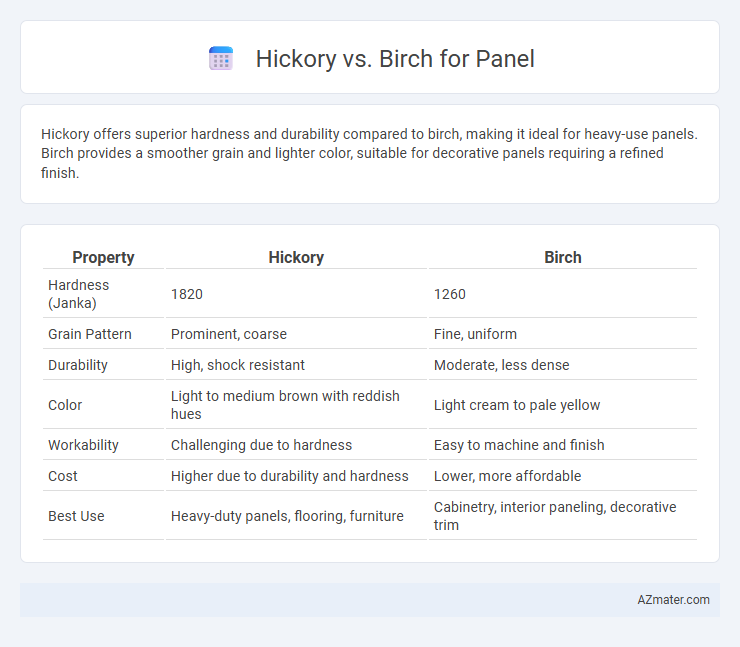
Hickory offers superior hardness and durability compared to birch, making it ideal for heavy-use panels. Birch provides a smoother grain and lighter color, suitable for decorative panels requiring a refined finish.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hickory | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 1820 | 1260 |
| Grain Pattern | Prominent, coarse | Fine, uniform |
| Durability | High, shock resistant | Moderate, less dense |
| Color | Light to medium brown with reddish hues | Light cream to pale yellow |
| Workability | Challenging due to hardness | Easy to machine and finish |
| Cost | Higher due to durability and hardness | Lower, more affordable |
| Best Use | Heavy-duty panels, flooring, furniture | Cabinetry, interior paneling, decorative trim |
Introduction to Hickory and Birch Wood
Hickory wood is renowned for its exceptional hardness, dense grain, and remarkable shock resistance, making it ideal for durable wood paneling that withstands heavy use. Birch wood features a fine, uniform texture and pale color, offering a smooth surface that is easily stained or painted, perfect for creating elegant and consistent wood panels. Both species provide distinct aesthetic and functional advantages, with hickory emphasizing toughness and natural rustic appeal, while birch prioritizes smoothness and versatility in interior applications.
Key Characteristics of Hickory
Hickory wood, known for its exceptional strength and density, offers superior durability compared to birch, making it an ideal choice for heavy-use paneling. Its rich, varied grain patterns and warm tones provide a rustic aesthetic that enhances interior spaces, contrasting with birch's lighter, more uniform appearance. Hickory's high shock resistance and hardness contribute to long-lasting, resilient panels suitable for both decorative and functional applications.
Key Characteristics of Birch
Birch panels are known for their smooth texture, fine grain, and light color that ranges from creamy white to pale yellow, making them ideal for modern and minimalist designs. The wood offers excellent stability and uniformity, reducing warping and making it suitable for intricate paneling and cabinetry. Birch also has good strength and durability, although it is generally softer than hickory, which makes it easier to work with but slightly less resistant to heavy impacts.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Hickory wood features a striking, varied grain pattern with bold streaks and a mix of light to dark brown hues, creating a rustic and dynamic appearance ideal for paneling. Birch offers a smoother, more uniform grain with subtle wavy patterns and a lighter, creamy color palette, promoting a clean and contemporary aesthetic. Choosing between Hickory and Birch for panels depends on whether a bold, textured look or a sleek, consistent finish is desired.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Hickory paneling boasts exceptional durability with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1,820, making it one of the hardest domestic hardwoods ideal for high-traffic areas. Birch panels, while slightly less hard, have a Janka hardness rating around 1,260 and offer moderate strength suitable for decorative applications. Both woods provide reliable stability, but hickory's superior hardness and resistance to wear ensure greater longevity and impact resistance compared to birch.
Workability and Ease of Use
Hickory offers exceptional workability with its dense, tough fibers, making it ideal for heavy-duty panels requiring high durability and impact resistance. Birch provides a smooth, fine grain that enhances ease of use, allowing for precise cuts and a cleaner finish, especially in detailed panel work. Both woods are versatile, but birch is generally preferred for projects needing easier handling and refined aesthetics, while hickory excels in rugged applications.
Cost and Availability
Hickory panels generally come at a higher price point due to their dense grain and durability, making them a premium choice in woodworking. Birch panels are more cost-effective and widely available, often sourced from sustainable plantations, which enhances their accessibility for large-scale projects. The availability of birch in various grades and thicknesses also contributes to its popularity for budget-conscious consumers seeking reliable quality.
Applications in Panel Manufacturing
Hickory offers superior strength and shock resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty panel applications such as cabinetry and furniture that require durability. Birch provides a smooth, fine grain that is favored in decorative panels and veneers, enhancing aesthetic appeal in interior design and laminates. Manufacturers often select hickory for structural panels and birch for high-quality, visually sensitive surfaces to balance robustness with elegant finishes.
Pros and Cons: Hickory vs Birch Panels
Hickory panels offer exceptional durability and a distinctive grain pattern, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and rustic designs, but they tend to be harder to work with and more expensive than birch. Birch panels provide a smooth, consistent grain and are easier to stain or paint, which makes them versatile and budget-friendly, although they are less resistant to dents and scratches compared to hickory. Both materials have excellent strength, but hickory's hardness rating of 1820 Janka surpasses birch's 1260, influencing their wear resistance and maintenance requirements.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Hickory offers superior durability and shock resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy-use projects, while birch excels with its smooth grain and consistent texture, perfect for refined finishes and cabinetry. Birch's lighter color allows for versatile staining options, whereas hickory's natural variation provides a unique, rustic appearance. Selecting the right wood depends on project demands: prioritize hickory for strength and impact resistance, or birch for a polished, uniform look.
Infographic: Hickory vs Birch for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com