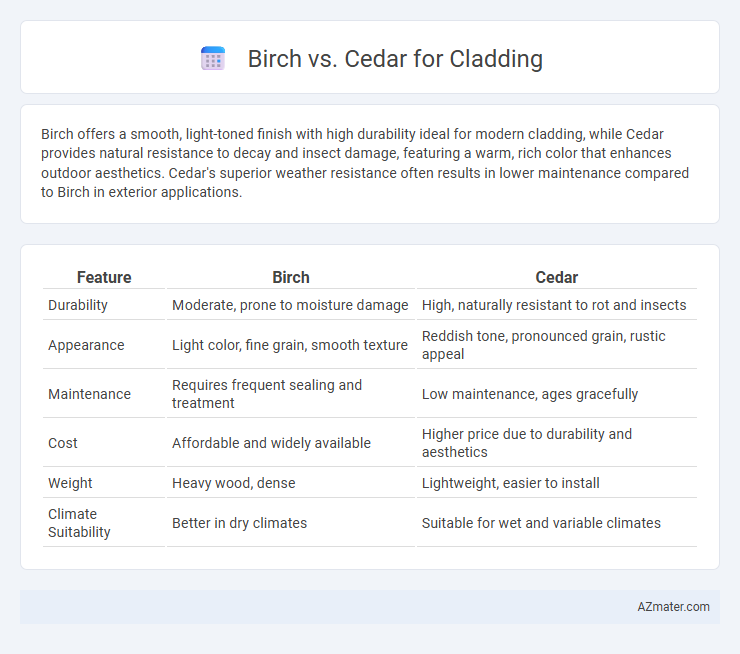
Birch offers a smooth, light-toned finish with high durability ideal for modern cladding, while Cedar provides natural resistance to decay and insect damage, featuring a warm, rich color that enhances outdoor aesthetics. Cedar's superior weather resistance often results in lower maintenance compared to Birch in exterior applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Birch | Cedar |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, prone to moisture damage | High, naturally resistant to rot and insects |
| Appearance | Light color, fine grain, smooth texture | Reddish tone, pronounced grain, rustic appeal |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent sealing and treatment | Low maintenance, ages gracefully |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | Higher price due to durability and aesthetics |
| Weight | Heavy wood, dense | Lightweight, easier to install |
| Climate Suitability | Better in dry climates | Suitable for wet and variable climates |
Introduction to Birch and Cedar Cladding
Birch cladding offers a smooth texture and pale color, making it a popular choice for modern and minimalist designs, while cedar cladding is valued for its rich reddish hue and natural resistance to decay and insects. Both woods provide excellent insulation and durability, but cedar's natural oils enhance longevity in outdoor applications. Choosing between birch and cedar depends on the desired aesthetic, climate conditions, and maintenance preferences.
Appearance and Aesthetic Differences
Birch cladding offers a light, smooth surface with a fine grain that creates a clean and modern aesthetic, while cedar features a richer, reddish hue with a pronounced grain pattern that adds warmth and rustic charm. Birch tends to present a more uniform and subtle appearance, enhancing contemporary designs, whereas cedar's natural knots and color variations contribute to a textured, natural look preferred in traditional or craftsman-style architecture. The choice between birch and cedar impacts the visual style, with birch suited for sleek, minimalist facades and cedar favored for inviting, organic exteriors.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Birch cladding offers a smooth finish but generally exhibits lower natural durability and a shorter lifespan compared to cedar, typically lasting around 10-15 years with proper maintenance. Cedar is highly valued for its natural resistance to decay, insects, and moisture, often enduring 20-30 years or more without significant deterioration. The superior longevity and resilience of cedar make it a preferred choice for exterior cladding in rugged or humid environments.
Weather Resistance and Climate Suitability
Birch cladding offers moderate weather resistance but performs best in dry, temperate climates due to its lower natural durability against moisture and decay. Cedar excels in weather resistance with high natural oils that repel water, insects, and fungi, making it ideal for humid or rainy climates. Choosing cedar for cladding provides superior longevity and protection in harsh, variable weather conditions compared to birch.
Maintenance Requirements for Birch vs Cedar
Birch cladding demands more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to moisture damage and fading, requiring regular sealing and staining to preserve its appearance. Cedar offers superior natural resistance to rot, insects, and weathering, leading to lower maintenance needs and longer intervals between treatments. Wood preservatives and periodic cleaning are essential for both, but cedar's durability makes it a preferred choice for reduced upkeep in exterior cladding.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Birch cladding offers moderate insulation properties with a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.11-0.13 W/m*K, providing decent energy efficiency for residential buildings. Cedar, known for its natural oils and cellular structure, boasts better insulation value with thermal conductivity around 0.08-0.10 W/m*K, contributing to superior energy retention and reduced heating costs. Choosing cedar cladding enhances building envelope performance by minimizing thermal bridging and improving overall energy efficiency compared to birch.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Birch offers a fast-growing, renewable resource with lower environmental impact due to its shorter harvesting cycle compared to cedar, which takes decades to mature. Cedar naturally contains oils that resist decay and insects, reducing the need for chemical treatments that can harm ecosystems. Choosing sustainably sourced birch or cedar certified by organizations like FSC ensures responsible forestry practices, minimizing deforestation and promoting biodiversity.
Cost Analysis: Birch vs Cedar
Birch cladding typically offers a lower initial cost compared to cedar, making it a budget-friendly option for many construction projects. Cedar, while more expensive upfront, provides superior natural resistance to decay and insects, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and lifespan, is crucial when choosing between birch and cedar for cladding.
Installation Process and Considerations
Birch cladding requires careful sealing and priming due to its porous nature, ensuring moisture resistance and preventing warping during installation, while Cedar offers natural rot resistance and dimensional stability, making it easier to install without extensive pretreatment. Both materials demand precise fastening techniques to accommodate wood expansion and contraction, with Birch needing more frequent maintenance to preserve appearance and durability. Selecting the appropriate fasteners and allowing for adequate ventilation behind the cladding are crucial considerations to extend the lifespan of either Birch or Cedar siding.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Birch cladding excels in interior applications due to its smooth texture and light color, making it ideal for modern and Scandinavian-style interiors. Cedar cladding offers superior durability and natural resistance to rot and insects, making it the best choice for exterior siding and outdoor structures in harsh weather conditions. Both woods perform well when treated, with birch preferred for aesthetic indoor projects and cedar favored for long-lasting outdoor cladding solutions.
Infographic: Birch vs Cedar for Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com