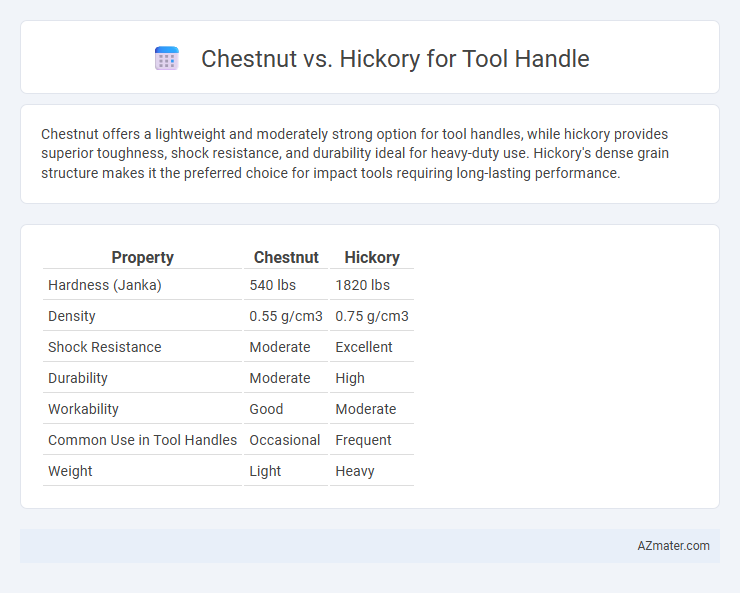
Chestnut offers a lightweight and moderately strong option for tool handles, while hickory provides superior toughness, shock resistance, and durability ideal for heavy-duty use. Hickory's dense grain structure makes it the preferred choice for impact tools requiring long-lasting performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chestnut | Hickory |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 540 lbs | 1820 lbs |
| Density | 0.55 g/cm3 | 0.75 g/cm3 |
| Shock Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Workability | Good | Moderate |
| Common Use in Tool Handles | Occasional | Frequent |
| Weight | Light | Heavy |
Introduction to Wood Choices for Tool Handles
Chestnut and hickory are popular wood choices for tool handles due to their durability and shock resistance. Hickory is renowned for its exceptional strength and flexibility, making it ideal for heavy-duty tools like hammers and axes. Chestnut offers a lighter weight and good workability, favored for tools requiring nimble handling and moderate impact resistance.
Chestnut and Hickory: Overview and Characteristics
Chestnut handles offer moderate strength and lightweight properties, making them suitable for light to medium-duty tools, with natural shock absorption and a fine, straight grain that resists splintering. Hickory, renowned for exceptional toughness, density, and shock resistance, is the preferred choice for heavy-duty tool handles subjected to high impact, such as hammers and axes, due to its superior hardness and flexibility. Both woods provide durability and comfort, but hickory's superior mechanical properties make it the industry standard for demanding applications, while chestnut serves well where lighter weight and moderate strength are sufficient.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Chestnut wood offers moderate strength and durability but tends to be less dense and softer than hickory, making it more prone to dents and wear over time. Hickory is renowned for its exceptional strength, hardness, and shock resistance, often preferred for tool handles requiring high impact endurance. The dense grain structure and superior toughness of hickory provide greater longevity and reliability in demanding applications compared to chestnut.
Shock Absorption: Which Wood Performs Better?
Hickory outperforms chestnut in shock absorption for tool handles due to its dense, fibrous grain structure that effectively dissipates impact forces. Chestnut, while lighter, lacks the same resilience and tends to transmit more vibration to the hand during use. This superior shock absorption makes hickory the preferred choice for hammer, axe, and other heavy-duty tool handles requiring durability and user comfort.
Workability and Machining Differences
Chestnut offers superior workability for tool handles due to its softer grain and lower density, making it easier to shape and sand compared to hickory. Hickory's dense, hard fibers provide greater strength and shock resistance but require more effort and specialized tools during machining to achieve fine detail. The balance between ease of machining and durability makes chestnut ideal for intricate designs, while hickory suits heavy-duty, impact-resistant applications.
Weight and Balance Considerations
Chestnut handles are generally lighter than hickory, offering easier maneuverability but potentially less impact resistance. Hickory's denser grain provides superior strength and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for heavy-duty tool use where balance and durability are critical. Choosing between chestnut and hickory depends on prioritizing lightweight comfort versus robust balance for prolonged handling.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Chestnut offers moderate resistance to moisture and decay, making it a suitable choice for tool handles exposed to occasional damp conditions. Hickory outperforms chestnut with superior natural resistance to moisture absorption and decay, providing enhanced durability in harsh environments. The higher density and tight grain structure of hickory contribute significantly to its longevity and strength in tool handle applications.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Chestnut tool handles tend to be more affordable due to the wood's wider availability and faster growth rate compared to hickory. Hickory, known for its superior strength and shock resistance, often commands a higher price because of limited supply and slower maturation. Market availability for chestnut handles is generally more consistent, while hickory handles may experience fluctuations due to regional supply constraints.
Common Applications in Tool Handles
Chestnut and hickory are both popular choices for tool handles due to their strength and shock resistance, but hickory is favored for high-impact tools like axes and hammers because of its superior toughness and flexibility. Chestnut, while durable and lightweight, is commonly used for handles on lighter hand tools such as rakes and garden hoes where less intensive force is applied. Hickory's dense grain structure also provides enhanced grip and longevity, making it the preferred material in professional-grade and heavy-duty tool handles.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Chestnut and Hickory
Hickory is widely regarded as the superior choice for tool handles due to its exceptional strength, shock resistance, and durability compared to chestnut. Chestnut offers a lighter weight and decent toughness but lacks the consistent density and impact absorption of hickory, which is crucial for heavy-duty tools. For long-term reliability and performance, hickory remains the preferred wood for professional-grade tool handles.
Infographic: Chestnut vs Hickory for Tool Handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com