Iroko offers superior durability and natural resistance to rot and insects compared to Larch, making it ideal for long-lasting outdoor posts. Larch is more affordable and environmentally sustainable but requires regular maintenance to prevent weathering and decay.
Table of Comparison
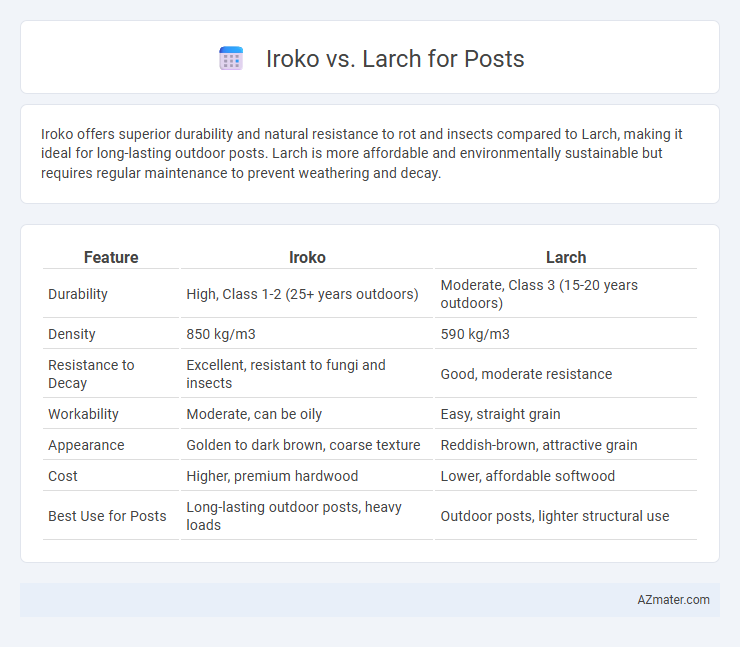
| Feature | Iroko | Larch |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, Class 1-2 (25+ years outdoors) | Moderate, Class 3 (15-20 years outdoors) |
| Density | 850 kg/m3 | 590 kg/m3 |
| Resistance to Decay | Excellent, resistant to fungi and insects | Good, moderate resistance |
| Workability | Moderate, can be oily | Easy, straight grain |
| Appearance | Golden to dark brown, coarse texture | Reddish-brown, attractive grain |
| Cost | Higher, premium hardwood | Lower, affordable softwood |
| Best Use for Posts | Long-lasting outdoor posts, heavy loads | Outdoor posts, lighter structural use |
Introduction to Iroko and Larch Wood
Iroko wood, native to West Africa, is renowned for its high density, durability, and natural resistance to decay and insects, making it an excellent choice for outdoor posts. Larch, a softwood from the Northern Hemisphere, offers strong resin content and moderate decay resistance, prized for its elasticity and ease of workability. Both woods provide longevity and strength for post applications, but Iroko's superior weather resistance often outperforms Larch in demanding environmental conditions.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Iroko (Milicia excelsa) is a tropical hardwood native to West Africa, thriving in countries such as Ghana, Nigeria, and Cote d'Ivoire, while Larch (genus Larix) is a deciduous conifer found primarily in the cooler regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including Siberia, Canada, and parts of Europe. Iroko trees grow slowly in dense, humid rainforests, developing durable, oily wood resistant to decay and insects, whereas Larch trees flourish in mountainous and boreal forests with faster growth rates and wood that is strong yet lightweight. The distinct botanical origins of Iroko and Larch influence their wood properties, suitability for outdoor posts, and environmental adaptability.
Appearance and Color Differences
Iroko wood features a rich, golden to medium brown color with a coarse, interlocking grain that darkens over time, offering a warm and luxurious appearance. Larch wood presents a lighter, pale yellow to reddish-brown hue with a straight grain and prominent knots, lending a more rustic and natural look. The color stability of Iroko contrasts with Larch's tendency to vary in tone, making Iroko preferable for a consistent, elegant finish on posts.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Iroko wood, known for its high density and natural oils, offers exceptional durability and resistance to rot and insect attack, typically lasting 25 to 40 years when used for posts. Larch wood, a dense softwood with good resin content, provides decent durability outdoors, with a lifespan of about 15 to 25 years depending on treatment and exposure. While both woods are suitable for posts, Iroko's superior natural durability generally ensures a longer lifespan and better performance in harsh weather conditions.
Resistance to Rot, Insects, and Weather
Iroko wood stands out for its exceptional resistance to rot, insects, and harsh weather conditions due to its dense grain and natural oils, making it ideal for outdoor posts. Larch offers good durability and moderate resistance to decay and insects but generally requires treatment to match Iroko's performance in wet or insect-prone environments. The high natural durability of Iroko often results in longer-lasting posts with less maintenance compared to larch in demanding outdoor applications.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Iroko wood exhibits superior structural strength and load-bearing capacity compared to larch, making it ideal for heavy-duty posts and supports in construction. With a Janka hardness of around 1,260 lbf, iroko offers enhanced durability and resistance to deformation under load, while larch, though strong with a Janka hardness of approximately 930 lbf, is more prone to bending and wear over time. The dense grain structure of iroko contributes to its higher stiffness and longevity, ensuring greater stability for post applications subject to heavy or dynamic loads.
Workability: Cutting, Shaping, and Finishing
Iroko offers excellent workability for posts, with its coarse grain and medium hardness allowing smooth cutting, shaping, and sanding, while producing minimal dulling on tools. Larch, being denser and more resinous, requires sharper tools for clean cuts and can pose challenges in shaping but finishes to a durable, weather-resistant surface. Both woods respond well to finishing treatments, though Iroko's stability makes it more forgiving during detailed woodworking processes.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Iroko wood offers high durability and natural resistance to rot and insect attacks, requiring minimal maintenance such as occasional oiling to maintain its rich color and prevent drying. Larch is moderately durable but more prone to decay over time, demanding regular protective treatments like staining or sealing to extend its lifespan. In terms of longevity, Iroko typically outperforms Larch, lasting up to 25-40 years with proper care compared to Larch's 15-25 years under similar conditions.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Iroko wood typically commands a higher price due to its durability and slow growth, making it less available compared to Larch, which is more abundant and grows faster, offering a cost-effective option for posts. Larch posts benefit from widespread availability in temperate regions, driving down costs and ensuring easier procurement for large projects. Market fluctuations often favor Larch for budget-conscious buyers, while Iroko remains a premium choice for long-term investment where access and availability may be limited.
Best Applications: Which Wood Suits Your Project?
Iroko offers excellent durability and resistance to decay, making it ideal for outdoor posts exposed to harsh weather conditions, such as decking supports and garden fencing. Larch is a more affordable option with high strength and natural water resistance, suited for structural posts in pergolas, carports, and landscaping projects. Choosing between Iroko and Larch depends on budget, aesthetic preference, and the specific environmental exposure of the post application.
Infographic: Iroko vs Larch for Post
 azmater.com
azmater.com