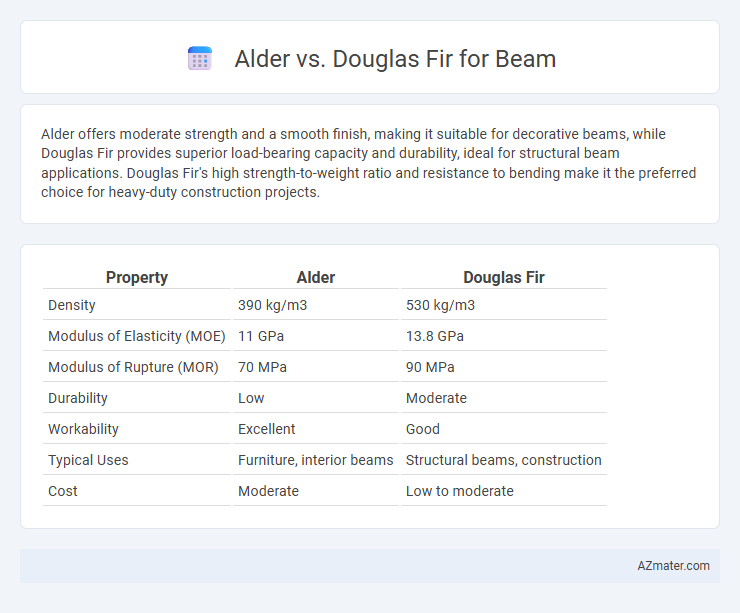
Alder offers moderate strength and a smooth finish, making it suitable for decorative beams, while Douglas Fir provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability, ideal for structural beam applications. Douglas Fir's high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to bending make it the preferred choice for heavy-duty construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alder | Douglas Fir |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 390 kg/m3 | 530 kg/m3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (MOE) | 11 GPa | 13.8 GPa |
| Modulus of Rupture (MOR) | 70 MPa | 90 MPa |
| Durability | Low | Moderate |
| Workability | Excellent | Good |
| Typical Uses | Furniture, interior beams | Structural beams, construction |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Alder and Douglas Fir Beams
Alder beams provide a smooth, consistent grain ideal for interior architectural applications, offering moderate strength and workability. Douglas fir beams are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to warping, making them a preferred choice for structural supports. Both species serve distinct purposes, with alder favored for aesthetic finishes and Douglas fir prized in heavy-duty load-bearing construction.
Key Differences in Wood Characteristics
Alder wood is known for its uniform, fine grain and softer texture, making it easier to work with but less durable compared to Douglas Fir, which boasts a stronger, denser structure ideal for heavy load-bearing beams. Douglas Fir's high strength-to-weight ratio and superior stiffness provide excellent resistance to bending and warping, essential for structural applications. In contrast, Alder tends to have a lower modulus of elasticity and is more susceptible to dents and scratches, limiting its use in construction where long-lasting performance is critical.
Strength and Structural Performance
Douglas Fir beams offer superior strength and structural performance compared to Alder, making them ideal for load-bearing applications in construction. With a higher modulus of elasticity and greater bending strength, Douglas Fir provides enhanced durability and resistance to deformation under heavy loads. Alder beams, while softer and less dense, are better suited for non-structural or decorative purposes due to their lower mechanical properties.
Durability and Longevity
Douglas Fir beams offer superior durability and longevity compared to Alder due to their dense grain structure and natural resistance to decay and insect damage, making them ideal for structural applications. Alder is softer and more prone to wear, which limits its lifespan when used as beams, especially in outdoor or high-stress environments. For long-lasting beams that maintain integrity under heavy loads, Douglas Fir is the preferred choice.
Workability and Ease of Construction
Alder offers excellent workability due to its softer texture and uniform grain, making it easier to cut, shape, and sand compared to Douglas Fir. Douglas Fir, while stronger and more durable, can be more challenging to work with because of its dense, resinous wood that dulls tools faster. For ease of construction, Alder is preferred in projects requiring intricate detailing, whereas Douglas Fir is chosen for structural beams where strength demands take priority.
Aesthetic Qualities and Appearance
Alder beams exhibit a warm, reddish-brown hue with a fine, consistent grain, providing a smooth and elegant appearance ideal for interior design. Douglas Fir beams boast a stronger yellowish to reddish tone with pronounced, straight grain patterns that enhance rustic and natural settings. Both woods offer unique aesthetic qualities, with Alder favored for refined, polished looks and Douglas Fir for robust, character-rich environments.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Alder beams generally cost less than Douglas fir, making them a budget-friendly option for construction projects. Douglas fir is more widely available in North America, especially in the Pacific Northwest, resulting in steady supply and competitive pricing. While Alder is less abundant and may have longer lead times, its lower price can offset availability challenges in some markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alder wood is considered more sustainable than Douglas Fir due to its faster growth rate and ability to regenerate quickly after harvesting, reducing environmental impact. Douglas Fir, while stronger and more durable for beams, often comes from older, slower-growing trees, leading to higher carbon sequestration but also greater deforestation concerns if not sourced responsibly. Choosing FSC-certified Alder or Douglas Fir ensures responsible forest management, minimizing ecological footprint while supporting sustainable construction practices.
Common Applications in Construction
Douglas Fir is commonly used for structural beams in residential and commercial construction due to its exceptional strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability. Alder, while less strong, is often applied in interior beams or decorative elements where aesthetics and ease of machining are prioritized over load-bearing capacity. The superior load-bearing properties of Douglas Fir make it the preferred choice in heavy framing and support structures.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Beam Project
Alder wood offers a smooth grain and medium strength, making it ideal for lightweight beams in interior applications where aesthetics matter. Douglas Fir provides superior strength, stiffness, and durability, suitable for load-bearing beams in structural projects exposed to varying conditions. Selecting Douglas Fir ensures resilience and support, while Alder excels in decorative, non-structural beam installations.
Infographic: Alder vs Douglas Fir for Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com