Eucalyptus veneer offers a sustainable, lightweight option with fine, uniform grain ideal for eco-friendly furniture, while walnut veneer provides rich, dark color and distinctive grain patterns suited for high-end, durable cabinetry. Choosing between eucalyptus and walnut veneers depends on the desired aesthetic, durability, and environmental impact of the project.
Table of Comparison
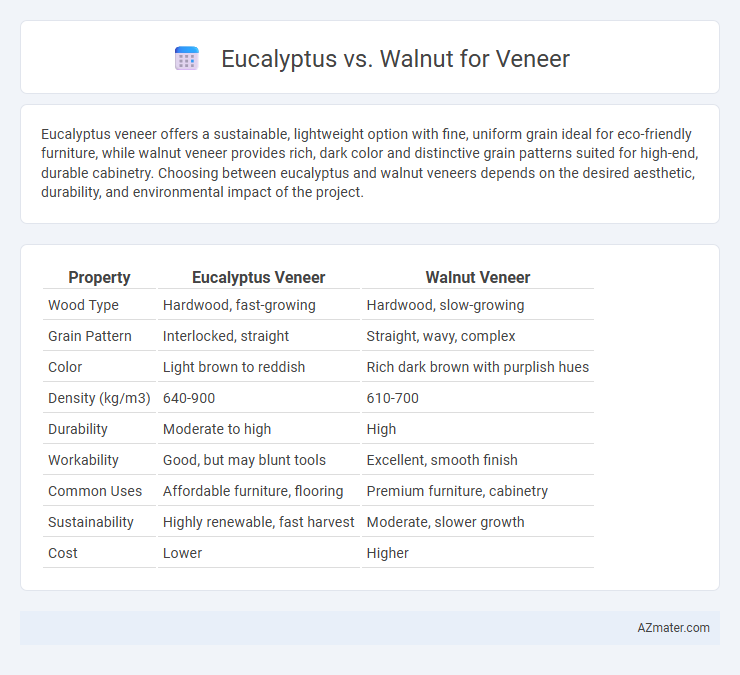
| Property | Eucalyptus Veneer | Walnut Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood, fast-growing | Hardwood, slow-growing |
| Grain Pattern | Interlocked, straight | Straight, wavy, complex |
| Color | Light brown to reddish | Rich dark brown with purplish hues |
| Density (kg/m3) | 640-900 | 610-700 |
| Durability | Moderate to high | High |
| Workability | Good, but may blunt tools | Excellent, smooth finish |
| Common Uses | Affordable furniture, flooring | Premium furniture, cabinetry |
| Sustainability | Highly renewable, fast harvest | Moderate, slower growth |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Overview of Eucalyptus and Walnut Veneers
Eucalyptus veneer is prized for its durability, fine grain, and warm honey-brown tones, making it suitable for modern and rustic furniture designs. Walnut veneer offers rich, deep brown hues with a smooth, straight grain pattern, favored for high-end cabinetry and classic woodwork. Both veneers provide excellent workability, but walnut is generally considered more luxurious due to its refined appearance and natural luster.
Botanical Differences: Eucalyptus vs Walnut
Eucalyptus, belonging to the Myrtaceae family, features fast-growing evergreen trees native primarily to Australia, characterized by smooth bark and long, narrow leaves with aromatic oils. Walnut trees, part of the Juglandaceae family, are deciduous hardwoods known for their compound leaves and large, round nuts, native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The botanical distinctions between Eucalyptus and Walnut influence their wood grain, density, and coloration, with Eucalyptus offering a lighter, varied grain and Walnut providing a darker, rich-toned veneer prized for fine furniture.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Eucalyptus veneer exhibits a smooth, fine texture with a consistent grain pattern, often showcasing warm, rich tones ranging from golden to deep brown hues. Walnut veneer is prized for its striking, varied grain patterns with dramatic curls, swirls, and straight lines, presenting a rich, chocolate-brown color that deepens over time. The distinct appearance and grain complexity of walnut make it a premium choice for high-end furniture, while eucalyptus offers a more uniform and versatile look suited for contemporary designs.
Color Variations and Finish Options
Eucalyptus veneer offers a warm, golden to reddish-brown color palette with subtle grain patterns, making it suitable for contemporary and rustic finishes, while Walnut veneer boasts rich, deep brown tones with purples and grays that enhance traditional and luxurious aesthetics. Eucalyptus finishes often include clear coats and natural oils that highlight its smooth texture, whereas Walnut veneer supports a broader range of finishes such as matte, satin, and high-gloss, thanks to its dense grain structure. Color variations in Walnut tend to be more pronounced, providing striking contrasts ideal for statement pieces, whereas Eucalyptus offers more uniformity for consistent design themes.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Walnut veneer offers superior durability and hardness, with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1010, making it highly resistant to dents and wear, ideal for high-traffic areas. Eucalyptus veneer, with a Janka hardness around 1190, provides excellent hardness and durability, slightly surpassing walnut in strength but often used for cost-effective and sustainable options. Both veneers deliver strong performance, but eucalyptus is favored for its environmental benefits, while walnut is preferred for its rich appearance and lasting resilience.
Workability and Cutting Characteristics
Eucalyptus veneer offers excellent workability with good cutting characteristics due to its uniform grain and moderate density, making it easy to machine and shape without splintering. Walnut veneer, known for its rich color and fine texture, presents a slightly higher density, requiring sharper blades and slower cutting speeds to avoid tear-out but yields a smooth finish. Both veneers respond well to sanding and finishing, but eucalyptus provides a more forgiving surface during intricate cuts, making it preferable for detailed veneer work.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Eucalyptus veneer outperforms walnut in sustainability due to its rapid growth rate and ability to thrive in diverse climates, resulting in lower carbon emissions and faster reforestation cycles. Walnut, while prized for its rich aesthetic, typically requires longer maturation periods and is often sourced from slower-growing hardwood forests, which can contribute to habitat disruption and higher ecological footprints. Using eucalyptus veneer supports environmental conservation by promoting renewable forestry practices and reducing deforestation pressures associated with traditional hardwood harvesting.
Common Applications in Interior Design
Eucalyptus veneer is widely used in contemporary interior design for its durability and warm, reddish-brown tones that complement modern and rustic styles. Walnut veneer, prized for its rich, dark grain and smooth texture, is often applied in high-end furniture, cabinetry, and wall paneling to create luxurious and classic aesthetics. Both veneers offer versatile applications but differ in cost and visual impact, making them suitable for distinct design themes and budgets.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Eucalyptus veneer offers superior cost efficiency compared to walnut, with eucalyptus wood generally priced 30% to 50% lower, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale projects. Walnut veneer excels in market availability within premium furniture and cabinetry sectors, often commanding higher prices due to its rich grain patterns and durability. Eucalyptus is widely accessible across Europe, South America, and Australia, while walnut is predominantly sourced from North America and Europe, impacting regional market dynamics and procurement costs.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Eucalyptus or Walnut
Eucalyptus veneer offers a cost-effective, sustainable option with a light, uniform grain ideal for modern, minimalist designs, while walnut veneer provides a rich, dark color and intricate grain patterns favored in luxury furniture and classic interiors. Selecting between eucalyptus and walnut veneers depends on the desired aesthetic, budget, and project durability requirements, as walnut is generally harder and more durable than eucalyptus. Considering factors such as wood hardness (Janka hardness of approximately 1010 for eucalyptus vs 1638 for walnut), grain appearance, and environmental impact will guide the perfect veneer choice.
Infographic: Eucalyptus vs Walnut for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com