Cedar plywood offers superior natural resistance to rot and insects, making it ideal for outdoor applications, while birch plywood provides greater strength and a smooth, hard surface that excels in cabinetry and furniture making. Birch is more cost-effective and easier to stain, whereas cedar's aromatic quality enhances aesthetic appeal and durability in moist environments.
Table of Comparison
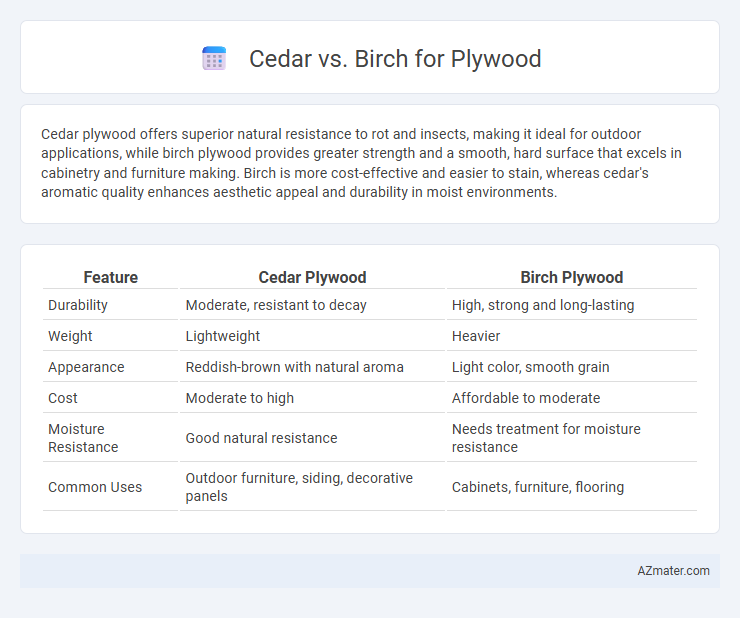
| Feature | Cedar Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to decay | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown with natural aroma | Light color, smooth grain |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable to moderate |
| Moisture Resistance | Good natural resistance | Needs treatment for moisture resistance |
| Common Uses | Outdoor furniture, siding, decorative panels | Cabinets, furniture, flooring |
Introduction to Cedar and Birch Plywood
Cedar plywood is renowned for its natural resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage, making it highly suitable for outdoor and marine applications. Birch plywood offers a smooth, fine grain with excellent strength and durability, often used in furniture and cabinetry where a clean finish is essential. Both types provide unique benefits, with cedar excelling in weather resistance and birch favored for structural stability and aesthetic versatility.
Key Characteristics of Cedar Plywood
Cedar plywood is renowned for its natural resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage, making it an ideal choice for outdoor and humid environment applications. The wood features a fine, straight grain with a smooth texture, providing excellent dimensional stability and a visually appealing, warm reddish-brown hue. Its lightweight nature and workability offer enhanced ease of handling and fabrication compared to birch plywood, which tends to be heavier and denser.
Key Characteristics of Birch Plywood
Birch plywood is known for its exceptional strength, smooth surface, and uniform grain, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry where a refined finish is essential. Compared to cedar, birch plywood offers superior durability and resistance to cracking and warping, contributing to its preference in structural applications. Its pale color and fine texture also allow for superior paint and stain adhesion, enhancing aesthetic versatility in design projects.
Durability Comparison: Cedar vs Birch
Birch plywood offers superior durability compared to cedar plywood due to its dense hardwood composition, making it more resistant to impact, wear, and deformation. Cedar plywood, while naturally resistant to rot and insect damage because of its aromatic oils, tends to be softer and less durable under heavy load or frequent use. For projects requiring long-term strength and resistance to physical stress, birch plywood is the preferred choice, whereas cedar excels in outdoor applications where moisture resistance is critical.
Appearance and Aesthetics
Cedar plywood features a warm, rich reddish-brown hue with distinctive knots and a straight grain pattern, making it ideal for rustic and natural design aesthetics. Birch plywood offers a lighter, creamy color with a smooth, even grain that provides a clean, modern look suitable for contemporary furniture and cabinetry. Both woods allow for versatile finishing options, but cedar's unique texture enhances character, while birch delivers consistent elegance.
Workability and Ease of Use
Cedar plywood offers excellent workability due to its lightweight and soft texture, making it easy to cut, shape, and sand with minimal effort. Birch plywood is denser and harder, which provides superior strength and durability but requires sharper tools and more effort during cutting and sanding. Both woods are suitable for various applications, but cedar is preferred for projects needing easier handling, while birch excels where structural integrity is critical.
Cost Differences: Cedar vs Birch
Cedar plywood generally costs more than birch due to its natural resistance to decay and moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Birch plywood is more affordable and favored for indoor use because of its smooth surface and durability. The price gap varies by grade and thickness, with cedar often commanding a premium for specialty exterior grades.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cedar plywood is often considered more sustainable due to cedar trees' natural resistance to decay, requiring fewer chemical treatments and resulting in a lower environmental footprint. Birch plywood, sourced primarily from fast-growing, responsibly managed forests, offers good sustainability when certified by organizations like FSC or PEFC. Both materials benefit from sustainable forestry practices, but cedar's durability can extend the lifespan of plywood products, potentially reducing resource consumption over time.
Ideal Applications for Cedar Plywood
Cedar plywood is ideal for outdoor applications such as siding, decking, and garden furniture due to its natural resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage. Its lightweight, stable structure combined with aromatic oils makes it perfect for use in humid environments and exterior projects where durability and weather resistance are essential. Unlike birch plywood, which excels in interior use and furniture making due to its smooth finish and strength, cedar plywood offers superior performance for exterior construction and decorative outdoor features.
Ideal Applications for Birch Plywood
Birch plywood is favored for applications requiring high strength, durability, and a smooth, clean finish, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and interior paneling. Its fine grain and light color allow for easy staining and painting, enhancing aesthetic flexibility in design projects. Compared to cedar plywood, birch offers superior structural integrity, making it suitable for load-bearing uses and precision woodworking.
Infographic: Cedar vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com