Douglas fir plywood offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for structural applications, while birch plywood provides a smooth surface with excellent sanding and finishing qualities, preferred for furniture and cabinetry. Douglas fir's natural resistance to moisture and decay contrasts with birch's higher density and fine grain for aesthetic appeal.
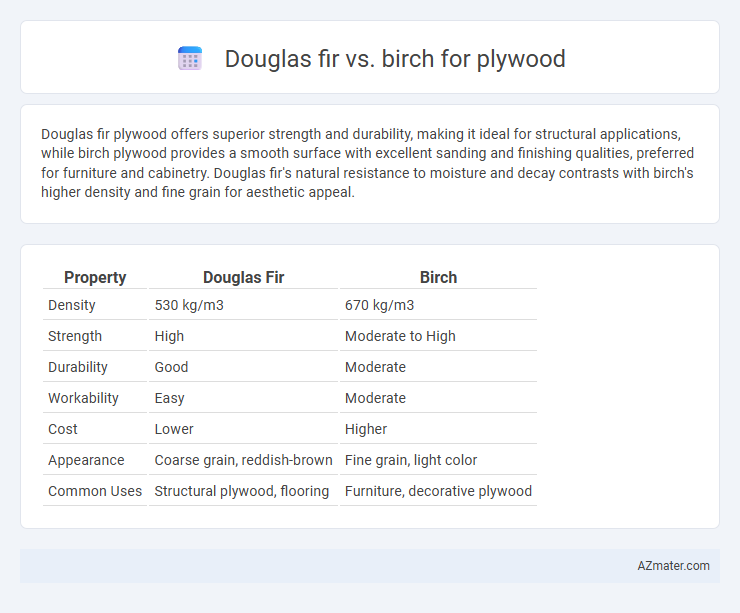
Table of Comparison
| Property | Douglas Fir | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 530 kg/m3 | 670 kg/m3 |
| Strength | High | Moderate to High |
| Durability | Good | Moderate |
| Workability | Easy | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Appearance | Coarse grain, reddish-brown | Fine grain, light color |
| Common Uses | Structural plywood, flooring | Furniture, decorative plywood |
Introduction to Douglas Fir and Birch Plywood
Douglas fir plywood is renowned for its exceptional strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to warping, making it ideal for construction and structural applications. Birch plywood offers a smooth, uniform surface with fine grain and excellent durability, preferred in furniture-making and decorative applications. Both types provide reliable performance, but Douglas fir excels in load-bearing projects, while birch is favored for its aesthetics and workability.
Wood Characteristics: Douglas Fir vs Birch
Douglas fir plywood is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for structural applications and high-load environments. Birch plywood offers a smooth surface, fine grain, and excellent sanding properties, preferred for furniture, cabinetry, and decorative uses due to its aesthetic appeal. Both woods provide stability, but Douglas fir tends to have higher impact resistance while birch excels in uniformity and finish quality.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Douglas fir plywood exhibits superior strength and durability compared to birch plywood, making it ideal for structural applications that require high load-bearing capacity. The dense grain and natural resistance of Douglas fir contribute to enhanced impact resistance and longevity in outdoor or heavy-use environments. Birch plywood, while offering a smooth finish and good dimensional stability, generally ranks lower in strength and is better suited for interior furniture and decorative purposes.
Aesthetic Differences: Grain and Color
Douglas fir plywood features a straight, tight grain with a reddish-brown hue that darkens over time, providing a warm, rustic appearance ideal for traditional and cabin-style interiors. Birch plywood exhibits a finer, uniform grain with a lighter, creamy-yellow color, offering a smooth, clean look suited for modern or Scandinavian designs. These aesthetic differences influence the choice based on desired ambiance and finish compatibility in woodworking projects.
Workability and Machining Properties
Douglas fir plywood offers excellent workability with smooth cutting and nailing characteristics, making it ideal for construction and structural applications. Birch plywood exhibits superior machining properties, providing clean edges and smooth surfaces, which are favored in fine woodworking and cabinetry. Both woods balance strength and ease of handling, but birch generally yields a more refined finish due to its tight grain structure.
Cost and Availability
Douglas fir plywood is generally more cost-effective due to its widespread availability and fast growth in North America, making it a popular choice for construction and industrial applications. Birch plywood, while offering superior strength and a smoother finish, typically carries a higher price tag due to limited supply and higher processing costs. Both woods are readily available, but Douglas fir's abundance ensures lower overall expenses and easier procurement.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Douglas fir plywood offers superior sustainability due to the species' fast growth rate and efficient land use, resulting in a lower carbon footprint compared to birch. Birch plywood, while durable, often comes from slower-growing trees, which may contribute to higher environmental impact and less renewable sourcing. Certification standards such as FSC and PEFC can help ensure both types meet sustainable forestry practices, but Douglas fir generally aligns better with eco-friendly construction goals.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Plywood
Douglas fir plywood excels in structural applications such as flooring, roofing, and framing due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and natural resistance to decay. Birch plywood offers a smooth, fine grain ideal for cabinetry, furniture, and interior paneling where aesthetics and a uniform surface are priorities. Selecting the right plywood depends on the intended use: Douglas fir is preferred for durability and load-bearing tasks, while birch is favored for detailed craftsmanship and visual appeal.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Douglas fir plywood offers superior resistance to moisture and decay compared to birch, making it a preferred choice for exterior and structural applications where durability is critical. Its natural oils and dense grain structure enhance its ability to withstand wet environments and inhibit fungal growth. Birch plywood, while strong and smooth, is more susceptible to moisture absorption and requires additional treatments for exterior use to improve its decay resistance.
Conclusion: Which Plywood is Better?
Douglas fir plywood offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to birch plywood, making it ideal for structural applications and outdoor use. Birch plywood is valued for its smooth surface, fine grain, and aesthetic appeal, often preferred for furniture and interior projects. For construction projects requiring robustness and weather resistance, Douglas fir plywood is the better choice, while birch excels in decorative and indoor applications.
Infographic: Douglas fir vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com