm amber to reddish-brown hue with a straight grain pattern, prized for its rich color and durability in fine woodworking. Birch veneer stands out for its pale cream to light yellow shades, uniform texture, and smooth grain, making it ideal for modern and minimalist designs. Both veneers are valued in furniture and cabinetry for their strength and ability to accept stains evenly, enhancing aesthetic versatility.
Botanical Overview: Tulipwood vs Birch
Tulipwood, derived from the Liriodendron tulipifera tree native to eastern North America, is characterized by its light yellow to orange-brown hues with subtle grain patterns, whereas Birch, primarily from Betula species found in the Northern Hemisphere, showcases pale cream colors with fine, even grain textures. Tulipwood veneer offers moderate hardness and a smooth finish, making it suitable for decorative applications, while Birch veneer provides superior stability and a consistent surface ideal for cabinetry and furniture. Both woods have distinct anatomical structures; tulipwood features porous vessels contributing to its texture, whereas birch exhibits a diffuse-porous structure with uniform cell patterns enhancing its workability.
Physical Properties Comparison
Tulipwood veneer is known for its moderate density, averaging around 650 kg/m3, offering good hardness and durability, while birch veneer has a slightly higher density of approximately 670 kg/m3, providing enhanced strength and stiffness. Tulipwood features a coarse, uneven grain with moderate workability, whereas birch exhibits a fine, even grain pattern and smooth texture, which facilitates easier sanding and finishing. Both woods demonstrate excellent stability for veneer applications, but birch's superior resistance to warping makes it preferable in high-moisture environments.
Color and Grain Differences
Tulipwood veneer exhibits a warm, golden to reddish-brown hue with smooth, straight to wavy grain patterns that add a rich, natural character to surfaces. Birch veneer, in contrast, features a lighter, creamy to pale yellow color with a fine, even grain that creates a clean and uniform appearance. These color and grain differences influence design choices, with Tulipwood offering a more vibrant and dynamic look and Birch providing a subtle, understated elegance for various woodworking applications.
Workability and Machining
Tulipwood offers excellent workability with a smooth, consistent grain that allows for precise machining and easy sanding, making it ideal for detailed veneer applications. Birch veneer maintains good workability but is slightly harder, requiring sharper tools and more careful handling to prevent chipping during machining. Both woods respond well to adhesives and finishes, yet tulipwood's softer texture generally facilitates superior edge quality in veneer production.
Durability and Longevity
Tulipwood veneer offers moderate durability, with good resistance to wear and impact, making it suitable for decorative surfaces that require longevity but are less exposed to heavy use. Birch veneer, known for its fine grain and hardness, provides exceptional durability and long-lasting performance, ideal for furniture and cabinetry that demand strength over time. Both woods have stable structures, but birch's higher density contributes to greater longevity in high-traffic applications.
Common Uses in Veneering
Tulipwood veneer is commonly used for high-end furniture, cabinetry, and decorative panels due to its striking grain patterns and warm reddish tones. Birch veneer is favored in commercial interiors, plywood facings, and budget-conscious furniture because of its fine grain and pale color that provides a neutral, versatile finish. Both materials offer durability and smooth sanding, but tulipwood's aesthetic appeal makes it a preferred choice for luxurious veneer applications.
Cost and Availability
Tulipwood veneer generally costs more than birch due to its limited availability and distinct grain patterns favored in high-end cabinetry and furniture. Birch veneer is widely available, sourced from fast-growing birch trees, making it a budget-friendly option with consistent supply in the woodworking industry. Cost-effectiveness and accessibility make birch the preferred choice for large-scale veneer projects, while tulipwood caters to niche markets requiring unique aesthetics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tulipwood veneer offers a more sustainable option due to its faster growth rate and higher yield per acre compared to birch, which contributes to reduced deforestation pressure. Birch veneer, while durable, often comes from slower-growing trees, increasing the environmental footprint associated with harvesting and processing. Choosing tulipwood supports regenerative forestry practices and lower carbon emissions in veneer production.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Tulipwood or Birch?
Tulipwood veneer offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with a striking grain pattern, ideal for adding warmth and character to furniture or cabinetry, while birch veneer provides a lighter, creamier tone with a fine, even grain perfect for modern, minimalist designs. Tulipwood's density and durability make it suitable for high-traffic surfaces, whereas birch's stability and smooth texture allow for easy finishing and painting. Selecting the right veneer depends on the desired aesthetic, durability requirements, and the type of finish planned for the project.
Infographic: Tulipwood vs Birch for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com