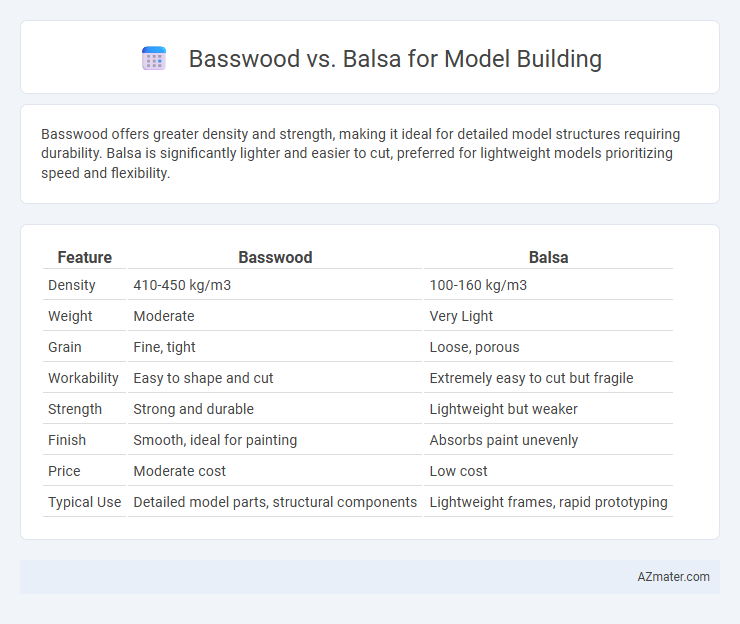
Basswood offers greater density and strength, making it ideal for detailed model structures requiring durability. Balsa is significantly lighter and easier to cut, preferred for lightweight models prioritizing speed and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Basswood | Balsa |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 410-450 kg/m3 | 100-160 kg/m3 |
| Weight | Moderate | Very Light |
| Grain | Fine, tight | Loose, porous |
| Workability | Easy to shape and cut | Extremely easy to cut but fragile |
| Strength | Strong and durable | Lightweight but weaker |
| Finish | Smooth, ideal for painting | Absorbs paint unevenly |
| Price | Moderate cost | Low cost |
| Typical Use | Detailed model parts, structural components | Lightweight frames, rapid prototyping |
Introduction to Model Building Woods
Basswood and balsa are the two most popular woods for model building due to their lightweight and workability. Basswood offers a fine, even grain that makes it ideal for intricate detailing and smooth finishes, while balsa is renowned for its exceptional lightness and ease of cutting. Model builders often choose basswood for structural stability and balsa for rapid prototyping and lightweight structures.
Overview of Basswood
Basswood is a popular choice in model building due to its fine, even texture and lightweight yet durable nature, making it ideal for detailed carving and structural elements. It offers a balanced strength-to-weight ratio, allowing model makers to create sturdy frameworks without adding excessive weight. This hardwood also sands smoothly and accepts glue and paint well, enhancing the overall finish and precision of model projects.
Overview of Balsa Wood
Balsa wood, known for its exceptional lightness and softness, is a preferred material in model building for creating lightweight structures with ease of shaping and cutting. Its low density allows for excellent buoyancy and enhances the aerodynamic performance of model airplanes and boats. While less dense and softer than basswood, balsa offers superior shock absorption, making it ideal for delicate model parts requiring flexibility and cushioning.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Basswood offers greater strength and durability compared to balsa, making it ideal for model building projects requiring structural integrity. Its dense grain provides resistance to dents and breakage, while balsa's lightweight, softer texture prioritizes ease of cutting over toughness. For models subjected to handling or stress, basswood ensures longer-lasting performance and stability.
Weight and Density Differences
Basswood features a density of approximately 22-30 pounds per cubic foot, making it heavier and denser compared to balsa, which typically has a density of 7-10 pounds per cubic foot. The higher density of basswood provides greater strength and durability, ideal for structural components in models requiring robustness. Balsa's lightweight and low density make it the preferred choice for projects demanding maximum weight reduction and ease of shaping.
Workability and Ease of Cutting
Basswood offers superior workability with a fine, even grain that resists splintering, making it easy to cut and shape precisely for detailed model building. Balsa is exceptionally lightweight and soft, allowing for rapid cutting and sanding, which benefits quick prototyping but may result in less structural stability. Model builders often prefer basswood for intricate parts due to its stiffness, while balsa is favored for larger, lightweight components.
Availability and Cost Analysis
Basswood offers widespread availability and a moderate price range, making it a popular choice for model builders seeking a balance between quality and affordability. Balsa wood, known for its extremely lightweight properties, tends to be more expensive and less readily available in some regions, which can impact budget considerations. Cost analysis reveals that while balsa's low density benefits detailed, delicate structures, basswood provides a sturdier, cost-effective alternative with easier accessibility in most craft stores.
Best Applications for Basswood
Basswood is ideal for model building that requires detailed carving and fine sanding due to its soft yet strong grain, making it perfect for architectural models and intricate miniatures. Its consistent texture and resistance to warping provide stability for precise cuts and glue joints in advanced hobby projects. Compared to balsa, basswood offers greater durability and weight, making it suitable for structural elements and components requiring more strength.
Ideal Uses for Balsa in Models
Balsa wood is ideal for lightweight model building due to its exceptional softness and low density, making it easy to cut, shape, and sand with precision tools. It is preferred for aerodynamic structures like model airplanes and gliders where minimal weight is crucial for optimal flight performance. Balsa's flexibility and shock-absorbent properties also enhance its use in detailed architectural models and scale replicas that require intricate craftsmanship.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Basswood offers a fine, smooth grain and moderate hardness, making it ideal for detailed carving and structural components in model building, while balsa's ultra-lightweight and soft texture provide ease of cutting and shaping for delicate parts. Selecting basswood is preferable for durability and stiffness in frameworks, whereas balsa suits prototypes and models requiring minimal weight. Consider project demands like precision, strength, and weight balance to determine the optimal wood choice.
Infographic: Basswood vs Balsa for Model Building
 azmater.com
azmater.com