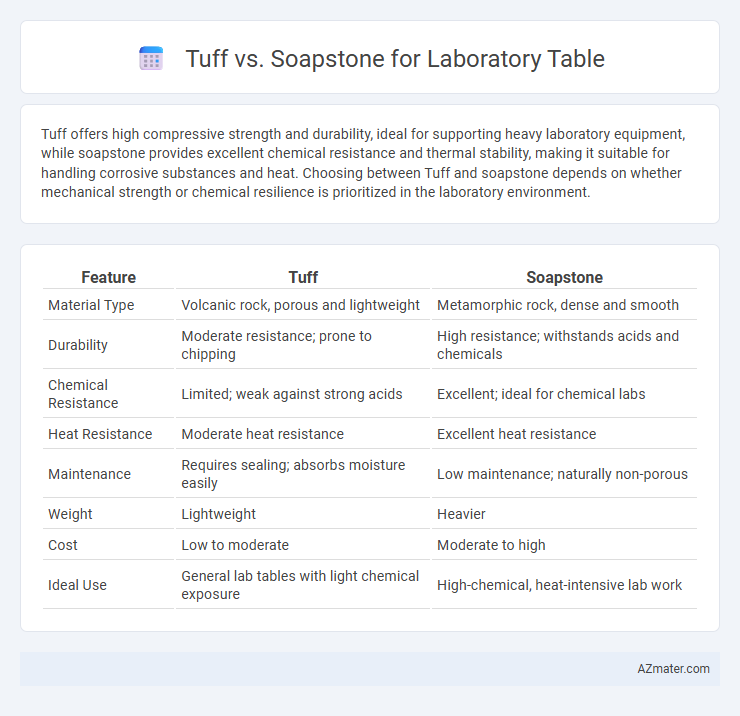
Tuff offers high compressive strength and durability, ideal for supporting heavy laboratory equipment, while soapstone provides excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for handling corrosive substances and heat. Choosing between Tuff and soapstone depends on whether mechanical strength or chemical resilience is prioritized in the laboratory environment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tuff | Soapstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Volcanic rock, porous and lightweight | Metamorphic rock, dense and smooth |
| Durability | Moderate resistance; prone to chipping | High resistance; withstands acids and chemicals |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited; weak against strong acids | Excellent; ideal for chemical labs |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | Excellent heat resistance |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing; absorbs moisture easily | Low maintenance; naturally non-porous |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Ideal Use | General lab tables with light chemical exposure | High-chemical, heat-intensive lab work |
Introduction to Laboratory Table Materials
Laboratory tables commonly utilize durable materials like Tuff and Soapstone for enhanced chemical resistance and longevity under rigorous lab conditions. Tuff, a volcanic rock, offers exceptional hardness and structural strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty laboratory use, while Soapstone provides superior resistance to acids and heat, favored in chemical laboratories requiring non-reactive surfaces. Selecting between Tuff and Soapstone depends on specific laboratory demands such as mechanical impact tolerance and chemical exposure levels.
Overview of Tuff and Soapstone
Tuff is a porous volcanic rock known for its lightweight nature and moderate resistance to chemicals, making it a budget-friendly option for laboratory tables. Soapstone, composed primarily of talc and magnesium silicate, offers superior chemical resistance and excellent heat retention, making it highly durable in harsh lab environments. Both materials provide unique benefits, with Tuff being more economical and Soapstone excelling in longevity and resistance to corrosive substances.
Physical Properties: Tuff vs Soapstone
Tuff exhibits lower density and hardness compared to soapstone, making it less resistant to scratches and chemical corrosion in laboratory environments. Soapstone's high talc content provides excellent thermal and chemical resistance, essential for handling acids and heat during experiments. The superior durability and non-porous nature of soapstone ensure a longer lifespan and easier maintenance for laboratory tables compared to tuff.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Tuff laboratory tables exhibit outstanding chemical resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, making them ideal for environments with frequent chemical exposure. Soapstone offers excellent resistance to a broad range of corrosive chemicals, especially acids, due to its natural mineral composition. Both materials prevent damage from chemical spills, but soapstone tends to be more resistant to strong acids, while Tuff surfaces provide superior durability against alkalis and organic solvents.
Durability and Longevity
Tuff laboratory tables are constructed from high-pressure laminate or reinforced materials, offering excellent resistance to scratches, chemicals, and moisture, which enhances durability in demanding lab environments. Soapstone lab tables, composed of natural metamorphic rock, provide exceptional chemical resistance and heat tolerance, ensuring long-lasting performance without warping or corrosion. While soapstone offers superior longevity in handling harsh chemicals and temperature fluctuations, Tuff surfaces provide cost-effective durability with easier maintenance and repair options.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Tuff laboratory tables require minimal maintenance due to their high resistance to chemicals, stains, and heat, enabling quick and effective cleaning with mild detergents and water. Soapstone surfaces also offer excellent chemical resistance but need periodic oiling to maintain their natural patina and prevent drying or cracking, making maintenance slightly more involved. Both materials are durable, yet Tuff's non-porous nature ensures easier stain removal and lower overall upkeep in demanding laboratory environments.
Heat Resistance in Lab Environments
Tuff offers moderate heat resistance suitable for routine laboratory tasks but may degrade under prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures. Soapstone exhibits superior heat resistance, making it ideal for lab tables that encounter direct contact with hot equipment or thermal processes. Its high thermal stability and low thermal conductivity ensure durability and safety in demanding lab environments.
Cost Analysis: Tuff vs Soapstone
Tuff offers a cost-effective alternative to soapstone for laboratory tables, typically priced 30-50% lower due to its abundant availability and simpler manufacturing process. Soapstone, known for its durability and chemical resistance, incurs higher upfront costs and maintenance expenses, often justified in specialized lab environments requiring superior heat and acid resistance. When budgeting for lab furnishings, consider Tuff for standard lab use with moderate chemical exposure, while soapstone suits high-intensity applications despite its premium price.
Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Tuff laboratory tables feature a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth, durable surfaces that complement contemporary lab environments, while soapstone offers a warm, natural appearance with subtle veining that adds character and timeless appeal. Soapstone's matte finish resists stains and scratches, enhancing its elegant design, whereas Tuff materials prioritize seamless integration with high-tech lab equipment through customizable color options and minimalist lines. Choosing between Tuff and soapstone balances the need for sophisticated style against practical durability and the desired ambiance of the laboratory space.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Lab
Tuff offers exceptional durability and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for high-traffic laboratory tables requiring long-term stability. Soapstone provides superior heat resistance and natural non-porosity, reducing the risk of contamination during sensitive experiments. Evaluating the specific lab activities and chemical exposures will guide the selection of the most suitable material, balancing durability with maintenance needs.
Infographic: Tuff vs Soapstone for Laboratory Table
 azmater.com
azmater.com