Elm offers a flexible and shock-resistant handle material ideal for tools requiring vibration absorption. Hickory provides superior strength and durability, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty tool handles.
Table of Comparison
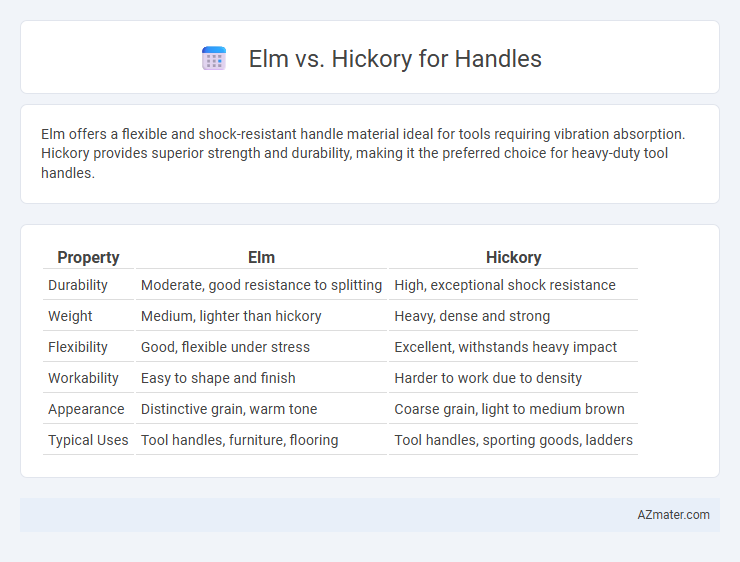
| Property | Elm | Hickory |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, good resistance to splitting | High, exceptional shock resistance |
| Weight | Medium, lighter than hickory | Heavy, dense and strong |
| Flexibility | Good, flexible under stress | Excellent, withstands heavy impact |
| Workability | Easy to shape and finish | Harder to work due to density |
| Appearance | Distinctive grain, warm tone | Coarse grain, light to medium brown |
| Typical Uses | Tool handles, furniture, flooring | Tool handles, sporting goods, ladders |
Introduction to Handle Materials: Elm vs Hickory
Elm handles offer natural resistance to splitting and excellent shock absorption, making them ideal for tools subject to heavy impacts. Hickory handles are renowned for superior strength, flexibility, and durability, often preferred for axes and hammers due to their high tensile strength. Selecting between elm and hickory hinges on balancing elasticity with ruggedness to optimize tool performance and longevity.
Key Characteristics of Elm Wood
Elm wood features interlocking grain that offers exceptional resistance to splitting, making it ideal for tool handles subjected to lateral stress. Its moderate density provides a balance of strength and flexibility, ensuring durability without excessive weight. The natural shock-absorbing properties of elm enhance its performance in handles, especially under repetitive impact.
Distinct Features of Hickory Wood
Hickory wood is distinguished by its exceptional hardness, density, and shock resistance, making it ideal for tool handles that require durability and strength. Its coarse, pronounced grain pattern offers a rugged texture and superior grip compared to smoother woods like elm. Hickory's natural resilience to impact and wear outperforms elm, which is softer and more prone to denting or breaking under heavy usage.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Elm handles offer excellent strength due to their interlocking grain structure, providing natural resistance to splitting and impact. Hickory is renowned for its superior toughness and shock absorption, making it highly durable under heavy use and repeated stress. While elm excels in flexibility and resilience, hickory's strength and hardness make it the preferred choice for demanding tool handles requiring long-lasting durability.
Flexibility and Shock Absorption
Elm handles offer excellent flexibility due to their interlocking grain structure, making them resistant to splitting and ideal for tools requiring durability under stress. Hickory excels in shock absorption, with its dense, strong fibers providing superior impact resistance, which reduces vibration and user fatigue during extended use. Hickory's combination of toughness and resilience often makes it the preferred choice for tool handles demanding both comfort and long-lasting performance.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Elm demonstrates superior resistance to moisture and decay compared to hickory, making it a preferred choice for handle materials exposed to damp conditions. Hickory, while exceptionally strong and impact-resistant, tends to absorb moisture more readily, increasing its susceptibility to rot and degradation over time. Elm's interlocking grain structure enhances its durability against environmental stress, ensuring longer-lasting performance in moist or outdoor settings.
Weight and Balance for Tool Handles
Elm wood offers a balanced weight that provides moderate heft for tool handles, enhancing control without causing fatigue during extended use. Hickory is denser and heavier, which improves durability and shock absorption, but can lead to quicker user fatigue if the tool is used intensively. For optimal tool performance, hickory handles are preferred in heavy-duty applications requiring strength and resilience, while elm handles suit tasks benefiting from lighter weight and improved maneuverability.
Workability: Shaping and Finishing
Elm offers excellent workability for handles, featuring a coarse but interlocked grain that provides durability while still allowing for smooth shaping and finishing with basic hand tools. Hickory is highly favored for its superior workability due to a dense, straight grain structure that responds well to both shaping and fine sanding, resulting in a strong, comfortable grip. Both woods excel in handle applications, but hickory's ease of finishing and resistance to splitting often make it the preferred choice for high-impact tools.
Cost and Availability
Hickory handles generally cost more than elm due to their superior strength and durability, making them preferred for heavy-duty tools but less budget-friendly. Elm wood is more readily available and offers a balance of toughness and flexibility at a lower price point, common in mid-range tool handles. Availability of both woods varies regionally, with elm being more abundant in North America, while hickory is widely sourced from both North America and Europe, affecting their market pricing and accessibility.
Choosing the Best Wood for Your Handle
Elm offers superior shock resistance and natural grip due to its interlocking grain, making it ideal for handles that require durability and comfort. Hickory stands out for its exceptional strength and flexibility, providing excellent impact absorption and longevity under heavy use. When choosing the best wood for your handle, prioritize elm for ergonomic comfort and hickory for rugged durability and resilience.
Infographic: Elm vs Hickory for Handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com